Abstract
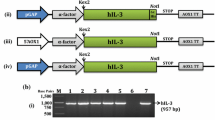
Interleukin-32 is a novel human cytokine implicated in several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Recombinant interleukin -32 can be produced and found to be useful in many fields. Until now, there has been no report on recombinant hIL-32 expressed in basidomycete fungus, Pleurotus eryngii. In this study, we examined whether the popular edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii could support the expression of novel protein hIL-32. A binary vector pCAMBIA1304 containing the hIL-32 gene was constructed and introduced into Pleurotus eryngii via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. The expression of hIL-32 was confirmed by PCR, Southern blot and western blot analysis. The recombinant hIL-32 reached a maximum expression level of 1.9 % of total soluble protein in transgenic mycelia. These results suggest that Pleurotus eryngii expression system can be effective for the production of rhIL-32 at an economically relevant level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berends E, Scholtmeijer K, Wosten HA, Bosch D, Lugones LG (2009) The use of mushroom-forming fungi for the production of N-glycosylated therapeutic proteins. Trends Microbiol 17:439–443
Bundock P, Hooykaas PJJ (1996) Integration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome by illegitimate recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:15272–15275
Bundock PA, Den Dulk-Ras A, Beijersbergen A, Hooykaas PJJ (1995) Trans-kingdom T-DNA transfer from Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 14:3206–3214
Chen X, Stone M, Schlagnhaufer C, Romaine CP (2000) A fruiting body tissue method for efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Agaricus bisporus. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4510–4513
Chen Q, Carroll HP, Gadina M (2006) The newest interleukins: recent additions to the ever-growing cytokine family. Vitam Horm 74:207–228
DeGroot MJA, Bundock P, Hooykaas PJJ, Beijersbergen AGM (1998) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of filamentous fungi. Nat Biotechnol 16:839–842
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol Adv 27:297–306
Fernandez JM, Hoeffler JP (1999) Gene expression systems. Academic, San Diego
Goda C, Kanaji T, Kanaji S, Tanaka G, Arima K, Ohno S, Izuhara K (2006) Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Int Immunol 18:233–240
Holsters M, De Waele D, Depicker A, Messens E, van Montague, Schell J (1978) Transfection and transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet 163:168–181
Joosten LA, Netea MG, Kim SH, Yoon DY, Oppers-Walgreen B, Radstake TR, Barrera P, van de Loo FA, Dinarello CA, van den Berg WB (2006) IL-32, a proinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3298–3303
Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA (2005) Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNF alpha. Immunity 22:131–142
Kim KH, Shim JH, Seo EH, Cho MC, Kang JW, Kim SH, Yu DY, Song EY, Lee HG, Sohn JH, Kim J, Dinarello CA, Yoon DY (2008) Interleukin-32 monoclonal antibodies for immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA. J Immunol Meth 333:38–50
Kim S, Sapkota K, Choi BS, Kim SJ (2010) Expression of human growth hormone gene in Pleurotus eryngii. Cent Eur J Biol (In press) doi:10.2478/s11535-010-0071-8 Online First™
Kobayashi H, Lin PC (2009) Molecular characterization of IL-32 in human endothelial cells. Cytokine 46:351–358
Kobayashi H, Huang J, Ye F, Shyr Y, Blackwell TS, Lin PC (2010) Interleukin-32beta propagates vascular inflammation and exacerbates sepsis in a mouse model. PLoS One 5:e9458
Li W, Liu Y, Mukhtar MM, Gong R, Pan Y, Rasool ST, Gao Y, Kang L, Hao Q, Peng G, Chen X, Wu J, Zhu Y (2008) Activation of interleukin-32 pro-inflammatory pathway in response to influenza A virus infection. PLoS ONE 3:e1985
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, Girardin SE, Walsh M, Park JS, Abraham E, Kim JM, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA, Kim SH (2005) IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL- 1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16309–16314
Netea MG, Lewis EC, Azam T, Joosten LA, Jaekal J, Bae SY, Dinarello CA, Kim SH (2008) Interleukin-32 induces the differentiation of monocytes into macrophage-like cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 9:3515–3520
Nevalainen KM, Teo VS, Bergquist PL (2005) Heterologous protein expression in filamentous fungi. Trends Biotechnol 23:468–474
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Pott GB, Zepp JA, Saavedra MT, Kim SH, Dinarello CA (2008) Endogenous IL-32 controls cytokine and HIV-1 production. J Immunol 181:557–565
Punt PJ, van Biezen N, Conesa A, Albers A, Mangnus J, van den Hondel C (2002) Filamentous fungi as cell factories for heterologous protein production. Trends Biotechnol 5:200–206
Rodriguez Estrada AE, Royse DJ (2007) Yield, size and bacterial blotch resistance of Pleurotus eryngii grown on cottonseed hulls/oak sawdust supplemented with manganese, copper and whole ground soybean. Bioresour Technol 98:1898–1906
Royse DJ (1999) Yield stimulation of king oyster mushroom, Pleurotus eryngii, by brewer’s grain and SpawnMate IISE®supplementation of cottonseed hull and woodchip substrate. Mushroom News 47(2):4–8
Scott OR, Bendich AJ (1994) Extraction of total cellular DNA from plant, algae and fungi. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA (eds) Plant molecular biology manual, D1. Kluwer, Dordercht, pp 1–8
Shioya M, Nishida A, Yagi Y, Ogawa A, Tsujikawa T, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Takayanagi A, Shimizu N, Fujiyama Y, Andoh A (2007) Epithelial overexpression of interleukin- 32alpha in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol 149:480–486
Shoda H, Fujio K, Yamaguchi Y, Okamoto A, Sawada T, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K (2006) Interactions between IL-32 and tumor necrosis factor alpha contribute to the exacerbation of immune-inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R166
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (ARPC), Republic of Korea, and was conducted with research funds from Gwangju University in 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sang Jun Chung and Seung Kim contributed equally to this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, S.J., Kim, S., Sapkota, K. et al. Expression of recombinant human interleukin-32 in Pleurotus eryngii . Ann Microbiol 61, 331–338 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0146-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0146-9