Abstract
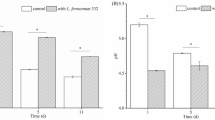
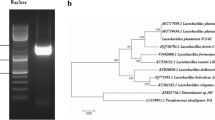
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of inoculated fermentation on the quality of Chinese sauerkraut. To this end we studied a co-culture system consisting of Lactobacillus plantarum Shanghai brewing 1.08 and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii CGMCC 3791 during inoculated sauerkraut fermentation. The nitrite concentrations in pickled cabbage and radish inoculated with starter cultures of L. plantarum and Z. rouxii were significantly lower than those in the spontaneous fermentation system during the whole fermentation process. In addition, co-culture of L. plantarum and Z. rouxii during the production of sauerkraut decreased the formation of biogenic amines in the pickled vegetables. Using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry we also compared the levels of volatile compounds in inoculated and naturally fermented Chinese sauerkraut. Sixty compounds were identified, with the sauerkraut inoculated with starter cultures containing overall higher contents of volatile compounds, including acids, alcohols, esters, and phenols. The structure of the microbial community during the production of sauerkraut was studied using phospholipid fatty-acid (PLFA) analysis. This analysis revealed that the brine of inoculated sauerkraut contained significantly higher contents of Gram-positive and fungal PLFAs and a lower content of Gram-negative PLFAs, suggesting that the improved quality of inoculated Chinese sauerkraut may be ascribed to the inhibition of the growth of Gram-positive during sauerkraut fermentation. These results may indicate a new strategy to enhance the quality of Chinese sauerkraut.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeniran O, Atanda O, Edema M, Oyewole O (2012) Effect of lactic acid bacteria and yeast starter cultures on the soaking time and quality of “Ofada” rice. Food Nutr 3:207–211
Ali AA, Mustafa MM (2009) Use of starter cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in the preparation of kisra, a Sudanese fermented food. Pak J Nutr 8(9):1349–1353
Beganovié J, Pavunc AL, Gjuraèié K, Špoljarec M, Šuškovié J, Kos B (2011) Improved sauerkraut production with probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum L4 and Leuconostoc mesenteroides LMG 7954. J Food Sci 76(2):124–129
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37(8):911–917
Buttery RG, Turnbaugh JG, Ling LC (1988) Contribution of volatiles to rice aroma. J Agric Food Chem 36(5):1006–1009
Dodds KL, Collins-Thompson DL (1984) Incidence of nitrite-depleting lactic acid bacteria in cured meats and in meat starter cultures. J Food Process Pres 47:7–10
Du ST, Zhang YS, Lin XY (2007) Accumulation of nitrate in vegetables and its possible implications to human health. Agric Sci (Chinese) 6(10):1246–1255
Dugo GM, Vilasi F, Torre L, Pellicanò TM (2006) Reverse phase HPLC/DAD determination of biogenic amines as dansyl derivatives in experimental red wines. Food Chem 95(4):672–676
Fan W, Shen H, Xu Y (2011) Quantification of volatile compounds in Chinese soy sauce aroma type liquor by stir bar sorptive extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Sci Food Agric 91(7):1187–1198
Federle TW, Dobbins DC, Thorntonmanning JR, Jones DD (1986) Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in subsurface soils. Ground Water 24(3):365–374
Frostegård A, Bååth E (1996) The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol Fert Soils 22(1):59–65
Giri A, Osako K, Okamoto A, Okazaki E, Ohshima T (2011) Effect of meat washing on the development of impact odorants in fish miso prepared from spotted mackerel. J Sci Food Agric 91(5):850–859
Ji FDI, Ji BP, Li B, Lu F (2009) Effect of fermentation on nitrate, nitrite and organic acid contents in traditional pickled Chinese cabbage. J Food Process Pres 33:175–186
Kedia G, Wang R, Patel H, Pandiella SS (2007) Use of mixed cultures for the fermentation of cereal-based substrates with potential probiotic properties. Process Biochem 42(1):65–70
Kimaryo V, Massawe G, Olasupo N, Holzapfel W (2000) The use of a starter culture in the fermentation of cassava for the production of “kivunde”, a traditional Tanzanian food product. Int J Food Microbiol 56(2):179–190
Kung HF, Tsai YH, Wei CI (2007) Histamine and other biogenic amines and histamine-forming bacteria in miso products. Food Chem 101(1):351–356
Latorre-Moratalla M, Bover-Cid S, Talon R, Garriga M, Zanardi E, Ianieri A, Fraqueza M, Elias M, Drosinos E, Vidal-Carou M (2010) Strategies to reduce biogenic amine accumulation in traditional sausage manufacturing. LWT-Food Sci Technol 43(1):20–25
Latorre-Moratalla ML, Veciana-Nogués T, Bover-Cid S, Garriga M, Aymerich T, Zanardi E, Ianieri A, Fraqueza MJ, Patarata L, Drosinos EH (2008) Biogenic amines in traditional fermented sausages produced in selected European countries. Food Chem 107(2):912–921
Lee SJ, Ahn B (2009) Comparison of volatile components in fermented soybean pastes using simultaneous distillation and extraction (SDE) with sensory characterisation. Food Chem 114(2):600–609
Leroy F, De Vuyst L (2004) Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 15(2):67–78
Liu ZF, Wei YX, Zhang JJ, Liu DH, Hu YQ, Ye XQ (2011) Changes in biogenic amines during the conventional production of stinky tofu. Int J Food Microbiol 46(4):687–694
Lu YM, Chen XH, Jiang M, Lv X, Rahman N, Dong MS, Yan GJ (2009) Biogenic amines in Chinese soy sauce. Food Control 20(6):593–597
Majumdar D (2003) The blue baby syndrome. Resonance 8(10):20–30
Mcfeeters RF, Thompson RL, Fleming HP (1984) Liquid Chromatographic analysis of sugars, acids, and ethanol in lactic acid vegetable fermentations. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 67(4–6):710–714
Moore-Kucera J, Dick RP (2008) PLFA profiling of microbial community structure and seasonal shifts in soils of a douglas-fir chronosequence. Microbiol Ecol 55(3):500–511
Muñoz D, Peinado RA, Medina M, Moreno J (2007) Biological aging of sherry wines under periodic and controlled microaerations with Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. capensis: effect on odorant series. Food Chem 100(3):1188–1195
Mugula J, Narvhus J, Sørhaug T (2003) Use of starter cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in the preparation of togwa, a Tanzanian fermented food. Int J Food Microbiol 83(3):307–318
Nout M (1991) Ecology of accelerated natural lactic fermentation of sorghum-based infant food formulas. Int J Food Microbiol 12(2–3):217–224
Oh CK, Oh MC, Kim SH (2004) The depletion of sodium nitrite by lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi. J Med Food 7(1):38–44
Qian M, Reineccius G (2002) Identification of aroma compounds in Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese by gas chromatography/olfactometry. J Dairy Sci 85(6):1362–1369
Rabie MA, Siliha H, el-Saidy S, el-Badawy AA, Xavier Malcata F (2011) Reduced biogenic amine contents in sauerkraut via addition of selected lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem 129(4):1778–1782
Raghavendra T, Sayania D, Madamwar D (2010) Synthesis of the ‘green apple ester’ ethyl valerate in organic solvents by Candida rugosa lipase immobilized in MBGs in organic solvents: effects of immobilization and reaction parameters. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 63:31–38
Rashad MM, Mahmoud EA, Abdou MH, Nooman UM (2011) Improvement of nutritional quality and antioxidant activities of yeast fermented soybean curd residue. Afr J Biotechnol 10(28):5504–5513
Saarinen M (2002) Determination of biogenic amines as dansyl derivatives in intestinal digesta and feces by reversed phase HPLC. Chromatographia 55(5):297–300
Steinhaus M, Sinuco D, Polster J, Osorio C, Schieberle P (2009) Characterization of the key aroma compounds in pink guava (Psidium guajava L.) by means of aroma re-engineering experiments and omission tests. J Agric Food Chem 57(7):2882–2888
Sun SY, Jiang WG, Zhao YP (2010) Profile of volatile compounds in 12 Chinese soy sauces produced by a high-salt-diluted state fermentation. J Inst Brewing 116(3):316–328
Tsai YH, Kung HF, Chang SC, Lee TM, Wei CI (2007) Histamine formation by histamine-forming bacteria in douchi, a Chinese traditional fermented soybean product. Food Chem 103(4):1305–1311
Xiong T, Guan Q, Song S, Hao M, Xie M (2012) Dynamic changes of lactic acid bacteria flora during Chinese sauerkraut fermentation. Food Control 26(1):178–181
Yan PM, Xue WT, Tan SS, Zhang H, Chang XH (2008) Effect of inoculating lactic acid bacteria starter cultures on the nitrite concentration of fermenting Chinese paocai. Food Control 19(1):50–55
Zhao J, Dai X, Liu X, Zhang H, Tang J, Chen W (2011) Comparison of aroma compounds in naturally fermented and inoculated Chinese soybean pastes by GC-MS and GC-Olfactometry analysis. Food Control 22(6):1008–1013
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31171742).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Zheng, J., Huang, J. et al. Reduced nitrite and biogenic amine concentrations and improved flavor components of Chinese sauerkraut via co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii . Ann Microbiol 64, 847–857 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0724-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0724-8