Abstract
Purpose
Salivary gland scintigraphy (SGS) provides an objective means of diagnosing salivary gland dysfunction in Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) patients and in thyroid cancer patients after radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. In the present study, SGS was performed in SS patients and in thyroid cancer patients post-RAI, and scintigraphic parameters were compared.
Methods
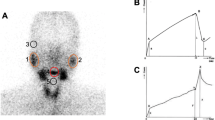
Twenty-eight SS patients (males:females = 1:27, age 53.3 ± 11.9 years), 28 controls (males:females = 3:25, age 54.1 ± 10.1 years), and 92 thyroid cancer patients (males:females = 28:64, age 46.2 ± 12.9) who had undergone a session of high-dose RAI therapy (mean dose, 5.2 ± 1.5 GBq) were included. SGS was performed using Tc-99m pertechnetate (925 MBq). Scintigraphic parameters (parotid uptake ratio PU, submandibular uptake ratio SU, percentage parotid excretion %PE, and percentage submandibular excretion %SE) were measured and compared for SS, thyroid cancer post-RAI, and control patients.
Results
PU, SU, %SE, and %PE were all significantly lower in SS than in post-RAI thyroid cancer or control patients (p < 0.05), whereas only %PE was significantly lower in post-RAI thyroid cancer patients than in controls (p < 0.05). SU and %SE were found to be correlated with the unstimulated whole salivary flow rate.
Conclusion
Scintigraphic parameters derived from SGS can play a crucial role in the detection of salivary gland dysfunction in SS patients and in post-RAI thyroid cancer patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manthorpe R. Sjogren’s syndrome criteria. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:482–4.
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, et al. Classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:554–8.
Alexander C, Bader JB, Schaefer A, Finke C, Kirsch CM. Intermediate and long-term side effects of high-dose radioiodine therapy for thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:1551–4.
Solans R, Bosch JA, Galofre P, Porta F, Rosello J, Selva-O’Callagan A, et al. Salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction (sicca syndrome) after radioiodine therapy. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:738–43.
Schall GL, Anderson LG, Wolf RO, Herdt JR, Tarpley Jr TM, Cummings NA, et al. Xerostomia in Sjogren’s syndrome. Evaluation by sequential salivary scintigraphy. JAMA. 1971;216:2109–16.
Sugihara T, Yoshimura Y. Scintigraphic evaluation of the salivary glands in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988;17:71–5.
Nishiyama S, Miyawaki S, Yoshinaga Y. A study to standardize quantitative evaluation of parotid gland scintigraphy in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2470–4.
Caglar M, Tuncel M, Alpar R. Scintigraphic evaluation of salivary gland dysfunction in patients with thyroid cancer after radioiodine treatment. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27:767–71.
Umehara I, Yamada I, Murata Y, Takahashi Y, Okada N, Shibuya H. Quantitative evaluation of salivary gland scintigraphy in Sjorgen’s syndrome. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:64–9.
Aung W, Yamada I, Umehara I, Ohbayashi N, Yoshino N, Shibuya H. Sjogren's syndrome: comparison of assessments with quantitative salivary gland scintigraphy and contrast sialography. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:257–62.
Adams BK, Al Attia HM, Parkar S. Salivary gland scintigraphy in Sjogren’s syndrome: are quantitative indices the answer? Nucl Med Commun. 2003;24:1011–6.
Hakansson U, Jacobsson L, Lilja B, Manthorpe R, Henriksson V. Salivary gland scintigraphy in subjects with and without symptoms of dry mouth and/or eyes, and in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 1994;23:326–33.
Hermann GA, Vivino FB, Shnier D, Krumm RP, Mayrin V, Shore JB. Variability of quantitative scintigraphic salivary indices in normal subjects. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:1260–3.
Raza H, Khan AU, Hameed A, Khan A. Quantitative evaluation of salivary gland dysfunction after radioiodine therapy using salivary gland scintigraphy. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:495–9.
Valdes Olmos RA, Keus RB, Takes RP, van Tinteren H, Baris G, Hilgers FJ, et al. Scintigraphic assessment of salivary function and excretion response in radiation-induced injury of the major salivary glands. Cancer. 1994;73:2886–93.
Liem IH, Olmos RA, Balm AJ, Keus RB, van Tinteren H, Takes RP, et al. Evidence for early and persistent impairment of salivary gland excretion after irradiation of head and neck tumours. Eur J Nucl Med. 1996;23:1485–90.
Stephens LC, Schultheiss TE, Price RE, Ang KK, Peters LJ. Radiation apoptosis of serous acinar cells of salivary and lacrimal glands. Cancer. 1991;67:1539–43.
Anjos DA, Etchebehere EC, Santos AO, Lima MC, Ramos CD, Paula RB, et al. Normal values of [99mTc]pertechnetate uptake and excretion fraction by major salivary glands. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:395–403.
Loutfi I, Nair MK, Ebrahim AK. Salivary gland scintigraphy: the use of semiquantitative analysis for uptake and clearance. J Nucl Med Technol. 2003;31:81–5.
Kim SJ, Choi HY, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Jun S, Nam HY, et al. Limited cytoprotective effects of amifostine in high-dose radioactive iodine 131-treated well-differentiated thyroid cancer patients: analysis of quantitative salivary scan. Thyroid. 2008;18:325–31.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant no. 02-2008-003 from the SNUBH Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J.Y., Jang, S.J., Lee, W.W. et al. Evaluation of Salivary Gland Dysfunction Using Salivary Gland Scintigraphy in Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients and in Thyroid Cancer Patients after Radioactive Iodine Therapy. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45, 161–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-011-0091-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-011-0091-y