Abstract
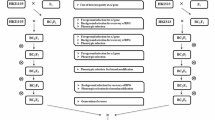
Improvement of quality protein maize (QPM) along with high content of lysine and tryptophan had foremost importance in maize breeding program. The efficient and easiest way of developing QPM hybrids was by backcross breeding in marker aided selection. Hence, the present investigation aimed at conversion of elite maize inbred line BML-7 into QPM line. CML-186 was identified to be a donor variety as it revealed high-quality polymorphism with BML-7 for opaque-2 gene specific marker umc1066. Non-QPM inbred line BML-7 was crossed with QPM donor CML-186 and produced F1 followed by the development of BC1F1 and BC2F1 population. Foreground selection was carried out with umc1066 in F1, and selected plants were used for BC1F1 and BC2F1 populations. Two hundred plants were screened in both BC1F1 and BC2F1 population with umc1066 for foreground selection amino acid modifiers. Foreground selected plants for both opaque-2 and amino acid modifiers were screened for background selection for BML-7 genome. Recurrent parent genome (RPG) was calculated for BC2F1 population plants. Two plants have shown with RPG 90–93% in two generation with back cross population. Two BC2F2 populations resulted from marker recognized BC2F1 individuals subjected toward foreground selection followed by tryptophan estimation. The tryptophan and lysine concentration was improved in all the plants. BC2F2 lines developed from hard endosperm kernels were selfed for BC2F2 lines and finest line was selected to illustrate the QPM version of BML-7, with 0.97% of tryptophan and 4.04% of lysine concentration in protein. Therefore, the QPM version of BML-7 line can be used for the development of single cross hybrid QPM maize version.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu PK (2015) Mapping QTLs for opaque2 modifiers influencing the tryptophan content in quality protein maize using genomic and candidate gene-based SSRs of lysine and tryptophan metabolic pathway. Plant Cell Rep 34:37–45
Dreher K, Khairallah M, Pandey S (2000) Is marker assisted selection cost effective compared to conventional plant breeding methods? The case of Quality Protein Maize. International Consortium on Agricultural Biotechnology Research (ICABR). ‘The economics of Agricultural Biotechnology’. Held in Revello, Italy, 24–28
Frisch M, Bohn M, Melchinger AE (1999) Comparison of selection strategies for marker-assisted backcrossing of a gene. Crop Sci 39:1295–1301
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Sharma PC, Ramesh B (1996) Microsatellites in plants: a new class of molecularmarkers. Curr Sci 70:45–54
Hospital F, Chevalet C, Mulsant P (1992) Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 132:1199–1210
Krishna MSR, Chinnababunaik V, Sokka Reddy S (2012) Assessment of genetic diversity among the QPM lines using SSR markers. Afr J Biotech 11(98):16427–16433
Krivanek AF, De Grote H, Gunaratna NS, Diallo AO, Friesen D (2007) Breeding and disseminating quality protein maize (QPM) for Africa. Afr J Biotech 6:312–324
Ortega EI, Bates LS (1983) Biochemical and agronomic studies of two modified hard-endosperm opaque-2 maize (Zea mays L.) populations. Cereal Chem 60:107–111
Pirona R, Hartings H, Lauria M, Rossi V, Motto M (2005) Genetic control of endosperm development and of storage products accumulation on maize seeds. Maydica 50:515–530
Ribaut JM, Hoisington D (2002) Stimulation experiments on efficiencies of gene introgression by back crossing. Crop Sci 42:557–565
Salvi ND, George L, Eapen S (2001) Plant regeneration from leaf base callus of turmeric and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of regenerated plants. Plant Cell. 66:113–119
Semagn K, Bjornstad A, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) An overview of molecular markers methods for plants. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2540–2568
Tyagi S, Bratu DP, Kramer FR (1998) Multicolor molecular beacons for allele discrimination. Nat Biotechnol 16:49–53
Vasal SK (2000) Quality protein maize story. Proceedings of workshop on improving human nutrition through agriculture. The role of international agricultural research. IRRI, Los Baños, pp 1–16
Vasal SK, Villegas E, Bjarnason M, Gelaw B, Goertz P (1980) Genetics modifiers and breeding strategies in developing hard endosperm opaque2 materials. In: Pollmer WG, Phipps RH (eds) Improvement of quality traits of maize for grains and silage use. Nighoff, The Hague, pp 37–73
Visscher PM (1996) Proportion of the variation in genetic composition in backcrossing programs explained by genetic markers. J Hered 87:136–138
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) Analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around Tm-2 locus of tomato during back cross breeding. Theor Appl Genet 77:353–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors state no conflict among them.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, M.S.R., Sokka Reddy, S. & Satyanarayana, S.D.V. Marker-assisted breeding for introgression of opaque-2 allele into elite maize inbred line BML-7. 3 Biotech 7, 165 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0842-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0842-2