Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated whether the maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) of primary tumor from the initial staging by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) of patients with breast cancer could identify patients at risk for early recurrence within 2 years, particularly in comparison to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage.
Methods
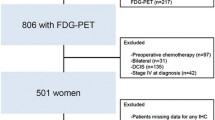
We reviewed the staging 18F-FDG PET/CT images of patients with primary breast cancer and their medical records. The SUVmax of the primary tumor was measured. The presence or absence of FDG uptake in the axillary lymph node (ALN) was also assessed. The patient’s pathologic primary tumor stage (pT), pathologic regional lymph node stage (pN), stage grouping, age, estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) status, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy history were evaluated with the FDG uptake parameters for recurrence within 2 years following the end of first-line therapy.
Results
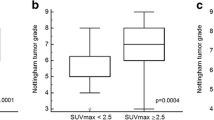
Recurrence within 2 years was present in 9.1 % (n = 40) out of the 441 patients assessed. The FDG uptake in ALN, pT, pN, stage grouping and neoadjuvant chemotherapy history were prognostic for early recurrence, while primary tumor SUVmax, age, and ER or PR status were not significant on logistic regression. On multivariate analysis, only the stage grouping (odds ratio 2.79; 95 % CI 1.73, 4.48; p < 0.0001) and neoadjuvant chemotherapy history (odds ratio 2.70; 95 % CI 1.22, 5.98; p = 0.0141) could identify patients at increased risk for recurrence within 2 years.
Conclusions
Primary tumor FDG uptake measured by SUVmax, and visual assessment of FDG uptake in the ALN in the initial staging PET/CT of patients with breast cancer may not have additional prognostic value compared with the AJCC stage grouping for early recurrence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao C, Chang JT, Wang H, Ng S, Hsueh C, Lee L, et al. Pretreatment primary tumor SUVmax measured by FDG-PET and pathologic tumor depth predict for poor outcomes in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma and pathologically positive lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;73(3):764–71.
Casali C, Cucca M, Rossi G, Barbieri F, Iacuzio L, Bagni B, et al. The variation of prognostic significance of Maximum Standardized Uptake Value of [18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography in different histological subtypes and pathological stages of surgically resected Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2010;69(2):187–93.
Kidd EA, Siegel BA, Dehdashti F, Grigsby PW. Pelvic lymph node F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake as a prognostic biomarker in newly diagnosed patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(6):1469–75.
Song BI, Lee SW, Jeong SY, Chae YS, Lee WK, Ahn BC, et al. 18F-FDG uptake by metastatic axillary lymph nodes on pretreatment PET/CT as a prognostic factor for recurrence in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(9):1337–44.
Oshida M, Uno K, Suzuki M, Nagashima T, Hashimoto H, Yagata H, et al. Predicting the prognoses of breast carcinoma patients with positron emission tomography using 2-deoxy-2-fluoro[18F]-D-glucose. Cancer. 1998;82(11):2227–34.
Alberini J, Lerebours F, Wartski M, Fourme E, Le Stanc E, Gontier E, et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) imaging in the staging and prognosis of inflammatory breast cancer. Cancer. 2009;115(21):5038–47.
Inoue T, Yutani K, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Shiba E, Noguchi S. Preoperative evaluation of prognosis in breast cancer patients by [(18)F]2-Deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose-positron emission tomography. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130(5):273–8.
Ueda S, Tsuda H, Asakawa H, Shigekawa T, Fukatsu K, Kondo N, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of uptake level using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging (18F-FDG PET/CT) in primary breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008;38(4):250–8.
Koolen BB, Vrancken Peeters MJ, Wesseling J, Lips EH, Vogel WV, Aukema TS, et al. Association of primary tumour FDG uptake with clinical, histopathological and molecular characteristics in breast cancer patients scheduled for neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012.
Gil Rendo A, Martnez-Regueira F, Zornoza G, Garca-Velloso MJ, Beorlegui C, Rodriguez Spiteri N. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and prognostic parameters in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2009;96(2):166–70.
Groheux D, Giacchetti S, Moretti J, Porcher R, Espi M, Lehmann Che J, et al. Correlation of high 18F-FDG uptake to clinical, pathological and biological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38(3):426–35.
Heudel P, Cimarelli S, Montella A, Bouteille C, Mognetti T. Value of PET-FDG in primary breast cancer based on histopathological and immunohistochemical prognostic factors. Int J Clin Oncol. 2010;15(6):588–93.
Hodgson NC, Gulenchyn KY. Is there a role for positron emission tomography in breast cancer staging? J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(5):712–20.
Shimoda W, Hayashi M, Murakami K, Oyama T, Sunagawa M. The relationship between FDG uptake in PET scans and biological behavior in breast cancer. Breast cancer. 2007;14(3):260–8.
Buck AK, Schirrmeister H, Mattfeldt T, Reske SN. Biological characterisation of breast cancer by means of PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31 Suppl 1:S80–7.
Kidd EA, Siegel BA, Dehdashti F, Rader JS, Mutch DG, Powell MA, et al. Lymph node staging by positron emission tomography in cervical cancer: relationship to prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(12):2108–13.
Nakajo M, Kajiya Y, Kaneko T, Kaneko Y, Takasaki T, Tani A, et al. FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging for breast cancer: prognostic value of maximum standardized uptake values and apparent diffusion coefficient values of the primary lesion. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(11):2011–20.
Dunnwald LK, Gralow JR, Ellis GK, Livingston RB, Linden HM, Specht JM, et al. Tumor metabolism and blood flow changes by positron emission tomography: relation to survival in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(27):4449–57.
Wahl RL, Siegel BA, Coleman RE, Gatsonis CG, Group PETS. Prospective multicenter study of axillary nodal staging by positron emission tomography in breast cancer: a report of the staging breast cancer with PET Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(2):277–85.
National Comprehensive Cancer N. NCCN guideline update: breast cancer version 1.2004. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw JNCCN. 2004;2(3):183–4.
Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction. Lancet. 2011;378(9805):1812–23.
Dedeurwaerder S, Fumagalli D, Fuks F. Unravelling the epigenomic dimension of breast cancers. Curr Opin Oncol. 2011;23(6):559–65.
Disclosure
The authors report nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O, J.H., Choi, W.H., Han, E.J. et al. The Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT for Early Recurrence in Operable Breast Cancer: Comparison with TNM Stage. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 47, 263–267 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-013-0232-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-013-0232-6