Abstract
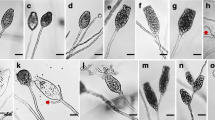
Tetracladium is a common aquatic hyphomycete genus, whose taxonomy has been based on the morphology and development of asexual spores. Ecological surveys have relied almost exclusively on spore morphology. Since selective pressures have resulted in convergent shapes, misidentifications are a concern. To supplement morphological information, we determined COX1, ITS and D1/D2 sequences as potential barcodes on 21 strains belonging to 7 described Tetracladium species and an unidentified strain. Attempts to amplify the IGS region were unsuccessful. The ratio of intraspecific to interspecific variability was optimal with ITS, which also provided the intuitively most acceptable cladogram. Typical conidia and their variability for the seven described species are illustrated. Internal node reliability depended less on total sequence length and more on the mixture of conserved and variable regions used to build cladograms. This finding can be exploited for quickly increasing phylogenetic accuracy without greatly increasing the amount of amplification and sequencing. The results have important implications for identifying freshwater hyphomycetes in the field but further work is required to establish if this method works with plant pathogens.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora DK, Hirsch PR, Kerry BR (1996) PCR-based molecular discrimination of Verticillium chlamydosporium isolates. Mycol Res 100:801–809
Aveskamp MM, De Gruyter J, Crous PW (2008) Biology and recent developments in the systematics of Phoma, a complex genus of major quarantine significance. Fungal Divers 31:1–18
Bärlocher F (ed) (1992a) The ecology of aquatic hyphomycetes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Bärlocher F (1992b) Stream ecology and its relevance to aquatic mycology. In: Bärlocher F (ed) The ecology of aquatic hyphomycetes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 16–37
Bärlocher F (2005) Freshwater fungal communities. In: Dighton J, Oudemans P, White J (eds) Chapter in: The fungal community, 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 39–59
Bärlocher F, Charette N, Letourneau A, Nikolcheva LG, Sridhar KR (2009) Sequencing DNA extracted from single conidia of aquatic hyphomycetes. Fungal Ecology, in press
Baschien C, Marvanová L, Szewzyk U (2006) Phylogeny of selected aquatic hyphomycetes based on morphological and molecular data. Nova Hedwig 83:311–352
Belliveau M, Bärlocher F (2005) Molecular evidence confirms multiple origin of aquatic hyphomycetes. Mycol Res 109:1407–1417
Cai L, Hyde KD, Tsui CKM (2006) Genera of freshwater fungi. Fungal Divers Res Ser 18:1–261
Cai L et al (2009). Polyphasic approach to Colletotrichum. Fungal Divers 39: xx–xx
Campbell J, Shearer C, Marvanová L (2006) Evolutionary relationships among aquatic anamorphs and teleomorphs: Lemonniera, Margaritispora, and Goniopila. Mycol Res 110:1025–1033
Das M, Royer TV, Leff LG (2008) Fungal communities on decaying leaves in streams: a comparison of two leaf species. Mycol Progr 7:267–275
Descals E (1987) Muestreo preliminar de hongos ingoldianos de Cataluña. Rev Ibér Micol 4:17–32
Descals E (1997) Ingoldian fungi: some field and laboratory techniques. Boll Soc Hist Nat Balears 40:169–221
Descals E, Rodríguez Pérez J (2002) Bases corológicas de Flora Micológica Ibérica. Números 1933–2069. Madrid, pp 200
Descals E, Webster J (1983) Four new staurosporous hyphomycetes from mountain streams. Trans Br Mycol Soc 80:67–75
Dix NJ, Webster J (1995) Fungal ecology. Chapman & Hall, London
Domsch KH, Gams W, Anderson T-H (2007) Compendium of soil fungi, 2nd edn. IHW-Verlag, Eching
Druzhinina IS, Kopchinskiy AG, Komoj M, Bissett J, Szakacs G, Kubicek CP (2005) An oligonucleotide barcode for species identification in Trichoderma and Hypocrea. Fungal Genet Biol 42:813–828
Fell JW, Boekhout T, Fonseca A, Scorzetti G, Statzell-Tallman A (2000) Biodiversity and systematics of basisiomycetous yeast as determined by large-subunit rDNA D1/D2 domain sequence analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1351–1371
Geiser DM, Jiménez-Gasco M, Kang S, Makalowska I, Veerarahavan N, Ward T, Zhang N, Kuldau G, O’Donnell K (2004) A DNA sequence database for identifying Fusarium. Eur J Plant Pathol 110:473–479
Gessner MO, Gulis V, Kuehn KA, Chauvet E, Suberkropp K (2007) Fungal decomposers of plant litter in aquatic ecosystems. In: Kubicek CP, Druzhinina IS, Druzhinina IS (eds) The mycota, vol. IV, environmental and microbial relationships. Springer, Berlin, pp 301–324
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc R Soc Lond 270:313–321
Hebert PDN, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM (2004) Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol 2(10). doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020312
Hennebert GL, Sutton BC (1994) Unitary parameters in conidiogenesis. In: Hawksworth DL (ed) Ascomycete systematics. Problems and perspectives in the nineties. NATO ASI series, series A: Life sciences, vol. 269. Plenum, New York, pp 65–76
Huang WY, Cai YZ, Surveswaran S, Hyde KD, Corke H, Sun M (2009) Molecular phylogenetic identification of endophytic fungi isolated from three Artemisia species. Fungal Divers 36:69–88
Hyde et al (2009a) Colletotrichum: a catalogue of confusion. Fungal Diversity 39: xx–xx
Hyde et al (2009b) Current names in Colletotrichum. Fungal Diversity 39: xx–xx
Ingold CT, Ellis EA (1952) On some hyphomycete spores, including those of Tetracladium maxilliformis, from Wheatfen. Trans Br Mycol Soc 35:158–161
Jeewon R, Liew ECY, Hyde KD (2002) Phylogenetic relationships of Pestalotiopsis and allied genera inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences and morphological characters. Mol Phylogenet Evol 25:378–392
Jeewon R, Liew ECY, Simpson JA, Hodgkiss IJ, Hyde KD (2003) Phylogenetic significance of morphological characters in the taxonomy of Pestalotiopsis species. Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:372–383
Kinzig AP, Pacala SW, Tilman D (eds) (2001) The functional consequences of biodiversity. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Knudsen B, Knudsen T, Flensborg M, Sandmann H, Heltzen M, Anderson A, Dickenson M, Bardram J, Steffensen PJ, Monsted S, Lauritzen T, Forsberg R, Thanbichler A, Bendtsen JD, Gorlitz L, Rasmussen J, Tordrup D, Vaerum M, Nygaard Ravn M, Hachenberg C (2008) CLC DNA Workbench version 3.6.1. CLC Bio
Kõljalg U, Larsson K-H, Abarenkov K, Nilsson RH, Alexander IJ, Eberhardt U, Erland S, Høiland K, Kjøller R, Larsson E, Pennanen T, Sen R, Taylor AFS, Tedersoo L, Vrålstad T, Ursing BM (2005) UNITE: a database providing web-based methods for the molecular identification of ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 166:1063–1068
Kurtzman DP (1994) Molecular taxonomy of the yeasts. Yeast 10:1727–1740
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26 S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371
Kvas M, Marasas WFO, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ, Steenkamp ET (2009) Diversity and evolution of Fusarium species in the Gibberella fujikuroi complex. Fungal Divers 34:1–21
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P (eds) (2002) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Marvanová L, Bärlocher F (2001) Hyphomycetes from Canadian streams. VI. Rare species in pure cultures. Czech Mycol 53:1–28
Matsushima T (1981) Matsushima mycological memoirs no. 2. Matsushima Fungus Collection, Kobe, pp 68
Matsushima T (1983). Matsushima mycological memoirs no. 3. Matsushima Fungus Collection, Kobe, pp 89
Min XJ, Hickey DA (2007) BARCODING: assessing the effect of varying sequence length on DNA barcoding of fungi. Mol Ecol Notes 7:365–373
Nikolcheva LG, Bärlocher F (2002) Phylogeny of Tetracladium based on 18S rDNA. Czech Mycol 53:285–295
Nikolcheva LG, Bärlocher F (2004) Taxon-specific fungal primers reveal unexpectedly high diversity during leaf decomposition in a stream. Mycol Progr 3:41–50
Nikolcheva LG, Cockshutt AM, Bärlocher F (2003) Diversity of freshwater fungi on decaying leaves—comparing traditional and molecular approaches. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2548–2554
O’Donnell K, Cigelnik E, Nirenberg HI (1998) Molecular systematics and phylogeography of the Giberella fujikoroi species complex. Mycologia 90:465–493
Pryce TM, Palladino S, Kay ID, Coombs GW (2003) Rapid identificaiton of fungi by sequencing the ITS1 and ITS2 regions using an automated capillary electrophoresis system. Med Mycol 41:369–381
Rambaut A (1996) Se-Al: sequence alignment editor. Available at http://evolve.zoo.ox.ac.uk/
Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN (2007) BOLD: the barcode of life data system (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol Ecol Notes 7:355-364
Roldán A, Descals E, Honrubia M (1987a) Notes on Tetracladium apiense Sinclair and Eicker. Cryptogam Mycol 8:219–225
Roldán A, Descals E, Honrubia M (1987b) Hifomicetos acuáticos en la Serranía de Cuenca. Bol Soc Micol Madr 11:179–184
Roldán A, Descals E, Honrubia M (1989) Pure culture studies on Tetracladium. Mycol Res 93:452–465
Rossman A (2007) Report of the planning workshop for all fungi DNA barcoding. Inoculum 58(6):1–5
Samson RA, Seifert KA, Kuijpers AFA, Houbraken JAMP, Frisvad JC (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of Penicillium subgenus Penicillium using partial β-tubulin sequences. Stud Mycol 49:175–200
Santos JM, Phillips AJL (2009) Resolving the complex of Diaporthe (Phomopsis) species occurring on Foeniculum vulgare in Portugal. Fungal Divers 34:111–125
Seena S, Wynberg N, Bärlocher F (2008) Fungal diversity during leaf decomposition in a stream assessed through clone libraries. Fungal Divers 30:1–14
Seifert KA, Samson RA, deWaard JR, Houbraken J, Levesque CA, Moncalvo JM, Louis-Seize G, Herbert PDN (2007) Prospects for fungus identification using CO1 DNA barcodes, with Penicillium as a test case. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:3901–3906
Sinclair RC, Eicker A (1981) Tetracladium apiense, a new aquatic species from South Africa. Trans Br Mycol Soc 76:515–517
Summerbell RC, Lévesque CA, Seifert KA, Bovers M, Fell JW, Diaz MR, Boekhout T, de Hoog GS, Stalpers J, Crous PW (2005) Microcoding: the second step in DNA barcoding. Philos Trans R Soc B 360:1897–1903
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and Other Methods). Version 4. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Takano Y, Horiguchi T (2005) Acquiring scanning electron microscopal, light microscopal and multiple gene sequence data from a single dinoflagellate cell. J Phycol 42:251–256
Tang AMC, Jeewon R, Hyde KD (2009) A re-evaluation of the evolutionary relationships within the Xylariaceae based on ribosomal and protein-coding gene sequences. Fungal Divers 34:127–155
Tsui CKM, Hyde KD (2003) Freshwater mycology. Fungal Divers Res Ser 10:1–350
Wannathes N, Desjardin DE, Hyde KD, Perry BA, Lumyong S (2009) A monograph of Marasmius (Basidiomycota) from Northern Thailand based on morphological and molecular (ITS sequences) data. Fungal Divers 37:209–306
Wulanderi NF, To-Anun C, Hyde KD, Duong LM, de Gruyter J, Meffert JP, Crous PW (2009) Phyllosticta citriasiana sp. nov., the cause of Citrus tan spot of Citrus maxima in Asia. Fungal Divers 34:23–39
Zhang Y, Fournier J, Pointing SB, Hyde KD (2008) Are Melanomma pulvis-pyrius and Trematosphaeria pertusa congeneric? Fungal Divers 33:47–60
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by a Discovery grant from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada to FB. It is a part of the project MSM00216222416 (LM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Letourneau, A., Seena, S., Marvanová, L. et al. Potential use of barcoding to identify aquatic hyphomycetes. Fungal Diversity 40, 51–64 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-009-0006-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-009-0006-8