Abstract
Purpose
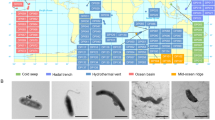
Archaea have important roles in global biogeochemical circulation. Although archaeal diversity and their ecological significance in deep-sea environments in the South China Sea (SCS) have been investigated, archaeal communities in deep-sea sediments below 2000 m water depth in the SCS are not well documented. The objective of our work was to investigate archaeal community structure in the four sediments (named as SCS2, SCS5, SCS8, and SCS10) collected from the SCS below 2000 m water depth.
Methods
Illumina high-throughput sequencing was employed to reveal archaeal community structure. Archaeal communities were evaluated with QIIM software.
Result
Archaeal communities in the four sediments were dominated by Thaumarchaeota (55%), Bathyarchaeota (24%), Woesearchaeota (6%), Nanohaloarchaeota (4%), and Euryarchaeota (3%). Thaumarchaeota were abundant in the four samples. However, in SCS10, this phylum was almost exclusively represented. We revealed for the first time the presence of Nanohaloarchaeota in SCS2, SCS5, and SCS8. Comparative analysis showed that (1) the archaeal communities varied between the samples and (2) the samples varied between the samples. The detected archaea in each sample are known to be potentially participating in the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles, and methane metabolism.
Conclusion
We present a comparative picture of archaeal communities, augmenting the current knowledge on archaeal diversity in deep-sea sediment environments in the SCS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brochier-Armanet C, Forterre P, Gribaldo S (2011) Phylogeny and evolution of the archaea: one hundred genomes later. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:274–281
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cavicchioli R (2011) Archaea—timeline of the third domain. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:51–61
Chen JQ, Wang FP, Jiang LJ, Yin XJ, Xiao X (2013) Stratified communities of active archaea in shallow sediments of the Pearl River estuary, Southern China. Curr Microbiol 67:41–50
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Di Meglio L, Santos F, Gomariz M, Almansa C, Lopez C, Anton J, Nercessian D (2016) Seasonal dynamics of extremely halophilic microbial communities in three Argentinian salterns. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Eme L, Doolittle WF (2015) Archaea. Curr Biol 25:R851–R855
Evans PN, Parks DH, Chadwick GL, Robbins SJ, Orphan VJ, Golding SD, Tyson (2015) Methane metabolism in the archaeal phylum Bathyarchaeota revealed by genome-centric metagenomics. Science 350: 434–438
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E, Methé B, TZ DS, Consortium HM, Petrosino JF, Knight R, Birren BW (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Han R, Zhang X, Liu J, Long QF, Chen LS, Liu DL, Zhu DR (2017) Microbial community structure and diversity within hypersaline Keke Salt Lake environments. Can J Microbiol 63:895–908
He Y, Li M, Perumal V, Feng X, Fang J, Xie J, Sievert SM, Wang F (2016) Genomic and enzymatic evidence for acetogenesis among multiple lineages of the archaeal phylum Bathyarchaeota widespread in marine sediments. Nat Microbiol 1:16035
Hu AY, Jiao NZ, Zhang CLL (2011) Community structure and function of planktonic crenarchaeota: changes with depth in the South China Sea. Microbial Ecol 62:549–563
Iino T, Tamaki H, Tamazawa S, Ueno Y, Ohkuma M, Suzuki K, Igarashi Y, Haruta S (2013) Candidatus Methanogranum caenicola: a novel methanogen from the anaerobic digested sludge, and proposal of Methanomassiliicoccaceae fam. nov and Methanomassiliicoccales ord. nov., for a, methanogenic lineage of the class Thermoplasmata. Microb Environ 28:244–250
Jiang HC, Dong HL, Ji SS, Ye Y, Wu NY (2007) Microbial diversity in the deep marine sediments from the Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea. Geomicrobiol J 24:505–517
Jiang L, Zheng Y, Chen J, Xiao X, Wang F (2011) Stratification of archaeal communities in shallow sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 99:739–751
Lazar CS, Baker BJ, Seitz K, Hyde AS, Dick GJ, Hinrichs KU, Teske AP (2016) Genomic evidence for distinct carbon substrate preferences and ecological niches of Bathyarchaeota in estuarine sediments. Environ Microbiol 18:1200–1211
Liao L, Xu XW, Wang CS, Zhang DS, Wu M (2009) Bacterial and archaeal communities in the surface sediment from the northern slope of the South China Sea. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 10:890–901
Lipp JS, Morono Y, Inagaki F, Hinrichs KU (2008) Significant contribution of archaea to extant biomass in marine subsurface sediments. Nature 454:991–994
Liu HD, Zhang CLL, Yang CY, Chen SZ, Cao ZW, Zhang ZW, Tian JW (2017) Marine group II dominates planktonic archaea in water column of the Northeastern South China Sea. Front Microbiol 8
Lloyd KG, Schreiber L, Petersen DG, Kjeldsen KU, Lever MA, Steen AD, Stepanauskas R, Richter M, Kleindienst S, Lenk S, Schramm A, Jorgensen BB (2013) Predominant archaea in marine sediments degrade detrital proteins. Nature 496:215–218
Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D, Stombaugh J, Knight R (2011) UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J 5:169–172
Moisander PH, Beinart RA, Voss M, Zehr JP (2008) Diversity and abundance of diazotrophic microorganisms in the South China Sea during intermonsoon. ISME J 2:954–967
Mora-Ruiz MDR, Cifuentes A, Font-Verdera F, Perez-Fernandez C, Farias ME, Gonzalez B, Orfila A, Rossello-Mora R (2018) Biogeographical patterns of bacterial and archaeal communities from distant hypersaline environments. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:139–150
Na H, Lever MA, Kjeldsen KU, Schulz F, Jorgensen BB (2015) Uncultured Desulfobacteraceae and Crenarchaeotal group C3 incorporate C-13-acetate in coastal marine sediment. Env Microbiol Rep 7:614–622
Niu MY, Fan XB, Zhuang GC, Liang QY, Wang FP (2017) Methane-metabolizing microbial communities in sediments of the Haima cold seep area, northwest slope of the South China Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93
Offre P, Spang A, Schleper C (2013) Archaea in biogeochemical cycles. Annu Rev Microbiol 67:437–457
Petersen SO, Hojberg O, Poulsen M, Schwab C, Eriksen J (2014) Methanogenic community changes, and emissions of methane and other gases, during storage of acidified and untreated pig slurry. J Applied Microbiol 117:160–172
Poulsen M, Schwab C, Jensen BB, Engberg RM, Spang A, Canibe N, Hojberg O, Milinovich G, Fragner L, Schleper C, Weckwerth W, Lund P, Schramm A, Urich T (2013) Methylotrophic methanogenic Thermoplasmata implicated in reduced methane emissions from bovine rumen. Nat Commun 4:1428
Schleper C, Jurgens G, Jonuscheit M (2005) Genomic studies of uncultivated archaea. Nat Reviews Microbiol 3:479–488
Stahl DA, de la Torre JR (2012) Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:83–101
Wang P, Li T, Hu A, Wei Y, Guo W, Jiao N, Zhang C (2010) Community structure of archaea from deep-sea sediments of the South China Sea. Microb Ecol 60:796–806
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Xia XM, Guo W, Liu HB (2015) Dynamics of the bacterial and archaeal communities in the northern South China Sea revealed by 454 pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. Deep-Sea Res Pt II117:97–107
Yu TT, Liang QY, Niu MY, Wang FP (2017) High occurrence of Bathyarchaeota (MCG) in the deep-sea sediments of South China Sea quantified using newly designed PCR primers. Env Microbiol Rep 9:374–382
Zhang Y, Su X, Chen F, Wang YY, Jiao L, Dong HL, Huang YY, Jiang HC (2012) Microbial diversity in cold seep sediments from the northern South China Sea. Geosci Front 3:301–316
Zhu D, Tanabe SH, Yang C, Zhang W, Sun J (2013) Bacterial community composition of South China Sea sediments through pyrosequencing-based analysis of 16S rRNA genes. PLoS One 8:e78501
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Philippe Oge at Univ Lyon, INSA de Lyon, CNRS UMR 5240 for revising this manuscript, and Manyu Kang at Tongji University for drawing Fig. 1.
Funding
This work was supported by the Academic Leader of Middle and Young People of Yangzhou University Grant to L.Z.; by the Practice Innovation Training Program for College Students in Jiangsu to Y. L (No. 201711117059Y); by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant (No. 41776156) to X.Z; by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (No. 201607020018) and the Team Project of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2016A030312014) to W.Z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
N/A
Informed consent
N/A
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhu, X., Zhang, W. et al. Archaeal communities in the deep-sea sediments of the South China Sea revealed by Illumina high-throughput sequencing. Ann Microbiol 69, 839–848 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-019-01477-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-019-01477-4