Abstract
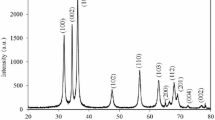
Degradation of hazardous dye effluents released from various industries has received lot of attention because of their serious health hazards. Herein, we report the synthesis of ZnO NPs using crude polysaccharides of Sechium edule fruits for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB). The fruits of S. edule were used as a source to extract polysaccharides by hot water method. The ZnO NPs synthesis was carried out by green chemistry route using extracted crude polysaccharides. The optical, morphological and chemical characteristics of ZnO NPs were characterized using UV–Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. FE-SEM revealed that the green-synthesized ZnO NPs having spherical- and triangle-shaped morphology with an average size of 30–100 nm. EDS showed the existence of Zn (51.64%), O (42.38%) and C (5.98%) elements. Photocatalytic ability of ZnO NPs was studied by the degradation of RhB under visible light irradiation. The ZnO NPs showed 95% degradation efficiency of RhB after 75 min under visible light irradiation and also exhibited good reusable stability up to 5 cycles. The greater photocatalytic activity and reusability show that the ZnO NPs synthesized using polysaccharides of S. edule fruits could be a promising photocatalyst in wastewater treatment and other remediation applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah FH, Bakar NHHA, Bakar MA (2022) Current advancements on the fabrication, modification, and industrial application of zinc oxide as photocatalyst in the removal of organic and inorganic contaminants in aquatic systems. J Hazard Mater 424:127416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127416
Abhishek T, Sharma A, Tejwan N et al (2021) A state of the art review on the synthesis, antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and tissue regeneration activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 295:102495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102495
Akir S, Barras A, Cof Y et al (2016) Eco-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with different morphologies and their visible light photocatalytic performance for the degradation of rhodamine b. J Ceram Int 42:10259–10265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.153
Arumugam M, Choi MY (2020) Effect of operational parameters on the degradation of methylene blue using visible light active BiVO 4 photocatalyst. Bull Korean Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1002/bkcs.11972
Arun J, Nirmala N, Priyadharsini P et al (2022) A mini-review on bioderived carbon and its nanocomposites for removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. Mater Lett 310:131476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131476
Barbosa H, Slater NKH, Marcos JC (2009) Protein quantification in the presence of poly (ethylene glycol ) and dextran using the Bradford method. Anal Biochem 395:108–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.07.045
Bharathi D, Bhuvaneshwari V (2019) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using pure bioflavonoid rutin and their biomedical applications: antibacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. Res Chem Intermed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-03717-9
Bharathi D, Ganesh J, Nandagopal T et al (2022a) Microbial approaches for sustainable remediation of dye - contaminated wastewater : a review. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02767-3
Bharathi D, Ganesh J, Nandagopal T et al (2022b) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of St -ZnO nanorods for methylene blue dye degradation. Mater Lett 311:131637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131637
Chen F, Huang G (2018) Extraction and antioxidant activities of cushaw polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1646–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.200
Chen L, Long R, Huang G, Huang H (2020a) Extraction and antioxidant activities in vivo of pumpkin polysaccharide. Ind Crop Prod 146:112199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112199
Chen Z, Zhao Y, Zhang M et al (2020b) Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of a new polysaccharide from Bletilla striata fibrous roots. Carbohydr Polym 227:115362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115362
Dayana S, Suresh P, Manikandan S et al (2021) Phycoremediation of wastewater for pollutant removal: a green approach to environmental protection and long-term remediation. Environ Pollut 290:117989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117989
Dutta G, Sugumaran A (2021) Bioengineered zinc oxide nanoparticles: chemical, green, biological fabrication methods and its potential biomedical applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 66:102853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102853
Elumalai K, Velmurugan S, Ravi S et al (2015) Bio-approach : Plant mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their catalytic reduction of methylene blue and antimicrobial activity. Adv Powder Technol 26:1639–1651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2015.09.008
Fan Y, Liu Y, Wu Y et al (2021) Natural polysaccharides based self-assembled nanoparticles for biomedical applications—a review. Int J Biol Macromol 192:1240–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.074
Goktas S, Goktas A (2021) A comparative study on recent progress in efficient ZnO based nanocomposite and heterojunction photocatalysts—a review. J Alloy Compound. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158734
Gopu M, Selvam K (2020) Polysaccharides from marine red algae Amphiroa rigida and their biomedical potential: an in-vitro study. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 29:101769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101769
Govarthanan M, Srinivasan P, Selvankumar T et al (2020) Utilization of funnel-shaped ivory flowers of Candelabra cactus for zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesis and their in-vitro anti-cancer and antibacterial activity. Mater Lett 273:127951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127951
Govarthanan M, Mythili R, Kim W et al (2021) Facile fabrication of (2D/2D) MoS2@MIL-88(Fe) interface-driven catalyst for efficient degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 414:125522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125522
Haounati R, El GA, Ouachtak H et al (2021) Design of direct Z-scheme superb magnetic nanocomposite photocatalyst Fe 3 O 4 / Ag 3 PO 4 @ Sep for hazardous dye degradation. Sep Purif Technol 277:119399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119399
Hashemifesharaki R, Xanthakis E, Altintas Z et al (2020) Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from the marshmallow roots: optimization, puri fi cation, structure, and bioactivity. Carbohydr Polym 240:116301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116301
Islam MA, Ali I, Karim SMA et al (2019) Removal of dye from polluted water using novel nano manganese oxide-based materials. J Water Process Eng 32:100911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100911
Kanagaraj T, Sahaya P, Kumar M et al (2022) organic dye degradation under both visible light and solar irradiation. Environ Res 205:112439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112439
Khan S, Naushad M, Govarthanan M, Iqbal J (2022) Emerging contaminants of high concern for the environment: current trends and future research. Environ Res 207:112609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112609
Kumar JA, Krithiga T, Manigandan S et al (2021) A focus to green synthesis of metal/metal based oxide nanoparticles : various mechanisms and applications towards ecological approach. J Clean Prod 324:129198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129198
Luque-morales PA, Lopez-peraza A, Nava-olivas OJ et al (2021) ZnO semiconductor nanoparticles and their application in photocatalytic degradation. Materials 14:7537
Madhan G, Begam AA, Varsha LV et al (2021) Facile synthesis and characterization of chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposite for enhanced antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Int J Biol Macromol 190:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.100
Makvandi P, Baghbantaraghdari Z, Zhou W et al (2021) Gum polysaccharide/nanometal hybrid biocomposites in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Biotechnol Adv 48:107711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107711
Mehdi M, Karimi H, Ghaedi M (2022) Nanofibers based quaternary CeO 2 / Co 3 O 4 / Ag / Ag 3 PO 4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst with enhanced degradation of organic dyes. Mater Res Bull 147:111629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111629
Nava OJ, Soto-Robles CA, Gómez-Gutiérrez CM et al (2017) Fruit peel extract mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Mol Struct 1147:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.06.078
Nguyen LTT, Vo DN, Nguyen LTH, Duong ATT (2022) Synthesis, characterization, and application of ZnFe 2 O 4 @ ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B under visible-light illumination. Environ Technol Innov. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102130
Preethi S, Abarna K, Nithyasri M et al (2020) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposite for antibacterial activity onto cotton fabrics and dye degradation applications. Int J Biol Macromol 164:2779–2787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.047
Rafiq A, Ikram M, Ali S et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. J Ind Eng Chem 97:111–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.02.017
Rajendrachari S, Taslimi P, Cahit A (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B ( RhB ) dye in waste water and enzymatic inhibition study using cauliflower shaped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a novel One-pot green synthesis method. Arab J Chem 14:103180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103180
Raman CD, Kanmani S (2016) Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: a review. J Environ Manage 177:341–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.034
Ramesh P, Saravanan K, Manogar P et al (2021) Sensing and bio-sensing research green synthesis and characterization of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial potential. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 31:100399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100399
Saravanan M, Gopinath V, Kumar M et al (2018) Microbial pathogenesis green synthesis of anisotropic zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and cytofriendly properties. Microb Pthogenes 115:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.12.039
Selvam K, Albasher G, Alamri O et al (2022a) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of novel Canthium coromandelicum leaves based copper oxide nanoparticles for the degradation of textile dyes. Environ Res 211:113046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113046
Selvam K, Allam AA, Ajarem JS et al (2022b) Annona reticulata leaves-assisted synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and assessment of cytotoxicity and photocatalytic impact. Mater Lett 309:131379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131379
Shi M, Wei X, Xu J et al (2017) Carboxymethylated degraded polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera: preparation and in vitro antioxidant activity. Food Chem 215:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.151
Su Y, Li L (2020) Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from four auriculariales. Carbohydr Polym 229:115407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115407
Sukumar K, Arumugam S, Thangaswamy S (2020) Optik eco-friendly cost-e ff ective approach for synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic performance. 202:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163507
Sundrarajan M, Jegatheeswaran S, Selvam S et al (2017) Green approach: Ionic liquid assisted synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnO in phyto medium and their antibacterial investigation. Mater Lett 201:31–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.04.088
Thambiraj SR, Reddy N, Phillips M et al (2019) Biological activities and characterization of polysaccharides from the three Australian Sweet Lupins Biological activities and characterization of polysaccharides from the three Australian Sweet Lupins. Int J Food Prop 22:522–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2019.1588298
Vaidehi D, Bhuvaneshwari V, Bharathi D, Sheetal BP (2018) Antibacterial and photocatalytic activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Solanum lycopersicum leaf extract. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad426
Vieira EF, Pinho O, Ferreira IMPLVO, Delerue-matos C (2019) Chayote (Sechium edule): a review of nutritional composition, bioactivities and potential applications. Food Chem 275:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.146
Vinotha V, Yazhiniprabha M, Selva D, Mahboob S (2020) Biogenic synthesis of aromatic cardamom-wrapped zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential antibacterial and mosquito larvicidal activity: an effective eco-friendly approach. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104466
Wang Y, Li Y, Ma X et al (2018) Industrial Crops & Products Extraction, puri fi cation, and bioactivities analyses of polysaccharides from Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Ind Crop Prod 122:596–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.011
Yang Q, Peng J, Xiao H et al (2022) Polysaccharide hydrogels: functionalization, construction and served as scaffold for tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 278:118952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118952
Zhao S, Han Z, Yang L et al (2020a) Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity evaluation of polysaccharides from Smilacina japonica. Int J Biol Macromol 151:576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.015
Zhao S, Xu H, Zhan Y, Gao Y (2020b) Ultrasonic extraction and determination of polysaccharide from Smilacina japonica. 35:1–4
Zhong R, Zhong Q, Huo M et al (2020) Preparation of biocompatible nano-ZnO/chitosan microspheres with multi-functions of antibacterial, UV-shielding and dye photodegradation. Int J Biol Macromol 146:939–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.217
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP 2021/68), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. This work was partly supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government (MOTIE) (No. 20194110100100, Full-scale feasibility study of the stability and efficiency improvement of a biogas production facility based on biomass from urban/living environments).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharathi, D., AlSalhi, M.S., Devanesan, S. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using green-synthesized ZnO nanoparticles from Sechium edule polysaccharides. Appl Nanosci 12, 2477–2487 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02502-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02502-w