Abstract
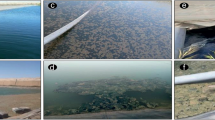
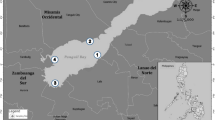
To characterize seasonal variation of microphytobenthos (MPB) biomass and composition in a Phragmites australis bed, the algal pigments in the top 20 mm of the sediments in a macrophyte marsh in a marine protected area in Yeoja Bay (Korea) were investigated monthly using high-performance liquid chromatography from November 2009 to December 2010, and compared with the upper and middle parts of a bare intertidal flat. Chlorophyll a (chla) concentration showed similar seasonal trends at all the sites, with bimodal peaks in April and August. The seasonal chla peaks were more pronounced on the bare flat than on the P. australis bed. While high amounts of pheophorbides a suggest an increased grazing activity during April–September on the bare flat, high ratios of pheophytins a/pheophorbides a on the P. australis bed indicate high levels of microbial degradation. While the dominance of diatoms characterized by high fuco/chla ratios appeared at all sites, the peaks of some accessory pigments (chlb, lutein, and zeaxanthin) at the P. australis bed led to the compositional difference in algal pigments from the bare sites. Altogether, our results suggest that the MPB biomass and composition in the P. australis bed are mediated by the vascular plant canopy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austen I, Anderson TJ, Edelvang K (1999) The influence of benthic diatoms and invertebrates on the erodibility of an intertidal mudflat, the Danish Wadden Sea. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 49:99–111
Barranguet C, Kromkamp J, Peene J (1998) Factor controlling primary production and photosynthetic characteristics of intertidal microphytobenthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 173:117–126
Bianchi ST, Findlay S (1991) Decomposition of Hudson estuary macrophytes: photosynthetic pigment transformations and decay constants. Estuaries 14:65–73
Bianchi ST, Findlay S, Fontvieille D (1991) Experimental degradation of plant materials in Hudson River sediments I. Heterotrophic transformations of plant pigments. Biogeochemistry 12:171–187
Bianchi ST, Findlay S, Dawson R (1993) Organic matter sources in the water column and sediments of the Hudson river estuary: the use of plant pigments as tracers. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 36:359–376
Blanchard GF, Guarini JM, Richard P, Gros P, Mornet F (1996) Quantifying the short-term temperature effect on light-saturated photosynthesis of intertidal microphytobenthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 134:309–313
Blanchard GF, Guarini JM, Orvain F, Sauriau PG (2001) Dynamic behaviour of benthic microalgal biomass in intertidal sediments. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 264:85–100
Borges AV (2005) Do we have enough pieces of the jigsaw to integrate CO2 fluxes in the Coastal Ocean? Estuaries 28(1):3–27
Brotas V, Plante-Cuny MR (1998) Spatial and temporal patterns of microphytobenthic taxa of estuarine tidal flats in the Tagus Estuary (Portugal) using pigment analysis by HPLC. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 171:43–57
Brotas V, Plante-Cuny MR (2003) The use of HPLC pigment analysis to study microphytobenthos communities. Acta Oecologia 24:109–115
Brotas V, Cabrita T, Portugal A, Serodio J, Catanno F (1995) Spatio-temporal distribution of microphytobenthic biomass in tidal flats of the Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Hydrobiologia 300–301:93–104
Cariou-Le Gall V, Blanchard G (1995) Monthly measurements of pigment concentration from an intertidal muddy sediment of Marennes-Oleron, France. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 121:171–179
Cartaxana P, Jesus B, Brotas V (2003) Phaeophorbide and phaeophytin a-like pigments as useful markers for intertidal microphytobenthos grazing by Hydrobia ulvae. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 58:293–297
Cartaxana P, Mendes CR, van Leeuwe MA, Brotas V (2006) Comparative study on microphytobenthic pigments of muddy and sandy intertidal sediments of the Tagus estuary. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 66:225–230
Choi JM, Lee YG, Woo HJ (2005) Seasonal and spatial variations of tidal flat sediments in Yeoja Bay, south coast of Korea. J Korean Earth Sci Soc 26:253–267
Choy EJ, Richard P, Kim KR, Kang CK (2009) Quantifying the trophic base for benthic secondary production in the Nakdong River estuary of Korea using stable C and N isotopes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 382:18–26
Colijn F (1982) Light absorption in the waters of the Ems-Dollard estuary and its consequences for the growth of phytoplankton and microphytobenthos. Neth J Sea Res 15:196–216
De Jong DJ, De Jonge VN (1995) Dynamics and distribution of microphytobenthic chlorophyll-a in the Western Scheldt estuary (SW Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 311:21–30
De Jonge VN, Colijn F (1994) Dynamics of microphytobenthos biomass in the Ems estuary measured as chlorophyll-a and carbon. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 104:185–196
Du GY, Son M, Misun Y, An S, Chung IK (2009) Microphytobenthic biomass and species composition in intertidal flats of the Nakdong River estuary, Korea. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 82:663–672
Du GY, Son M, An S, Chung IK (2010) Temporal variation in the vertical distribution of microphytobenthos in intertidal flats of the Nakdong River estuary, Korea. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 86:62–70
Hwang DW, Kim G, Lee YW, Yang HS (2005) Estimating submarine inputs of groundwater and nutrients to a coastal bay using radium isotopes. Mar Chem 96:61–71
Janousek CN (2009) Taxonomic composition and diversity of microphytobenthos in southern California marine wetland habitats. Wetlands 29:163–175
Jesus B, Brotas V, Ribeiro L, Mendes CR, Cartaxana P, Paterson DM (2009) Adaptations of microphytobenthos assemblages to sediment type and tidal position. Cont Shelf Res 29:1624–1634
Kang CK, Kim JB, Lee KS, Kim JB, Lee PY, Hong JS (2003) Trophic importance of benthic microalgae to macrozoobenthos in coastal bay systems in Korea: dual stable C and N isotope analyses. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 259:79–92
Kang CK, Lee YW, Choy EJ, Shin JK, Seo IS, Hong JS (2006) Microphytobenthos seasonality determines growth and reproduction in intertidal bivalves. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 315:113–127
Kühl M, Lassen C, Jørgensen B (1994) Light penetration and light intensity in sandy marine sediments measured with irradiance and scalar irradiance fiber-optic microprobes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 105:139–148
Lucas CH, Holligan PM (1999) Nature and ecological implications of algal pigment diversity on the Molenplaat tidal flat (Westerschelde estuary, SW Netherlands). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 180:51–64
MacIntyre HL, Geider RJ, Miller DC (1996) Microphytobenthos: the ecological role of the ‘secret garden’ of unvegetated, shallow-water marine habitats. I. Distribution, abundance and primary production. Estuaries 19:186–201
McLusky DS (1989) The estuaine ecosystem, secondth edn. Chmapman and Hall, New York
Méléder V, Barillé L, Rincé Y, Morançais M, Rosa P, Gaudin P (2005) Spatio-temporal changes in microphytobenthos structure analysed by pigment composition in a macrotidal flat (Bourgneuf Bay, France). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 297:83–99
Miller DC, Geider RJ, MacIntyre HL (1996) Mecophytobenthos: the ecological role of the “secret garden” of unvegetated, shallow-water marine habitats. II. Role in sediment stability and shallow-water food webs. Estuaries 19:202–212
Montagna P, Coull B, Herring T, Dudley B (1983) The relationship between abundances of meiofauna and their suspected micobial food (diatoms and bacteria). Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 17:381–394
Montani S, Magni P, Abe N (2003) Seasonal and interannual patterns of intertidal microphytobenthos in combination with laboratory and areal production estimates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 249:79–91
Park HJ, Lee WC, Choy EJ, Choi KS, Kang CK (2011) Reproductive cycle and gross biochemical composition of the ark shell Scapharca subcrenata (Lischke, 1869) reared on subtidal mudflats in a temperate bay of Korea. Aquaculture 321–323:149–157
Pinckney J, Zingmark RG (1993) Biomass and production of benthic microalgal communities in estuarine habitats. Estuaries 16:887–897
Pinckney J, Paerl HW, Fitzpatrick M (1995) Impacts of seasonality and nutrients on microbial mat community structure and function. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 123:207--216
Plante-Cuny MR, Barranguet C, Bonin D, Grenz C (1993) Does chlorophyllide a reduce reliability of chlorophyll a measurements in marine coastal sediments? Aquat Sci 55:19–30
Reise K (1985) Tidal flat ecology: an experimental approach to species interactions. Springer, Berlin
Shim HB, Cho WB, Choi BH (2009) Distribution of halophytes in coastal salt marsh and on sand dunes in Korea. Korean J Pl Taxon 39:264–276
Soetaert K, Hoffmann M, Meire P, Starink M, Oevelen D, Regenmortel S, Cox T (2004) Modeling growth and carbon allocation in two reed beds (Phragmites australis) in the Scheldt estuary. Aquat Bot 79:211–234
Sullivan MJ, Moncreiff CA (1988) Primary production of edaphic algal communities in a Mississippi salt marsh. J Phycol 24:49–58
Tyler AC, McGlathery KJ, Anderson IC (2003) Benthic algae control sediment-water column fluxes of organic and inorganic nitrogen compounds in a temperate lagoon. Limnol Oceanogr 48:2125–2137
Underwood GJC, Kromkamp J (1999) Primary production by phytoplankton and microphytobenthos in estuaries. Adv Ecol Res 29:93–153
Underwood GJC, Philips J, Saunders K (1998) Distribution of estuarine benthic diatom species along salinity and nutrient gradients. Eur J Phycol 33:173–183
Van der Grinten E, Janssen APHM, De Mutsert K, Barranguet C, Admiraal W (2005) Temperature- and light-dependent performance of the cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya foveolarum and the diatom Nitzschia perminuta in mixed biofilms. Hydrobiologia 548:267–278
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems. Academic, New York
Whitcraft CR, Levin LA (2007) Regulation of benthic algal and animal communities by salt marsh plants: impact of shading. Ecology 88:904–917
Wolfstein K, Colijn F, Doerffer R (2000) Seasonal dynamics of microphytobenthos biomass and photosynthetic characteristics in the northern German Wadden Sea, obtained by the photosynthetic light dispensation system. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 51:651–662
Zapata M, Rodrlguez F, Garrido JL (2000) Separation of chlorophylls and carotenoids from marine phytoplankton: a new HPLC method using a reversed phase C8 column and pyridine-containing mobile phases. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 195:29–45
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2009-0074280).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.J., Choy, E.J. & Kang, CK. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Microphytobenthos on the Common Reed Phragmites australis bed in a Marine Protected Area of Yeoja Bay, Korea. Wetlands 33, 737–745 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-013-0433-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-013-0433-x