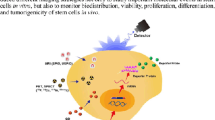
Abstract
Molecular imaging is a fast growing biomedical research that allows the visual representation, characterization and quantification of biological processes at the cellular and subcellular levels within intact living organisms. In vivo tracking of cells is an indispensable technology for development and optimization of cell therapy for replacement or renewal of damaged or diseased tissue using transplanted cells, often autologous cells. With outstanding advantages of bioluminescence imaging, the imaging approach is most commonly applied for in vivo monitoring of transplanted stem cells or immune cells in order to assess viability of administered cells with therapeutic efficacy in preclinical small animal models. In this review, a general overview of bioluminescence is provided and recent updates of in vivo cell tracking using the bioluminescence signal are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao F, Lin S, Xie X, Ray P, Patel M, Zhang X, et al. In vivo visualization of embryonic stem cell survival, proliferation, and migration after cardiac delivery. Circulation. 2006;113(7):1005–14.
Zeiser R, Nguyen VH, Beilhack A, Buess M, Schulz S, Baker J, et al. Inhibition of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cell function by calcineurin-dependent interleukin-2 production. Blood. 2006;108(1):390–9.
Berman SC, Galpoththawela C, Gilad AA, Bulte JW, Walczak P. Long-term MR cell tracking of neural stem cells grafted in immunocompetent versus immunodeficient mice reveals distinct differences in contrast between live and dead cells. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65(2):564–74.
Acton P, Zhou R. Imaging reporter genes for cell tracking with PET and SPECT. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;49(4):349–60.
Zhang Y, Ruel M, Beanlands RS, Dekemp RA, Suuronen EJ, DaSilva JN. Tracking stem cell therapy in the myocardium: applications of positron emission tomography. Curr Pharm Design. 2008;14(36):3835–53.
Ahn BC. Applications of molecular imaging in drug discovery and development process. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(4):459–68.
Chao F, Shen Y, Zhang H, Tian M. Multimodality molecular imaging of stem cells therapy for stroke. BioMed Res Int. 2013;2013:849819.
Yang CY, Hsiao JK, Tai M-F, Chen ST, Cheng HY, Wang JL, et al. Direct labeling of hMSC with SPIO: the long-term influence on toxicity, chondrogenic differentiation capacity, and intracellular distribution. Mol Imag Biol. 2011;13(3):443–51.
Kraitchman DL, Bulte JW. In vivo imaging of stem cells and beta cells using direct cell labeling and reporter gene methods. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(7):1025–30.
Keyaerts M, Caveliers V, Lahoutte T. Bioluminescence imaging: looking beyond the light. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(3):164–72.
Baker M. Whole-animal imaging: the whole picture. Nature. 2010;463(7283):977–80.
Verhaegen M, Christopoulos TK. Recombinant Gaussia luciferase. Overexpression, purification, and analytical application of a bioluminescent reporter for DNA hybridization. Anal Chem. 2002;74(17):4378–85.
Thompson EM, Nagata S, Tsuji FI. Cloning and expression of cDNA for the luciferase from the marine ostracod Vargula hilgendorfii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(17):6567–71.
Lorenz W, Cormier M, O’Kane D, Hua D, Escher A, Szalay A. Expression of the Renilla reniformis luciferase gene in mammalian cells. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1996;11(1):31–7.
Nealson K, Hastings JW. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979;43(4):496.
Fraga H. Firefly luminescence: a historical perspective and recent developments. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2008;7(2):146–58.
Close DM, Xu T, Sayler GS, Ripp S. In vivo bioluminescent imaging (BLI): noninvasive visualization and interrogation of biological processes in living animals. Sensors. 2010;11(1):180–206.
Lorenz WW, McCann RO, Longiaru M, Cormier MJ. Isolation and expression of a cDNA encoding Renilla reniformis luciferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(10):4438–42.
Loening AM, Fenn TD, Wu AM, Gambhir SS. Consensus guided mutagenesis of Renilla luciferase yields enhanced stability and light output. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2006;19(9):391–400.
Maguire CA, Deliolanis NC, Pike L, Niers JM, Tjon-Kon-Fat L-A, Sena-Esteves M, et al. Gaussia luciferase variant for high-throughput functional screening applications. Anal Chem. 2009;81(16):7102–6.
Tannous BA. Gaussia luciferase reporter assay for monitoring biological processes in culture and in vivo. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(4):582–91.
Ziegler M, Baldwin TO. Biochemistry of bacterial bioluminescence. Curr Top Bioenerg. 1981;12:65–113.
Tu S-C, Mager HI. Biochemistry of bacterial bioluminescence. Photochem Photobiol. 1995;62(4):615–24.
de Almeida PE, van Rappard JR, Wu JC. In vivo bioluminescence for tracking cell fate and function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(3):H663–71.
Ahn BC. Molecular imaging; biological and medical applications. Republic of Korea: Kyungpook National University Press; 2009.
Liang Y, Walczak P, Bulte JW. Comparison of red-shifted firefly luciferase Ppy RE9 and conventional Luc2 as bioluminescence imaging reporter genes for in vivo imaging of stem cells. J Biomed Opt. 2012;17(1):0160041–6.
Seliger H, Buck J, Fastie W, McElroy W. The spectral distribution of firefly light. J Gen Physiol. 1964;48(1):95–104.
Seliger H, McElroy W. The colors of firefly bioluminescence: enzyme configuration and species specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964;52(1):75.
Czupryna J, Tsourkas A. Firefly luciferase and RLuc8 exhibit differential sensitivity to oxidative stress in apoptotic cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20073.
Kitayama A, Yoshizaki H, Ohmiya Y, Ueda H, Nagamune T. Creation of a thermostable firefly luciferase with pH-insensitive luminescent color. Photochem Photobiol. 2003;77(3):333–8.
Kajiyama N, Nakano E. Isolation and characterization of mutants of firefly luciferase which produce different colors of light. Protein Eng. 1991;4(6):691–3.
Shapiro E, Lu C, Baneyx F. A set of multicolored Photinus pyralis luciferase mutants for in vivo bioluminescence applications. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2005;18(12):581–7.
Branchini BR, Ablamsky DM, Davis AL, Southworth TL, Butler B, Fan F, et al. Red-emitting luciferases for bioluminescence reporter and imaging applications. Anal Biochem. 2010;396(2):290–7.
Bhaumik S, Gambhir S. Optical imaging of Renilla luciferase reporter gene expression in living mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(1):377–82.
Luker KE, Luker GD. Applications of bioluminescence imaging to antiviral research and therapy: multiple luciferase enzymes and quantitation. Antiviral Res. 2008;78(3):179–87.
Zhao H, Doyle TC, Wong RJ, Cao Y, Stevenson DK, Piwnica-Worms D, et al. Characterization of coelenterazine analogs for measurements of Renilla luciferase activity in live cells and living animals. Mol Imag. 2004;3(1):43–54.
Loening AM, Dragulescu-Andrasi A, Gambhir SS. A red-shifted Renilla luciferase for transient reporter-gene expression. Nat Methods. 2010;7(1):5–6.
Loening AM, Wu AM, Gambhir SS. Red-shifted Renilla reniformis luciferase variants for imaging in living subjects. Nat Methods. 2007;4(8):641–3.
Griesenbach U, Vicente CC, Roberts MJ, Meng C, Soussi S, Xenariou S, et al. Secreted Gaussia luciferase as a sensitive reporter gene for in vivo and ex vivo studies of airway gene transfer. Biomaterials. 2011;32(10):2614–24.
Bovenberg MSS, Degeling MH, Tannous BA. Enhanced Gaussia luciferase blood assay for monitoring of in vivo biological processes. Anal Chem. 2011;84(2):1189–92.
Wurdinger T, Badr C, Pike L, de Kleine R, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO, et al. A secreted luciferase for ex vivo monitoring of in vivo processes. Nat Methods. 2008;5(2):171–3.
Badr CE, Hewett JW, Breakefield XO, Tannous BA. A highly sensitive assay for monitoring the secretory pathway and ER stress. PLoS One. 2007;2(6):e571.
Hiramatsu N, Kasai A, Hayakawa K, Nagai K, Kubota T, Yao J, et al. Secreted protein-based reporter systems for monitoring inflammatory events: critical interference by endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Immunol Methods. 2006;315(1):202–7.
Tannous BA, Kim D-E, Fernandez JL, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO. Codon-optimized Gaussia luciferase cDNA for mammalian gene expression in culture and in vivo. Mol Ther. 2005;11(3):435–43.
Santos EB, Yeh R, Lee J, Nikhamin Y, Punzalan B, Punzalan B, et al. Sensitive in vivo imaging of T cells using a membrane-bound Gaussia princeps luciferase. Nat Med. 2009;15(3):338–44.
Derzelle S, Duchaud E, Kunst F, Danchin A, Bertin P. Identification, characterization, and regulation of a cluster of genes involved in carbapenem biosynthesis in Photorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68(8):3780–9.
Meighen EA. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991;55(1):123–42.
Contag CH, Contag PR, Mullins JI, Spilman SD, Stevenson DK, Benaron DA. Photonic detection of bacterial pathogens in living hosts. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18(4):593–603.
Francis KP, Joh D, Bellinger-Kawahara C, Hawkinson MJ, Purchio TF, Contag PR. Monitoring bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus infections in living mice using a novel luxABCDE construct. Infect Immun. 2000;68(6):3594–600.
Min J-J, Nguyen VH, Kim H-J, Hong Y, Choy HE. Quantitative bioluminescence imaging of tumor-targeting bacteria in living animals. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(4):629–36.
Min J-J, Kim H-J, Park JH, Moon S, Jeong JH, Hong Y-J, et al. Noninvasive real-time imaging of tumors and metastases using tumor-targeting light-emitting Escherichia coli. Mol Imag Biol. 2008;10(1):54–61.
Mezzanotte L, Que I, Kaijzel E, Branchini B, Roda A, Löwik C. Sensitive dual color in vivo bioluminescence imaging using a new red codon optimized firefly luciferase and a green click beetle luciferase. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e19277.
Wang J, Najjar A, Zhang S, Rabinovich B, Willerson JT, Gelovani JG, et al. Molecular imaging of mesenchymal stem cell mechanistic insight into cardiac repair after experimental myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5(1):94–101.
Mezzanotte L, Aswendt M, Tennstaedt A, Hoeben R, Hoehn M, Löwik C. Evaluating reporter genes of different luciferases for optimized in vivo bioluminescence imaging of transplanted neural stem cells in the brain. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013;8(6):505–13.
Leng L, Wang Y, He N, Wang D, Zhao Q, Feng G, et al. Molecular imaging for assessment of mesenchymal stem cells mediated breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(19):5162–70.
Nakajima Y, Kimura T, Sugata K, Enomoto T, Asakawa A, Kubota H, et al. Multicolor luciferase assay system: one-step monitoring of multiple gene expressions with a single substrate. Biotechniques. 2005;38(6):891.
Kitayama Y, Kondo T, Nakahira Y, Nishimura H, Ohmiya Y, Oyama T. An in vivo dual-reporter system of cyanobacteria using two railroad-worm luciferases with different color emissions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004;45(1):109–13.
Kidd S, Caldwell L, Dietrich M, Samudio I, Spaeth EL, Watson K, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells alone or expressing interferon-β suppress pancreatic tumors in vivo, an effect countered by anti-inflammatory treatment. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(5):615–25.
Abe K. Therapeutic potential of neurotrophic factors and neural stem cells against ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20(10):1393–408.
Koelling S, Miosge N. Stem cell therapy for cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9(11):1399–405.
Lee DS. Optical imaging for stem cell differentiation to neuronal lineage. Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2012;46(1):1–9.
Sunwoo M, Yun H, Song S, Ham J, Hong J, Lee JE, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can modulate longitudinal changes in cortical thickness and its related cognitive decline in patients with multiple system atrophy. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:118.
Cihova M, Altanerova V, Altaner C. Stem cell based cancer gene therapy. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(5):1480–7.
Devine SM, Cobbs C, Jennings M, Bartholomew A, Hoffman R. Mesenchymal stem cells distribute to a wide range of tissues following systemic infusion into nonhuman primates. Blood. 2003;101(8):2999–3001.
van der Bogt KE, Sheikh AY, Schrepfer S, Hoyt G, Cao F, Ransohoff KJ, et al. Comparison of different adult stem cell types for treatment of myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 2008;118(14 suppl 1):S121–9.
Yang JJ, Liu ZQ, Zhang JM, Wang H-b HSY, Liu JF, et al. Real-time tracking of adipose tissue-derived stem cells with injectable scaffolds in the infarcted heart. Heart Vessel. 2013;28(3):385–96.
Kim JE, Ahn B-C, Lee HW, Hwang MH, Shin SH, Lee SW et al. In vivo monitoring of survival and proliferation of hair stem cells in a hair follicle generation animal model. Mol Imag. 2013;12(5).
Cao F, Wagner RA, Wilson KD, Xie X, Fu J-D, Drukker M, et al. Transcriptional and functional profiling of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3474.
Caspi O, Huber I, Kehat I, Habib M, Arbel G, Gepstein A, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes improves myocardial performance in infarcted rat hearts. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(19):1884–93.
Caspi O, Lesman A, Basevitch Y, Gepstein A, Arbel G, Habib IHM, et al. Tissue engineering of vascularized cardiac muscle from human embryonic stem cells. Circ Res. 2007;100(2):263–72.
Kutschka I, Kofidis T, Chen IY, von Degenfeld G, Zwierzchoniewska M, Hoyt G, et al. Adenoviral human BCL-2 transgene expression attenuates early donor cell death after cardiomyoblast transplantation into ischemic rat hearts. Circulation. 2006;114(1 supp):I-I174–80.
Shi M, Li J, Liao L, Chen B, Li B, Chen L, et al. Regulation of CXCR4 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells by cytokine treatment: role in homing efficiency in NOD/SCID mice. Haematologica. 2007;92(7):897–904.
Zhang D, Fan G-C, Zhou X, Zhao T, Pasha Z, Xu M, et al. Over-expression of CXCR4 on mesenchymal stem cells augments myoangiogenesis in the infarcted myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(2):281–92.
Cheng Z, Ou L, Zhou X, Li F, Jia X, Zhang Y, et al. Targeted migration of mesenchymal stem cells modified with CXCR4 gene to infarcted myocardium improves cardiac performance. Mol Ther. 2008;16(3):571–9.
Wang H, Cao F, De A, Cao Y, Contag C, Gambhir SS, et al. Trafficking mesenchymal stem cell engraftment and differentiation in tumor-bearing mice by bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27(7):1548–58.
Tang Y, Shah K, Messerli SM, Snyder E, Breakefield X, Weissleder R. In vivo tracking of neural progenitor cell migration to glioblastomas. Hum Gene Ther. 2003;14(13):1247–54.
Akbar S, Fazle M, Abe M, Yoshida O, Murakami H, Onji M. Dendritic cell-based therapy as a multidisciplinary approach to cancer treatment: present limitations and future scopes. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(26):3113–9.
Gao JQ, Okada N, Mayumi T, Nakagawa S. Immune cell recruitment and cell-based system for cancer therapy. Pharm Res. 2008;25(4):752–68.
Costa GL, Sandora MR, Nakajima A, Nguyen EV, Taylor-Edwards C, Slavin AJ, et al. Adoptive immunotherapy of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via T cell delivery of the IL-12 p40 subunit. J Immunol. 2001;167(4):2379–87.
Rabinovich BA, Ye Y, Etto T, Chen JQ, Levitsky HI, Overwijk WW, et al. Visualizing fewer than 10 mouse T cells with an enhanced firefly luciferase in immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(38):14342–6.
Edinger M, Cao YA, Verneris MR, Bachmann MH, Contag CH, Negrin RS. Revealing lymphoma growth and the efficacy of immune cell therapies using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Blood. 2003;101(2):640–8.
Tang Q, Adams JY, Tooley AJ, Bi M, Fife BT, Serra P, et al. Visualizing regulatory T cell control of autoimmune responses in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat Immunol. 2005;7(1):83–92.
Nguyen VH, Zeiser R, Chang DS, Beilhack A, Contag CH, Negrin RS. In vivo dynamics of regulatory T-cell trafficking and survival predict effective strategies to control graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic transplantation. Blood. 2007;109(6):2649–56.
Shin IJ, Shon S-M, Schellingerhout D, Park J-Y, Kim J-Y, Lee SK, et al. Characterization of partial ligation-induced carotid atherosclerosis model using dual-modality molecular imaging in ApoE knock-out mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e73451.
Lee HW, Jeon YH, Hwang M-H, Kim J-E, T-i P, Ha J-H, et al. Dual reporter gene imaging for tracking macrophage migration using the human sodium iodide symporter and an enhanced firefly luciferase in a murine inflammation model. Mol Imag Biol. 2013;15(6):703–12.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Medical Cluster R&D Support Project of Daegu Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation, Republic of Korea (2013), grants from the National Nuclear R&D Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2012M2A2A7014020, 2009–0078234) and grants from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea. (A111345).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors Jung Eun Kim, Kalimuthu Senthilkumar, Byeong-Cheol Ahn declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosure
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Animal Studies
The in vivo mouse data are reprinted with permission from Kim et al. [67].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.E., Kalimuthu, S. & Ahn, BC. In Vivo Cell Tracking with Bioluminescence Imaging. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49, 3–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-014-0309-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-014-0309-x