Abstract
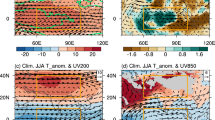
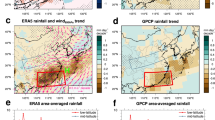
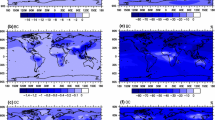
In this paper, we have compared and contrasted competing influences of greenhouse gases (GHG) warming and aerosol forcing on Asian summer monsoon circulation and rainfall based on CMIP5 historical simulations. Under GHG-only forcing, the land warms much faster than the ocean, magnifying the pre-industrial climatological land-ocean thermal contrast and hemispheric asymmetry, i.e., warmer northern than southern hemisphere. A steady increasing warm-ocean-warmer-land (WOWL) trend has been in effect since the 1950’s substantially increasing moisture transport from adjacent oceans, and enhancing rainfall over the Asian monsoon regions. However, under GHG warming, increased atmospheric stability due to strong reduction in mid-tropospheric and near surface relative humidity coupled to an expanding subsidence areas, associated with the Deep Tropical Squeeze (DTS, Lau and Kim, 2015b) strongly suppress monsoon convection and rainfall over subtropical and extratropical land, leading to a weakening of the Asian monsoon meridional circulation. Increased anthropogenic aerosol emission strongly masks WOWL, by over 60% over the northern hemisphere, negating to a large extent the rainfall increase due to GHG warming, and leading to a further weakening of the monsoon circulation, through increasing atmospheric stability, most likely associated with aerosol solar dimming and semi-direct effects. Overall, we find that GHG exerts stronger positive rainfall sensitivity, but less negative circulation sensitivity in SASM compared to EASM. In contrast, aerosols exert stronger negative impacts on rainfall, but less negative impacts on circulation in EASM compared to SASM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R. J., and S. C. Sherwood, 2010: Aerosol-cloud semi-direct effect and land-sea temperature contrast in a GCM. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L07702, doi:10.1029/2010GL042759.
Anderson, A., R. J. Charlson, S. E. Schwartz, R. Knutti, O. Boucher, H. Rodhe, and J. Heintzenberg, 2003: Climate forcing by aerosols - A hazy picture. Science, 300, 1103–1104, doi:10.1126/science.1084777.
Annamalai, H., J. Hafner, K. P. Sooraj, and P. Pillai, 2013: Global warming shifts the monsoon circulation, drying South Asia. J. Climate, 26, 2701–2718, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00208.1.
Bollasina, M. A., Y. Ming, and V. Ramaswamy, 2011: Anthropogenic aerosols and the weakening of the South Asian summer monsoon. Science, 334, doi:10.1126/science.1204994.
Bollasina, M. A., Y. Ming, V. Ramaswamy, M. D. Schwarzkopf, and V. Naik, 2014: Contribution of local and remote anthropogenic aerosols to the twentieth century weakening of the South Asian monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 680–687, doi:10.1002/2013GL058183.
Cheng, Q., and T. Zhou, 2014: Multidecadal variability of North China aridity and its relationship to PDO during 1900-2010. J. Climate, 27, 1210–1222, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00235.1.
Chung, C. E., and V. Ramanathan, 2006: Weakening of north Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J. Climate, 19, 2036–2045.
Cowan, T., and W. Cai, 2011: The impact of Asian and non-Asian anthropogenic aerosols on 20th century Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L11703, doi:10.1029/2011GL047268.
Dai, A., 2006: Recent climatology, variability and tends in global surface humidity. J. Climate, 19, 3589–3606.
Dai, A., 2011: Drought under global warming: A review. Clim. Change, 2, 45–65, doi:10.1002/wcc.81.
Del Genio, A. D., 2012: Representing the sensitivity of convective cloud systems to tropospheric humidity in general circulation models. Suv. Geophys., 33, 637–656, doi:10.1007/s10712-011-9148-9.
Dickinson, R. E., G. A. Meehl, and W. M. Washington, 1987: Ice-albedo feedback in a CO2-doubling simulation. Clim. Change, 10, 241–248, doi:10.1007/BF00143904.
Ding, Y., Z. Wang, and Y. Sun, 2008: Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol., 28, 1139–1161, doi:10.1002/joc.1615.
Fan, J., L. R. Leung, D. Rosenfeld, Q. Chen, Z. Li, J. Zhang, and H. Yan, 2013: Microphysical effects determine macrophysical response for aerosol impacts on deep convective clouds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 110, E4581–4590, doi:10.1073/pnas.1316830110.
Fan, J. W., D. Rosenfeld, Y. Yang, C. Zhao, L. R. Leung, and Z. Li, 2015: Substantial contribution of anthropogenic air pollution to catastrophic floods in Southwest China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 6066–6075, doi: 0.1002/2015GL064479.
Fu, Q., and Feng, S., 2014: Responses of terrestrial aridity to global warming. J. Geophys. Res., 119, 7863–7875, doi:10.1002/2014JD-021608.
Ganguly, D., P. J. Rasch, H. Wang, and J.-H. Yoon, 2012: Climate response of the South Asian monsoon system to anthropogenic aerosols. J. Geophys. Res., 117, D13209, doi:10.1029/2012JD017508.
Holton, J. R., 1992: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology. 3rd Edition, Academic Press, 511 pp.
IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, the contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Stocker, T. F. et al. Eds., Cambridge University Press, 1535 pp.
Jin, Q., J. Wei, and Z.-L. Yang, 2014: Positive response of Indian summer rainfall to Middle East dust. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 4068–4074, doi:10.1002/2014GL059980.
Kim, M.-K., W. K. M. Lau, K.-M. Kim, J. Sang, Y.-H. Kim, and W.-S. Lee, 2015: Amplification of ENSO effects on Indian summer monsoon by absorbing aerosols. Climate Dyn., doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2722-y.
Kiehl, J. T., 2007: Twentieth century climate model response and climate sensitivity. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L22710, doi:10.1029/2007GL-031383.
Krishnamurthy, L., and V. Krishnamurthy, 2014: Decadal scale oscillations and trend in the Indian monsoon rainfall. Climate Dyn., 43, 319–331, doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1870-1.
Lau, W., 2014: Atmospheric Science: Desert dust and monsoon rainfall. Nat. Geosci., 7, 255–256, doi:10.1038/ngeo2115.
Lau, W., 2016: The aerosol-monsoon climate system of Asia: A new paradigm. J. Meteorol. Res., 29, 1–11, doi:10.1007/s13351-015-5999-1.
Lau, W., and M. T. Li, 1984: The monsoon of East Asia and its global associations - A survey. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 65, 114–125.
Lau, W., and K.-M. Kim, 2006: Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall, and circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L21810, doi:10.1029/2006GL027546.
Lau, W., M. K. Kim, and K. M. Kim, 2006: Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: The role of the Tibetan Plateau. Climate Dyn., 26, 855–864, doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0114-z.
Lau, W., and Coauthors, 2008: The Joint Aerosol-Monsoon Experiment: A new challenge in monsoon climate research. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 89, 369–383, doi:10.1175/BAMS-89-3-369.
Lau, W., and K.-M. Kim, 2010: Fingerprinting the impacts of aerosols on long-term trends of the Indian summer monsoon regional rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L16705, doi:10.1029/2010GL043255.
Lau, W., H. T. Wu, and K.-M. Kim, 2013: A canonical response in rainfall characteristics to global warming from CMIP5 model projections. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, doi:10.1002/grl.50420.
Lau, W., and K.-M. Kim, 2015a: Impacts of absorbing aerosols on the Asian monsoon: An interim assessment. World Sci. Series on Asian-Pacific Weather and Climate, Vol. 6, Climate Change: Decadal and Beyond. Chang, C. P. et al. Eds., World Scientific, 376pp.
Lau, W., and K.-M. Kim, 2015b: Robust responses of the Hadley circulation and global dryness form CMIP5 model CO2 warming projections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 112, 3630–3635, doi:10.1073/pnas.1418682112.
Lau, W., K.-M. Kim, J. J. Shi, T. Matsui, M. Chin, Q. Tan, C. Peters-Lidard, and W. K. Tao, 2016: Impacts of aerosol-monsoon interaction on rainfall and circulation over Northern India and the Himalaya Foothills. Climate Dyn., doi:0.1007/s00382-016-3430-y.
Lee, J., and B. Wang, 2014: Future change of global monsoon in the CMIP5. Clim. Dyn., 42, 101–119, doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1564-0.
Li, C., and M. Yanai, 1996: The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land-sea thermal contrast. J. Climate, 9, 358–375.
Li, X., M. Ting, C. Li, and N. Henderson, 2015: Mechanisms of Asian summer monsoon changes in response to anthropogenic forcing in CMIP5 models. J. Climate, 28, 4107–4125, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00559.1.
Li, Z., and Coauthors, 2016: Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys., 54, 866–929, doi:10.1002/2015RG000500.
Liu, Y., J. Sun, and B. Yang, 2009: The effects of black carbon and sulphate aerosols in China regions on East Asia monsoons. Tellus, 61, 642–656, doi:10.1111/j.1600-0889.2009.00427.x.
Ma, S., and Coauthors, 2017: Detectable anthropogenic shift toward heavy precipitation over eastern China. J. Climate, 30, 1381–1396, doi:10. 1175/JCLI-D-16-0311.1.
Man, W., T. Zhou, and J. H. Jungclaus, 2014: Effects of large volcanic eruption on global summer climate and East Asian monsoon changes during the last millenium: Analysis of MPI-ESM simulations. J. Climate, 27, 7394–7409, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00739.1.
Meehl, G. A., J. M. Arblaster, and W. D. Collins, 2008: Effects of black carbon aerosols on the Indian monsoon. J. Climate, 21, 2869–2882, doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1777.1.
Menon, S., J. Hansen, L. Nazarenko, and Y. Luo, 2002: Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 297, 2250–2253, doi:10.1126/science.1075159.
Polson, D., M. Bollasina, G. C. Hegerl, and L. J. Wilcox, 2014: Decreased monsoon precipitation in the Northern Hemisphere due to anthropogenic aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 6023–6029, doi:10.1002/2014GL060811.
Ramanathan, V., and G. Carmichael, 2008: Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci., 1, 221–227, doi:10.1038/ngeo156.
Ramanathan, V., and Y. Feng, 2009: Air pollution, greenhouse gases and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Atmos. Environ., 43, 37–50, doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.09.063.
Randles, C. A., and V. Ramaswamy, 2008: Absorbing aerosols over Asia: A Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory general circulation model sensitivity study of model response to aerosol optical depth and aerosol absorption. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D21203, doi:10.1029/2008JD-010140.
Robock, A., 2000: Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev. Geophys., 38, 191–219, doi:10.1029/1998RG000054.
Rosenfeld, D., U. Lohmann, G. B. Raga, C. D. O’Dowd, M. Kulmala, S. Fuzzi, A. Reissell, and M. O. Andreae, 2008: Flood or drought: How do aerosols affect precipitation? Science, 321, 1309–1313, doi:10.1126/science.1160606.
Roxy, M. K., K. Ritika, P. Terray, R. Murtugudde, K. Ashok, and B. Goswami, 2015: Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient. Nat. Commun., 6, 7423, doi:10.1038/ncomms8423.
Santer, B. D., and Coauthors, 2013: Identifying human influences on atmospheric temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 110, 26–33, doi:10. 1073/pnas.1210514109.
Satheesh, S. K., and K. K. Moorthy, 2005: Radiative effects of natural aerosols: A review. Atmos. Environ., 39, 2089–2110, doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv. 2004.12.029.
Sherwood, S. C., W. Ingram, Y. Tsushima, M. Satoh, M. Roberts, P. L. Vidale, and P. A. O’Gorman, 2010: Relative humidity changes in a warmer climate. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D09104, doi:10.1029/2009JD-012585.
Song, F., T. Zhou, and Y. Qian, 2014: Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to natural and anthropogenic forcings in the 17 latest CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 596–603, doi:10.1002/2013GL058705.
Tokinaga, H., S. P. Xie, A. Timmermann, S. McGregor, T. Ogata, H. Kubota, and Y. M. Okumura, 2012: Regional patterns of tropical Indo-Pacific climate change: Evidence of the Walker circulation weakening. J. Climate, 25, 1689–1709, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00263.1.
Turner, A. G., and H. Annamalai, 2012: Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Change, 2, 587–595, doi:10.1038/NCLIMATE1495.
Vecchi, G. A., and B. J. Soden, 2007: Global warming and the weakening of the tropical circulation. J. Climate, 20, 4316–4340, doi:10.1175/JCLI4258.1.
Vinoj, V., P. J. Rasch, H. Wang, J.-H. Yoon, P.-L. Ma, K. Landu, and B. Singh, 2014: Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat. Geosci., 7, 308–314, doi:10.1038/ngeo2107.
Wang, B., J. Liu, H. Kim, P. Webster, and S. Yim, 2012: Recent change of the global monsoon precipitation (1979-2008). Climate Dyn., 39, 1123–1135, doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1266-z.
Wang, B., J. Liu, H. Kim, P. Webster, S. Yim, and B. Xiang, 2013: Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon intensified by mega-El Niño/southern oscillation and Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 110, 5347–5352, doi:10.1073/pnas.1219405110.
Wang, C., D. Kim, A. M. L. Ekman, M. C. Barth, and P. J. Rasch, 2009: Impact of anthropogenic aerosols on Indian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L21704, doi:10.1029/2009GL040114.
Wang, T., H. J. Wang, O. H. Otterå, Y. Q. Gao, L. L. Suo, T. Furevik, and L. Yu, 2013b: Anthropogenic agent implicated as a prime driver of shift in precipitation in eastern China in the late 1970s. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 12433–12450, doi:10.5194/acp-13-12433-2013.
Webster, P. J., V. O. Magaña, T. N. Palmer, J. Shukla, R. A. Tomas, M. Yanai, and T. Yasunari, 1998: Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14451–14510, doi:10.1029/97JC02719.
Yatagai, A., K. Kamiguchi, O. Arakawa, A. Hamada, N. Yasutomi, and A. Kitoh, 2012: APHRODITE: Constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 1401–1415, doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00122.1.
Ye, J., W. Li, L. Li, and F. Zhang, 2013: “North drying and south wetting” summer precipitation trend over China and its potential linkage with aerosol loading. Atmos. Res., 125, 12–19, doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2013. 01.007.
Yu, R., B. Wang, and T. Zhou, 2004: Tropospheric cooling and summer monsoon weakening trend over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, L22212, doi:10.1029/2004GL021270.
Yu, R., and T. Zhou, 2007: Seasonality and three dimensional structure of the interdecadal change in East Asian monsoon. J. Climate, 20, 5344–5355.
Zhang, H., Z. Wang, P. Guo, and Z. Wang, 2009: A modeling study of the effects of direct radiative forcing due to carbonaceous aerosol on the climate in East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 57–66, doi:10.1007/s00376-009-0057-5.
Zhang, L., and T. Li, 2016: Relative roles of anthropogenic aerosols and greenhouse gases in land and oceanic monsoon changes during past 156 years in CMIP5 models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 5295–5301, doi:10. 1002/2016GL069282.
Zhou, T., D. Gong, J. Li, and B. Li, 2009: Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon: Recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorol. Z., 18, 455–467, doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0396.
Zhou, T., R. Yu, H. Li, and B. Wang, 2008: Ocean forcing to changes in global monsoon precipitation over the recent half-century. J. Climate, 21, 3833–3852, doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2067.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, W.KM., Kim, KM. Competing influences of greenhouse warming and aerosols on Asian summer monsoon circulation and rainfall. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 53, 181–194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-017-0033-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-017-0033-4