Abstract
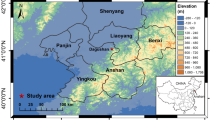
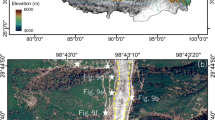
The karst mountainous areas of southwestern China are widely distributed and affluent in mineral resources. However, mining activities induced numerous large-scale landslides in this area, resulting in tremendous loss of lives and property to residents. As a result, it is crucial to figure out the triggering mechanism and failure modes of mining landslides for landslide prevention. In this paper, the environment characteristics and triggering mechanism of mining landslides in karst mountainous areas of southwestern China were analyzed by investigating a few mining landslides. Specifically, it can be attributed to the natural environment and human activities, which are topography, lithology, geological structure, karst hydrogeology, rainfall, and mining activities. On the other hand, a unified failure mode classification system for mining landslides in karst mountainous areas of Southwest China was established based on the international landslide classification system and different slope structures (subhorizontal bedding layered slope, bedding layered slope, anti-dip layered slope, lateral layered slope, oblique inclined bedding layered slope). In this classification system, the basic failure modes were analyzed in detail, and the mining impact mechanisms for each failure mode were revealed. The corresponding mechanical models and stability criteria for mining-induced flexural topple and planar slide were summarized. This study not only identifies and rapidly classifies mining landslides in the karst mountainous areas of southwestern China, but also further facilitates the prediction and evaluation of the stability of mining-induced unstable rock masses.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All authors consent to publish all data and materials and comply with field standards.
Code availability
Not applicable (this manuscript has no software application or custom code).
References
Adhikary DP, Dyskin AV (2007) Modelling of progressive and instantaneous failures of foliated rock slopes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 40(4):349–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-006-0085-8
Adhikary DP, Dyskin AV, Jewell RJ, Stewart DP (1997) A study of the mechanism of flexural toppling failure of rock slopes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 30(2):75–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020126
Ali S, Kamran E, Bibhu M (2018) Degradation of a discrete infilled joint shear strength subjected to repeated blast-induced vibrations. Int J Min Sci Technol 28(4):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.04.015
Arca D, Kutoglu HS, Becek K (2018) Landslide susceptibility mapping in an area of underground mining using the multicriteria decision analysis method. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7085-5
Aydan Ö, Kawamoto T (1992) The stability of slopes and underground openings against flexural toppling and their stabilisation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 25(3):143–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01019709
Ban YX, Fu X, Xie Q, Cui JF, Xu H (2021) A simplified calculation method for ultimate mining dimension in thin coal seam. Geotech Geol Eng (prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10706-021-01717-Y
Benko B, Stead D (1998) The Frank slide: a reexamination of the failure mechanism. Can Geotech J 35(2):299–311. https://doi.org/10.1139/t98-005
Bentley SP, Siddle HJ (1996) Landslide research in the South Wales coalfield. Eng Geol 43(1):65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(95)00084-4
Bowa VM, Xia YY (2018) Stability analyses of jointed rock slopes with counter-tilted failure surface subjected to block toppling failure mechanisms. Arab J Sci Eng 43(10):5315–5331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3168-4
Chen HR, Qin SQ, Xue L, Yang BC, Zhang K (2018) A physical model predicting instability of rock slopes with locked segments along a potential slip surface. Eng Geol 242:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.05.012
Chen LQ, Zhao CY, Li B, He K, Ren CF, Liu XJ, Liu DL (2021) Deformation monitoring and failure mode research of mining-induced Jianshanying landslide in karst mountain area, China with ALOS/PALSAR-2 images. Landslides 18:2739–2750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01678-6
Cipriano DM, Giuliana M, Marco V (2014) Deep-seated gravitational slope deformations in western Sicily: controlling factors, triggering mechanisms, and morphoevolutionary models. Geomorphology 208:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.11.023
Cui FP, Li B, Xiong C, Yang ZP, Peng JQ, Li JS, Li HW (2022) Dynamic triggering mechanism of the Pusa mining-induced landslide in Nayong County, Guizhou Province, China. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 13(1):123–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.2017020
Dahal RK, Hasegawa S (2008) Representative rainfall thresholds for landslides in the Nepal Himalaya. Geomorphology 100(3–4):429–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.01.014
Dai ZY (2019) Study on deformation and failure mechanism and similar simulation test of consequent bedding rock slope after underground mining. Dissertation, Chongqing University, China (in Chinese)
Di Maggio C, Madonia G, Vattano M (2014) Deep-seated gravitational slope deformations in western Sicily: Controlling factors, triggering mechanisms, and morphoevolutionary models. Geomorphology 208:173–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorPh.2013.11.023
de Freitas MH, Watters RJ (1973) Some field examples of toppling failure. Geotechnique 23(4):495–513. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1973.23.4.495
Deniz A, Hakan SK, Kazimierz B (2018) Landslide susceptibility mapping in an area of underground mining using the multicriteria decision analysis method. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7085-5
Detwiler RL, Rajaram H (2007) Predicting dissolution patterns in variable aperture cracks: evaluation of an enhanced depth-averaged computational model. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005147
Do TN, Wu JH (2020) Simulating a mining-triggered rock avalanche using DDA: a case study in Nattai North, Australia. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105386
Erginal AE, Türkes M, Ertek TA, Baba A, Bayrakdar C (2008) Geomorphological investigation of the excavation-induced Dündar landslide, Bursa—Turkey. Geogr Ann A 90(2):109–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0459.2008.00159.x
Fan XM, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Zheng G, Huang RQ, Dai LX, Ju YZ (2019) The “long” runout rock avalanche in Pusa, China, on August 28, 2017: a preliminary report. Landslides 16(1):139–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1084-z
Feng L (2013) Failure models of nearly horizontal rock slopes with the upper hard and lower soft. Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, China (in Chinese)
Feng Z, Li B, Yin YP, He K (2014) Rockslides on limestone cliffs with subhorizontal bedding in the southwestern calcareous area of China. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 14(9):2627–2635. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-2627-2014
Feng Z, Li B, Cai QP, Cao JW (2016) Initiation mechanism of the Jiweishan landslide in Chongqing, Southwestern China. Environ Eng Geosci. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.22.4.341
Ge YF, Tang HM, Ez Eldin MAM, Chen HZ, Zhong P, Zhang L, Fang K (2019) Deposit characteristics of the Jiweishan rapid long-runout landslide based on field investigation and numerical modeling. B Eng Geol Environ 78(6):4383–4396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1422-3
Goeppert N, Goldscheider N, Scholz H (2011) Karst geomorphology of carbonatic conglomerates in the Folded Molasse zone of the Northern Alps (Austria/Germany). Geomorphology 130(3–4):289–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.04.011
Goodman RE, Bray JW (1976) Toppling of rock slopes. In: Proceedings of ASCE specialty conference on rock engineering for foundations and slopes, pp 201–234
Gu DM, Huang D, Yang WD, Zhu JL, Fu GY (2017) Understanding the triggering mechanism and possible kinematic evolution of a reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Landslides 14(6):2073–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0845-4
He K, Chen CL (2014) Stability analysis of Puzi landslide in Chongqing. Appl Mech Mater 580–583:923–926. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.580-583.923
He KQ, Yu GM, Li XR (2009) The regional distribution regularity of landslides and their effects on the environments in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Environ Geol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1482-y
He K, Chen CL, Li B (2019a) Case study of a rockfall in Chongqing, China: movement characteristics of the initial failure process of a tower-shaped rock mass. B Eng Geol Environ 78(5):3295–3303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1364-9
He K, Yin YP, Li B, Chen CL (2019b) The mechanism of the bottom-crashing rockfall of a massive layered carbonate rock mass at Zengziyan, Chongqing, China. J Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1141-6
Hoek E, Bray J (1981) Rock slope engineering. The Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, London
Hu QJ, Shi RD, Zheng LN, Cai QJ, Du LQ, He LP (2018) Progressive failure mechanism of a large bedding slope with a strain-softening interface. B Eng Geol Environ 77(1):69–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0996-x
Hu J, Liu HL, Li LP, Zhou S, Zhang Q, Sun SQ (2019) Stability analysis of dangerous rockmass considering rainfall and seismic activity with a case study in China’s Three Gorges area. Pol J Environ Stud 28(2):631–645. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/78925
Huang RQ (2015) Understanding the mechanism of large-scale landslides. In: Lollino G, Giordan D, Crosta GB, Corominas J, Azzam R, Wasowski J, Sciarra N (eds) Engineering geology for society and territory—volume 2: landslide processes. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09057-3_2
Huang D, Yang WD, Chen ZQ (2018) Analysis on collapse mechanism of Wangxia dangerous rock considering weathering effect of weak foundation. Yangtze River 49(06):64–69+78. https://doi.org/10.1623/j.cnki.1001-4179.2018.06.011 ((in Chinese))
Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L (2014) The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 11(2):167–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
International Geotechnical Society’s UNESCO Working Party on World Landslide Inventory (WP/WLI) (1990) A suggested method for reporting a landslide. Bull Inter Assoc Eng Geol 41:5–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02590201
Jian L, Gao JG, Dao Y (2014) The elemental association characteristics of Pb-Zn deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou border area in Southwest China. Adv Mater Res 868:117–120. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.868.117
Jiang XZ, Lei MT, Gao YL (2017) Formation mechanism of large sinkhole collapses in Laibin, Guangxi, China. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7128-1
Kulatilake Pinnaduwa HSW, Ge YF (2014) Investigation of stability of the critical rock blocks that initiated the Jiweishan landslide in China. Geotech Geol Eng 32(5):1291–1315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9806-z
Li AH, Wang SJ (1994) Progressive failure model for slope with plane sliding surface and its application. J Eng Geol 2(1):1–8
Li WX, Wen L, Liu XM, Hou XB, Liu L (2009) Regional horizontal displacements and its effect on shaft in mining areas. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 8(S2):3926–4190 ((in Chinese))
Li B, Feng Z, Wang GZ, Wang WP (2016a) Processes and behaviors of block topple avalanches resulting from carbonate slope failures due to underground mining. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5529-1
Li B, Feng Z, Zhang Q, Zhao CY, Yan JK et al (2016b) Study on disaster mode and early identification of catastrophic landslide disaster in karst mountainous area. Science Press, Beijing ((in Chinese))
Li ZQ, Xue YG, Li SC, Zhang LW, Wang D, Li B, Zhang W, Ning K, Zhu JY (2017) Deformation features and failure mechanism of steep rock slope under the mining activities and rainfall. J Mt Sci-Engl 14(1):31–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3781-6
Li H, Zhong ZL, Liu XR, Sheng Y, Yang DM (2018) Micro-damage evolution and macro-mechanical property degradation of limestone due to chemical effects. Int J Rock Mech Min 110:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.07.011
Li ZW, Xu XL, Zhu JX, Xu CH, Wang KL (2019) Effects of lithology and geomorphology on sediment yield in karst mountainous catchments. Geomorphology 343:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.07.001
Li H, Zhong ZL, Eshiet KII et al (2020a) Experimental investigation of the permeability and mechanical behaviours of chemically corroded limestone under different unloading conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(4):1587–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01961-y
Li J, Zhu HL, Li B, He K, Gao Y (2020b) Key problems of mining induced collapse and slide disaster in mountainous area of coal measure strata in Southwest China. Carsol Sin 39(4):453–466 ((in Chinese))
Li SC, Wang XT, Xu ZH, Mao DQ, Pan DD (2021) Numerical investigation of hydraulic tomography for mapping karst conduits and its connectivity. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105967
Li T, Chen M, Wei D, Lu WB, Yan P (2022) Disturbance effect of blasting stress wave on crack of rock mass in water-coupled blasting. KSCE J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1837-z
Lin F, Wu LZ, Huang RQ, Zhang H (2018) Formation and characteristics of the Xiaoba landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou, China. Landslides 15(4):669–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0897-5
Liu HC, Chen MD, Li KW, Hu XW, Liu WZ, Liu JD (1993) Study on environmental geological evaluation of reservoir area. Chengdu, China (in Chinese)
Luo K, Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Wang XC, Wilde SA, Zhou W, Tian LY (2019) New insights into the origin of early Cambrian carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn deposits in South China: a case study of the Maliping Pb–Zn deposit. Gondwana Res 70:88–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2018.12.015
Lv XF, Zhou HY, Wang ZW, Cai Y (2018) Movement and failure law of slope and overlying strata during underground mining. J Geophys Eng 15(4):1638–1650. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2140/aab8b2
Marian M, Işık Y, Martin B, Karel K (2012a) Influence of underground mining activities on the slope deformation genesis: Doubrava Vrchovec, Doubrava Ujala and Staric case studies from Czech Republic. Eng Geol 147:37–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.014
Marian M, Işık Y, Martin B, Karel K (2012b) Deformation of slopes as a cause of underground mining activities: three case studies from Ostrava-Karviná coal field (Czech Republic). Environ Monit Assess 184(11):6709–6733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2453-4
Martha TR, Roy P, Govindharaj KB, Kumar KV, Diwakar PG, Dadhwal VK (2015) Landslides triggered by the June 2013 extreme rainfall event in parts of Uttarakhand state, India. Landslides 12(1):135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0540-7
Moosavi E, Shirinabadi R, Gholinejad M (2016) Prediction of seepage water pressure for slope stability at the Gol-E-Gohar open pit mine. J Min Sci 52(6):1069–1079. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739116061601
Nunoo S (2018) Lessons learnt from open pit wall instabilities: case studies of BC open pit hard rock mines. J Min Sci 54(5):804–812. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739118054915
Poisel R, Bednarik M, Holzer R, Liščák P (2005) Geomechanics of hazardous landslides. J Mt Sci-Engl. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973194
Poisel R, Angerer H, Pöllinger M, Kalcher T, Kittl H (2009) Mechanics and velocity of the Lärchberg-Galgenwald landslide (Austria). Eng Geol 109(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.01.002
Rohn J, Resch M, Schneider H, Fernandez-Steeger TM, Czurda K (2004) Large-scale lateral spreading and related mass movements in the Northern Calcareous Alps. B Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-003-0201-x
Salmi EF, Nazem M, Karakus M (2017) Numerical analysis of a large landslide induced by coal mining subsidence. Eng Geol 217:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.12.021
Stephen PB, Howard JS (1996) Landslide research in the South Wales coalfield. Eng Geol 43(1):65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(95)00084-4
Sun SQ, Li LP, Li SC, Zhang QQ, Hu C (2017) Rockfall hazard assessment on Wangxia Rock Mass in Wushan (Chongqing, China). Geotech Geol Eng 35(4):1895–1905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0203-2
Tang FQ (2009) Research on mechanism of mountain landslide due to underground mining. J Coal Sci Eng (china) 15(4):351–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-009-0403-3
Tang HM, Zou ZX, Xiong CR, Wu YP, Hu XL, Wang LQ, Lu S, Criss RE, Li CD (2015) An evolution model of large consequent bedding rockslides, with particular reference to the Jiweishan rockslide in Southwest China. Eng Geol 186:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.021
Tang JX, Dai ZY, Wang YL, Zhang L (2019) Fracture failure of consequent bedding rock slopes after underground mining in mountainous area. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(8):2853–2870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01876-8
Tao ZG, Geng Q, Zhu C, He MC, Cai H, Pang SH, Meng XZ (2019) The mechanical mechanisms of large-scale toppling failure for counter-inclined rock slopes. J Geophys Eng 16(3):541–558. https://doi.org/10.1093/jge/gxz020
Vanneschi C, Eyre M, Venn A, Coggan JS (2019) Investigation and modeling of direct toppling using a three-dimensional distinct element approach with incorporation of point cloud geometry. Landslides 16(8):1453–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01192-w
Varnes DJ (1978) Slope movement types and processes. In: Schuster RL, Krizek RJ (eds) Landslides, analysis and control, special report 176: transportation research board. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC
Wang FW, Li TL (2009) Landslide disaster mitigation in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Springer, Berlin
Wang ZQ, Yan EC, Yin XM, Zhang QM, Tang RX (2014) Study on collapse mechanism of anti inclined rock slope: a case study of Honglianchi Iron Mine slope in Hefeng, Hubei Province. J Cent South Univ (sci Tech) 45(07):2295–2302 ((in Chinese))
Wang LY, Chen WZ, Tan XY, Tan XJ, Yuan JQ, Liu Q (2019) Evaluation of mountain slope stability considering the impact of geological interfaces using discrete fractures model. J Mt Sci-Engl 16(09):2184–2202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5527-3
Wang J, Wang C, Xie C, Zhang H, Tang YX, Zhang ZJ, Shen CY (2020) Monitoring of large-scale landslides in Zongling, Guizhou, China, with improved distributed scatterer interferometric SAR time series methods. Landslides 17(8):1777–1795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01407-5
Wu Y, He SM, Li XP (2010) Mechanism of action of cracks water on rock landslide in rainfall. J Cent South Univ T 17(6):1383–1388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0646-6
Xia KZ, Chen CX, Liu XM, Fu H, Pan YC, Deng YY (2016) Mining-induced ground movement in tectonic stress metal mines: a case study. B Eng Geol Environ 75(3):1089–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0886-2
Xie LF, Yan EC, Ren XB, Lu GD (2015) Sensitivity analysis of bending and toppling deformation for anti-slope based on the grey relation method. Geotech Geol Eng 33(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9817-9
Xie HB, Ji ZW, Xu ZF, Chen HQ (2019) Study on the stability criteria of anti-dipped mountain above goaf. J HeNan Polytech Univ (nat Sci) 38(03):32–40 ((in Chinese))
Xing AG, Xu Q, Zhu YQ, Zhu JL, Jiang Y (2016) The August 27, 2014, rock avalanche and related impulse water waves in Fuquan, Guizhou, China. Landslides 13(2):411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0679-5
Xiong F, Liu XR, Ran Q, Li B, Zhong ZL, Yang ZP, Zhou XH (2021) Study on instability failure mechanism of karst mountain with deep and large fissures under the mining-fissure water coupling. J China Coal Soc 46(11):3445–3458. https://doi.org/10.1322/j.cnki.jccs.2020.1690
Xu Q, Fan XM, Huang RQ, Yin YP, Hou SS, Dong XJ, Tang MG (2010) A catastrophic rockslide-debris flow in Wulong, Chongqing, China in 2009: background, characterization, and causes. Landslides 7(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0179-y
Xu T, Xu Q, Deng ML, Ma TH, Yang TH, Tang CA (2014) A numerical analysis of rock creep-induced slide: a case study from Jiweishan Mountain, China. Environ Earth Sci 72(6):2111–2128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3119-7
Xu Q, Liu H, Ran J, Li W, Sun X (2016) Field monitoring of groundwater responses to heavy rainfalls and the early warning of the Kualiangzi landslide in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Landslides 13(6):1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0717-3
Yang YC, Xing HG, Yang XG, Chen ML, Zhou JW (2018) Experimental study on the dynamic response and stability of bedding rock slopes with weak interlayers under heavy rainfall. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7624-y
Yin YP, Sun P, Zhang M, Li B (2011) Mechanism on apparent dip sliding of oblique inclined bedding rockslide at Jiweishan, Chongqing, China. Landslides 8(1):49–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0237-5
Yu XY, Mao XW (2020) A preliminary discrimination model of a deep mining landslide and its application in the Guanwen coal mine. B Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01565-4
Yu D, Huang XH, Li ZY (2020a) Variation patterns of landslide basal friction revealed from long-period seismic waveform inversion. Nat Hazards 100(1):313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03813-y
Yu JL, Zhao JJ, Yan HY, Lai QY, Huang RQ, Liu XW, Li YC (2020b) Deformation and failure of a high-steep slope induced by multi-layer coal mining. J Mt Sci-Engl 17(12):2942–2960. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11629-019-5941-6
Zhang Q, López DL (2019) Use of time series analysis to evaluate the impacts of underground mining on the hydraulic properties of groundwater of dysart woods, Ohio. Mine Water Environ 38(3):566–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-019-00619-z
Zhang YN, Tang JX, Li GD, Teng JY (2016) Influence of depth-thickness ratio of mining on the stability of a bedding slope with its sliding surface in concave deformation. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(6):1117–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.09.022
Zhang M, McSaveney M, Shao H, Zhang CY (2018) The 2009 Jiweishan rock avalanche, Wulong, China: precursor conditions and factors leading to failure. Eng Geol 233:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.12.010
Zhao JJ, Xiao JG, Lee ML, Ma YT (2016) Discrete element modeling of a mining-induced rock slide. Springerplus. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3305-z
Zheng D, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Liu FZ (2015) Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: a case study of Kaiyang Phosphorite Mine rockfalls. Eng Geol 197:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
Zheng Y, Chen CX, Meng F, Liu TT, Xia KZ (2020) Assessing the stability of rock slopes with respect to flexural toppling failure using a limit equilibrium model and genetic algorithm. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103619
Zhu YQ, Xu SM, Zhuang Y, Dai XJ, Lv G, Xing AG (2019) Characteristics and runout behaviour of the disastrous 28 August 2017 rock avalanche in Nayong, Guizhou, China. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105154
Zuan P, Huang Y (2018) Prediction of sliding slope displacement based on intelligent algorithm. Wirel Pers Commun 102(4):3141–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5333-1
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 52074042) and the National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2018YFC1504802). The authors are sincerely thankful to Profs. Bin Li, Zhongping Yang, FangPeng Cui and Dr. Fei Xiong for their great support to this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 52074042) and National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2018YFC1504802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ZZ had the initial idea for the manuscript, YX performed the literature search and data analysis, ZZ and YX drafted the manuscript and revised most of the manuscript according to reviewers’ comments, NW put forward detailed modification ideas, crucial for the revised manuscript and drew some modified figures, and XL and GG commented on previous versions of the manuscript and provided some modification suggestions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Z., Xu, Y., Wang, N. et al. Environmental characteristics and unified failure mode classification system for mining landslides in the karst mountainous areas of southwestern China. Carbonates Evaporites 38, 2 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00818-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00818-w