Abstract
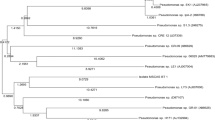
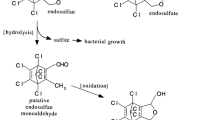
Endosulfan contamination is one of the major concerns of soil ecosystem, which causes detrimental effects not only to humans but also to animals and plants. Therefore, the aim of this study was to isolate and identify a novel bacterial strain capable of degrading endosulfan in agriculture contaminated soils. A novel bacterial strain was isolated from the sugarcane field contaminated with endosulfan, and was named as ZAM1 strain. The ZAM1 bacterial strain was further identified as Pseudomonas mendocina based on the biochemical and molecular analysis. 16sRNA sequence analysis of ZAM1 strain shows maximum similarity with known endosulfan-degrading bacteria (Pseudomonas putida), respectively. Enrichment was carried out using the endosulfan as sole sulfur source. The ZAM1 strain was able to use α and β endosulfan as a sole sulfur source. Our results showed that ZAM1 strain degrades endosulfan >64.5% (50 mg/l) after 12 days of incubation. The residues were analyzed by GC–MS analysis and confirmed the formation of metabolites of dieldrin, 2 heptanone, methyl propionate, and endosulfan lactone compounds. Hence, these results indicate that the ZAM1 strain is a promising bacterial source for detoxification of endosulfan residues in the environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal M, Naraharisetti SB, Dandapat S, Degen GH, Malik JK (2008) Perturbations in immune responses induced by concurrent sub chronic exposure to arsenic and endosulfan. Toxicol 251:51–60
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Arias AH, Marcelo TP, Jorge EM (2011) Multi-year monitoring of estuarine sediments as ultimate sink for DDT, HCH and other organochlorinated pesticides in Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 172:17–32
Arshad M, Hussain S, Saleem M (2008) Optimization of environmental parameters for biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan in soil slurry by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 104(2):364–370
Astoviza MJ, Cappelletti N, Bilos C, Migoya CM, Colombo JC (2016) Massive airborne endosulfan inputs related to intensive agriculture in Argentina’s Pampa. Chemoshpere 44:1459–1466
Awasthi N, Singh AK, Jain RK, Khangarot BS (2003) Degradation and detoxification of endosulfan isomers by a defined co-culture of two Bacillus strains. Appl Microb Biotechnol 62:279–283
Bajaj A, Pathak A, Mudiam MR, Mayilraj S, Manickam N (2010) Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas sp. strain IITR01 capable of degrading α-endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. J Appl Microbiol 109:2135–2143
Becker L, Scheringe M, Schenker U, Hungerbuhler K (2011) Assessment of the environmental persistence and long-range transport of endosulfan. Environ Pollut 159:1737–1743
Cappuccino J, Sherman N (2008) Microbiology, a laboratory manual. Pearson Education Inc., New York
Choudhary N, Joshi SC (2003) reproductive toxicity of endosulfan in male Albino Rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:0285–0289
Defo MA, Njine T, Nola M, Beboua FS (2011) Microcosm study of the long term effect of endosulfan on enzyme and microbial activities on two groundnut soils of Yaounde-Cameroon. Afr J Agric Res 6:2039–2050
Desalegn B, Takasuga T, Harada KH, Hitomi T, Fujii Y, Yan HR, Wang P, Senevirathna S, Koizumi A (2011) Historical trends in human dietary intakes of endosulfan and toxaphene in China, Korea and Japan. Chemosphere 83:1398–1405
Ernst WR, Doe JK, Julien G, Hennigar P (1991) Toxicity to aquatic organisms of off -target deposition of endosulfan applied by aircraft. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:103–114
Filonov AE, Puntus IF, Karpov AV et al (2006) Assessment of naphthalene biodegradation efficiency of Pseudomonas and Burkholderia strains tested in soil model systems. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:216–224
Fox JE, Gulledge J, Engelhaupt E, Burow ME, McLachlan JA (2007) Pesticides reduce symbiotic efficiency of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia and host plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10282–10287
Goebel H, Gorbach S, Knauf W, Rimpau RH, Huttenbach H (1982) Properties, effects, residues and analytics of the insecticide endosulfan. Residue Rev 83:40–41
Goswami S, Dileep KS (2009) Biodegradation of α and β endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial strain Bordetella sp. B9. Biodegradation 20(2):199–207
Guo FZ, Zhang LS, Wei JL, Li YB, Shi ZX, Yang YM, Zhou XQ, Sun ZW (2015) Endosulfan induced the arrest of the cell cycle through inhibiting the signal pathway mediated by PKC-α and damaging the cytoskeleton in spermatogonial cells of mice in vitro. Toxicol Res 4:508–518
Harner T, Pozo K, Gouin T, Macdonald AM, Hung H, Cainey J, Peters A (2006) Global pilot study for persistent organic pollutants (POPs) using PUF disk passive air samplers. Environ Pollut 144:445–452
Jaya R, Mohineesh Ray R, Dogra TD, Raina A (2013) Acute oral toxicity and histopathological study of combination of endosulfan and cypermethrin in Wistar Rats. Toxicol Int 20:61–67
Jamil K, Shaik AP, Mahboob M, Krishna D (2004) Effect of organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides (monocrotophos, chlorpyriphos, dimethoate, and endosulfan) on human lymphocytes invitro. Drug Chem Toxicol 27:133–144
Jesitha K, Nimisha KM, Manjusha CM, Harikumar PS (2015) Biodegradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Environ Process 2:225–240
Kalyani SS, Sharma J, Singh S, Lata DP (2009) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading microorganism from tropical acid soil. J Environ Sci Health B 44:663–672
Kumar M, Philip L (2006a) Endosulfan mineralization by bacterial isolates and possible degradation pathway identification. Bioremediat J 10:179–190
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3, integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Kirby ML, Barlow RL, Bloomquist JR (2001) Neurotoxicity of the organochlorine insecticide heptachlor to murine striatal dopaminergic pathways. Toxicol Sci 61:100–106
Kafilzadeh F, Ebrahimnezhad M, Tahery CY (2015) Isolation and identification of endosulfan-degrading bacteria and evaluation of their bioremediation in Kor River, Iran. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 6:39–46
Kim YK, Kim SH, Choi SC (2001) Kinetics of endosulfan degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biotechnol Lett 23:163–166
Kullman WS, Matsumura F (2006) Metabolic pathways utilized by Phanerochaete chrysosporium for degradation of the cyclodiene pesticide endosulfan. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:593–600
Kwon GS, Kim JE, Kim TK, Sohn HY, Koh SC, Shin KS, Kim DG (2002) Klebsiella pneumoniae KE-1 degrades endosulfan without formation of the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:255–259
Kumar M, Philip L (2006b) Bioremediation of endosulfan contaminated soil and water optimization of operating conditions in laboratory scale reactors. J Hazard Mater 136:354–364
Li W, Dai Y, Xue B, Li Y, Peng X, Zhang J, Yan Y (2009) Biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan in aqueous medium and soil by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain CS5. J Hazard Mater 167(1):209–216
Liu W, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Xie H, Song Y (2009) Assessment of the genotoxicity of endosulfan in earthworm and white clover plants using the comet assay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:742–746
Liao XM, Huang M, Liu CY, Abid WPS (2004) Effects of pesticides on soil biochemical characteristics of a paddy soil. J Environ Sci 16:252–255
Qu C, Xing X, Albanese S, Doherty A, Huang H, Lima A, Qi S, Devivo B (2015) Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric organochlorine pesticides along the plain-mountain transect in central China, Regional source vs. long-range transport and air–soil exchange. Atmos Environ 122:31–40
Sand G, Singh DK (2009) Biodegradation of α and β-endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial Strain bordetella sp B9. Biodegradation 20:199–207
Sandhu HS, Brar RS (2009) Pesticides in textbook of veterinary toxicology. Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana
Sarfraz H et al (2007) Screening of soil fungi for in vitro degradation of endosulfan. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(7):939–945
Schafer KS, Kegley SE (2002) Persistent toxic chemicals in the US food supply. J Epidemiol Community Health 56(11):813–817
Seralathan MV, Sivanesan S, Nargunanathan S, Bafana A, Kannan K, Chakrabarti T (2015) Chemotaxis-based endosulfan biotransformation, enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading bacteria. Environ Technol 36:60–67
Sethunathan N, Megharaj M, Chen ZL, Williams BD, Lewis G, Naidu R (2004) Algal degradation of a known endocrine disrupting insecticide, α-Endosulfan, and its metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, in liquid medium and soil. J Agric Food Chem 52:3030–3035
Shinggu DY, Maitera ON, Barminas JT (2015) Determination of organochlorine pesticides residue in fish, water and sediment in Lake Geriyo Adamawa State Nigeria. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem 8:212–220
Shivaramaiah HM, Kennedy IR (2006) Biodegradation of endosulfan by a soil bacterium. J Environ Sci Health Part B 41(6):895–905
Singh PB, Singh V (2007) Pesticide bioaccumulation and plasma sex steroids in fishes during breeding phase from north India. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 55:223–237
Siddique T, Okeke BC, Arshad M, Frankenberger WT Jr (2003) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan degrading microorganisms. J Environ Qual 32:47–54
Sutherland TD, Horne I, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2002a) Gene cloning and molecular characterization of a two-enzyme system catalyzing the oxidative detoxification of b-endosulfan. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6237–6245
Sutherland TD, Weir KM, Lacey MJ, Horne I, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2002b) Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of degrading endosulfate, the toxic metabolite of endosulfan. J Appl Microbiol 92:541–548
Sutherland TD, Weir KM, Lacey MJ, Horne I, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2002c) Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of degrading endosulphate, the toxic metabolite of endosulfan. J App Microbiol 92:541–548
Sunitha S, Murthy VK, Mahmood R (2012) Degradation of endosulfan by mixed bacterial cultures enriched from endosulfan contaminated soils of Southern India. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinform 2:31–35
Thangadurai P, Sumathi S (2014) Biodegradation of endosulfan by soil bacterial cultures. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 94:38–47
Tiemann U (2008) In vivo and in vitro effects of the organochlorine pesticides DDT, TCPM, methoxychlor and lindane on the female reproductive tract of mammals, a review. Reprod Toxicol 25:316–326
Vani T, Saharan N, Roy SD, Ritesh R, Pal AK, Siddaiah GM, Kumar R (2012) Alteration in haematological and biochemical parameters of Catla catla exposed to sub-lethal concentration of cypermethrin. Fish Physiol Biochem 6:577–584
Verma A, Ali D, Farooq M, Pant AB, Ray RS, Hans RK (2011) Expression and inducibility of Endosulfan metabolizing gene in Rhodococcus strain isolated from earthworm gut microflora for its application in bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 102:2979–2984
Weber J, Halsall CJ, Muir D, Teixeira T, Small J, Solomon K, Hermanson M, Hung H, Bidleman T (2010) Endosulfan, a global pesticide, a review of its fate in the environment and occurrence in the arctic. Sci Total Environ 408:2966–2984
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Syed JH, Jun L, Zhang G, Jones KC (2015) Current status of persistent organic pesticides residues in air, water, and soil, and their possible effect on neighboring countries, a comprehensive review of India. Sci Total Environ 511:123–137
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Mohammed Sathak College of Arts & Science (University of Madras), Chennai, for providing the lab facilities to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZAM carried out experimental work; SA, AT, and AA helped in statistical analysis and drafting the manuscript; HAQ and JAB helped in manuscript editing; MO has designed the work and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mir, Z.A., Ali, S., Tyagi, A. et al. Degradation and conversion of endosulfan by newly isolated Pseudomonas mendocina ZAM1 strain. 3 Biotech 7, 211 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0823-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0823-5