Abstract
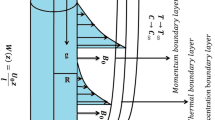
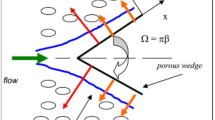
This exertion is part of a liable approach for the advancement of nanotechnology and nanoscience to scrutinize the thermal and rheological aspects of the nanofluids. The conformist heat transport fluids are broadly reported to be one of the notable reasons of the reduced enactment of heat transport tools, boosting the energy charges. For this concern to be stable, nanofluids have been familiarized as probable proxies to the conformist fluids because of their intensify aptitude of heat transport coefficient. Here, the up-front goal is to investigate the aspect of nonlinear radiated and chemical reaction with aspects of Arrhenius activation energy in Carreau nanofluid. Additionally, mixed convection, MHD, and new mass flux theory is explored. The framed system is envisioned numerically via bvp4c. Temperature field intensifies against enhanced values of radiation and thermophoresis parameters, respectively. Concentration has conflicted performance for escalating activation energy and Brownian motion parameters, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(u,v,w\) :
-
Velocity components
- \(x,y,z\) :
-
Space coordinates
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\Gamma\) :
-
Material rate constant
- \(n\) :
-
Power law index
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity
- \(B_{0}\) :
-
Magnetic strength
- \(\rho_{f}\) :
-
Fluid density
- \(g\) :
-
Gravity
- \((\rho c)_{f}\) :
-
Heat capacity of fluid
- \(\xi_{T}\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Nanofluid ambient temperature
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Nanofluid ambient concentration
- \(D_{B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(D_{T}\) :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- \(q_{r}\) :
-
Radiative heat flux
- \(k^{ * }\) :
-
Mean absorption coefficient
- \(\sigma^{ * }\) :
-
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- \(k_{r}\) :
-
Reaction rate
- \(m( - 1 < m < 1)\) :
-
Fitted rate constant
- \(E_{A}\) :
-
Activation energy
- \(\kappa\) :
-
Boltzmann constant
- \(U_{w} (x,\,t),V_{w} (y,\,t)\) :
-
Stretching velocities
- \(\xi_{C}\) :
-
Solutal expansion coefficient
- \(T\) :
-
Nanofluid temperature
- \(T_{w}\) :
-
Wall temperature
- \(C\) :
-
Nanoparticles concentration
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\tau\) :
-
Effective heat capacity ratio
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(a,b,\beta\) :
-
Positive constants
- MHD:
-
Magnetohydrodynamics
- ODEs:
-
Ordinary differential equations
- PDEs:
-
Partial differential equations
- HAM:
-
Homotopy analysis method
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless variable
- \(We\) :
-
Local Weissenberg number
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetic parameter
- \(S\) :
-
Unsteadiness parameter
- \(\lambda^{*}\) :
-
Thermal buoyancy parameter
- \(N^{*}\) :
-
Buoyancy ratio parameter
- \(R_{d}\) :
-
Thermal radiation parameter
- \(\theta_{w}\) :
-
Temperature ratio parameter
- \(N_{b}\) :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(N_{t}\) :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(\Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Le\) :
-
Lewis number
- \(E_{A}\) :
-
Activation energy parameter
- \(\Lambda_{1}\) :
-
Reaction rate parameter
- \(\Lambda_{2}\) :
-
Temperature difference parameter
- \(\tau_{xz} ,\tau_{yz}\) :
-
Surface shear stresses
- \(C_{fx} ,C_{fy}\) :
-
Skin friction coefficients
- \(Nu_{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \({\text{Re}}_{x}\) :
-
Local Reynolds number
- \(f\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\phi\) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
References
Anwar MS (2020) Numerical study of transport phenomena in a nanofluid using fractional relaxation times in Buongiorno model. Phys Scr 95:035211
Bestman AR (1991) Radiative heat transfer to flow of a combustible mixture in a vertical pipe. Int J Energy Res 15:179–184
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Chamkha AJ, Aly AM, Mansour MA (1970) Similarity solution for unsteady heat and mass transfer from a stretching surface embedded in a porous medium with suction/injection and chemical reaction effects. Chem Eng Commun 2010:846–858
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME 231:99–106
Gireesha BJ, Mahanthesh B, Makinde OD, Muhammad T (2018) Effects of Hall current on transient flow of dusty fluid with nonlinear radiation past a convectively heated stretching plate. Defect Diff Forum 237:352–363
Gireesha BJ, Sampathkumar PB (2018) Hall effects on dusty nanofluid two-phase transient flow past a stretching sheet using KVL model. J Mol Liq 256:139–147
Hayat T, Rashid M, Alsaedi A (2019) Nonlinear radiative heat flux in Oldroyd-B nanofluid flow with Soret and Dufour effects. Appl Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01028-y
Hosseinzadeh K, Gholinia M, Jafari B, Ghanbarpour A, Olfian H, Ganji DD (2018) Nonlinear thermal radiation and chemical reaction effects on Maxwell fluid flow with convectively heated plate in a porous medium. Heat Transf. https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.21404
Hsiao KL (2017) To promote radiation electrical MHD activation energy thermal extrusion manufacturing system efficiency by using Carreau-nanofluid with parameters control method. Energy 130:486–499
Irfan M, Khan M (2019) Simultaneous impact of nonlinear radiative heat flux and Arrhenius activation energy in flow of chemically reacting Carreau nanofluid. Appl Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01012-6
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA, Ayaz M (2018) Modern development on the features of magnetic field and heat sink/source in Maxwell nanofluid subject to convective heat transport. Phy Letters A 382:1992–2002
Irfan M, Khan WA, Khan M, Gulzar MM (2019) Influence of Arrhenius activation energy in chemically reactive radiative flow of 3D Carreau nanofluid with nonlinear mixed convection. J Phys Chem Solids 125:141–152
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA, Rafiq K (2020a) Physical aspects of shear thinning/thickening behavior in radiative flow of magnetite Carreau nanofluid with nanoparticle mass flux conditions. Appl Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01323-z
Irfan M, Rafiq K, Khan WA, Khan M (2020b) Numerical analysis of steady Carreau nanofluid flow with variable conductivity. Appl Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01331-z
Khan MI, Afzal S, Hayat T, Waqas M, Alsaedi A (2020) Activation energy for the Carreau-Yasuda nanomaterial flow: Analysis of the entropy generation over a porous medium. J Mol Liq 297:111905
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA (2018) Thermophysical properties of unsteady 3D flow of magneto Carreau fluid in presence of chemical species: A numerical approach. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-0964-4
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA, Alshomrani AS (2017) A new modeling for 3D Carreau fluid flow considering nonlinear thermal radiation. Results Phy 7:2692–2704
Kumar PBS, Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Shehzad SA (2018) Quadratic convective flow of radiated nano-Jeffrey liquid subject to multiple convective conditions and Cattaneo-Christov double diffusion. Appl Math Mech 39:1331–1326
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR (2017) Unsteady three-dimensional MHD flow of a nano Eyring-Powell fluid past a convectively heated stretching sheet in the presence of thermal radiation, viscous dissipation and Joule heating. J Ass Arab Uni Basic Appl Sci 23:75–84
Mahanthesh B, Shashikumar NS, Gireesha BJ, Animasaunc IL (2019) Effectiveness of Hall current and exponential heat source on unsteady heat transport of dusty TiO2-EO nanoliquid with nonlinear radiative heat. J Comput Design Eng. 6:551–561
Mahanthesh B, Shehzad SA, Ambreen T, Khan SU (2020) Significance of Joule heating and viscous heating on heat transport of MoS 2-Ag hybrid nanofluid past an isothermal wedge. J Ther Ana Calorimetry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09578-y
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017) Buoyancy effects on the MHD nanofluid flow past a vertical surface with chemical reaction and activation energy. Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:1340–1346
Narayana PVS, Tarakaramu N, Makinde OD, Venkateswarlu B, Sarojamma G (2018) MHD stagnation point flow of viscoelastic nanofluid past a convectively heated stretching surface. Comput Anal Heat Transf fluids Solids 387:106–120
Qi C, Tang J, Ding Z, Yan Y, Guo L, Ma Y (2019) Effects of rotation angle and metal foam on natural convection of nanofluids in a cavity under an adjustable magnetic field. Commun. Heat Mass Transf Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.104349
Ramesh GK (2020) Analysis of active and passive control of nanoparticles in viscoelastic nanomaterial inspired by activation energy and chemical reaction. Physica A Statistical Mech Appl 550:123964
Rashid M, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Ahmed B (2019) Magnetohydrodynamic flow of Maxwell nanofluid with binary chemical reaction and Arrhenius activation energy. Appl Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01143-w
Sajid T, Sagheer M, Hussain S, Bilal M (2018) Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Maxwell nanofluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy. AIP Adv 10(1063/1):5019218
Sharidan S, Mahmood T, Pop I (2016) Similarity solutions for the unsteady boundary layer flow and heat transfer due to a stretching sheet. Int J Appl Mech Eng 11:647–654
Sheremet MA, Pop I, Rosca NC (2016) Magnetic field effect on unsteady natural convection in a wavy-walled cavity filled with a nanofluid: Buongiorno's mathematical model. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 61:211–222
Waqas M, Jabeen S, Hayat T, Shehz SA, Alsaedi A (2020) Numerical simulation for nonlinear radiated Eyring-Powell nanofluid considering magnetic dipole and activation energy. Int Commu Heat Mass Transf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.104401
Wen D, Ding Y (2005) Formulation of nanofluids for natural convective heat transfer applications. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 26:855–864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irfan, M., Anwar, M.S., Rashid, M. et al. Arrhenius activation energy aspects in mixed convection Carreau nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation. Appl Nanosci 10, 4403–4413 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01498-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01498-5