Abstract
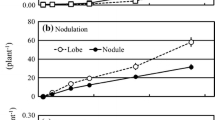
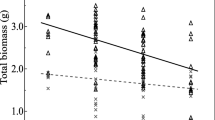
We have analysed the growth and symbiotic performance of actinorhizal Discaria trinervis at various Ca supply regimes. We aimed at discriminating between specific, if any, effects on nodulation and general growth stimulation by Ca. The hypothesis that a high Ca supply would interfere with nodulation by Frankia was also tested. Results showed that plant growth increased with Ca supply. Nodulation was stimulated by moderate levels of Ca, but inhibited by Ca higher than 0.77 mM. Growth of nodules was less affected by Ca than shoot and root growth. Ca concentration of symbiotic plants increased with Ca supply, but nitrogen concentration was independent of Ca at concentrations which did not impair plant growth. All together, these results show that Ca has a positive effect on the establishment and functioning of the symbiosis between Discaria trinervis and Frankia. However, the positive influence of Ca was more likely due to a promotion of plant growth rather than a direct effect on nodule growth and nitrogen fixation itself. At high levels of Ca supply nodulation was impaired. Given the intercellular infection pathway in Discaria trinervis, we suggest that the increment of Ca availability would strengthen its root cell walls, thus decreasing Frankia penetration of the root.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bateman, D.F. and Lunsden, R.D. 1965. Relation between calcium content and nature of pectic substances in bean hypocotyls of different ages to susceptibility to an isolate of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 55: 734–738.
Caetano-Anollés, G., Lagares, A., and Favelukes, G. 1989. Adsorption of Rhizobium meliloti to alfalfa roots: Dependence on divalent cations and pH. Plant and Soil 117: 67–74.
Cárdenas, L., Holdaway-Clarke, T.L., Sanchez, F., Quinto, C., Feijó, J.A., Kunkel, J.G., and Hepler, P.K. 2000. Ion changes in legume root hairs responding to Nod factors. Plant Physiology 123: 443–452.
Chaia, M.E. 1998. Isolation of an effective strain of Frankia from nodules of Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae). Plant and Soil 205: 99–102.
Crannell, W.K., Tanaka, W., and Myrold, D.D. 1994. Calcium and pH interaction on root nodulation of nursery-grown red alder (Alnus rubra Bong.) seedlings by Frankia. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 26: 607–614.
Huss-Danell, K. 1978. Nitrogenase activity measurements in intact plants of Alnus incana. Physiologia Plantarum 43: 372–376.
Huss-Danell, K. 1997. Actinorhizal symbioses and their N2 fixation. New Phytologist 136: 375–405.
Huss-Danell, K., Gentili, F., Valverde, C., Wall, L.G., and Wiklund, A. 2002. Phosphorus is important in nodulation of actinorhizal plants. In: Nitrogen Fixation and Sustainable Agriculture: Global Perspectives. Finan, T., O’Brian, M., Layzell, D., Vessey, K., and Newton, W., eds. CAB International Publishing, Wallingford, UK, pp. 163–166.
Jackson, M.L. 1958. Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, sections 8-13 and 8-33.
Krauss, A. 1971. Einfluss der Ernährung des Salats mit Massennährstoffen auf den Befall mit Botrytis cinera Pers. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde 128: 12–23.
Lodeiro, A.R., Lagares, A., Martínez, E.N., and Favelukes, G. 1995. Early interactions of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli and bean roots: Specificity in the process of adsorption and its requirement of Ca+2 and Mg+2 ions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61: 1571–1579.
Lowther, W.L. and Loneragan, J.F. 1968. Calcium and nodulation in subterraneum clover (Trifolium subterraneum L.). Plant Physiology 43: 1362–1366.
Marschner, H. 1995. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, London, UK.
Nittayajarn, A. and Baker, D.D. 1989. Methods for the quantification of Frankia cell biomass. Plant and Soil 118: 199–204.
Prégent, G. and Camiré, C. 1985. Mineral nutrition, dinitrogen fixation, and growth of Alnus crispa and Alnus glutinosa. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 15: 855–861.
Richardson, A.E., Djordjevic, M.A., Rolfe, B.G., and Simpson, R.J. 1988. Effect of pH, Ca and Al on the exudation from clover seedlings of compounds that induce the expression of nodulation genes in Rhizobium trifolii. Plant and Soil 109: 37–47.
Robson, A.D. 1983. Mineral nutrition (Chapter 2). In: Nitrogen Fixation (Volume 3, Legumes). Broughton, W.J., ed. Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 37–55.
Séguin, A. and Lalonde, M. 1989. Detection of pectinolytic activity and pel homologous sequences in Frankia. Plant and Soil 118: 221–229.
Tisa, L.S.and Ensign, J.C. 1987. The calcium requirement for functional vesicle development and nitrogen fixation of Frankia strains EAN1pec and CpI1. Archives of Microbiology 149: 24–29.
Valverde, C. and Wall, L.G. 1999a. Time course of nodule development in Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae)-Frankia symbiosis. New Phytologist 141: 345–354.
Valverde, C. and Wall, L.G. 1999b. Regulation of nodulation in Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae)-Frankia symbiosis. Canadian Journal of Botany 77: 1302–1310.
Valverde, C. and Wall, L.G. 2002. Nodule distribution on the roots of actinorhizal Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae) growing in pots. Environmental and Experimental Botany 47: 95–100.
Valverde, C., Wall, L.G., and Huss-Danell, K. 2000. Regulation of nodulation and nodule mass relative to nitrogenase activity and nitrogen demand in seedlings of Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae). Symbiosis 28: 49–62.
Valverde, C., Ferrari, A., and Wall, L.G. 2002. Phosphorus and the regulation of nodulation in the actinorhizal symbiosis between Discaria trinervis and Frankia BCU110501. New Phytologist 153: 43–52.
Wall, L.G., Valverde, C., and Huss-Danell, K. 2003. Regulation of nodulation in the absence of N2 is different in actinorhizal plants with different infection pathways. Journal of Experimental Botany 54: 1253–1258.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valverde, C., Ferrari, A. & Gabriel Wall, L. Effects of calcium in the nitrogen-fixing symbiosis between actinorhizal Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae) and Frankia . Symbiosis 49, 151–155 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-009-0046-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-009-0046-6