Abstract
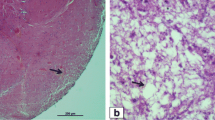
Viral nervous necrosis (VNN) causes high mortality in marine fish, especially in the grouper, worldwide and in China. Since there is no effective vaccine or drug to deal with VNN, early detection and prevention is important to block its outbreak. In this study, a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was developed for the rapid, convenient, and sensitive detection of the VNN pathogen, nervous necrosis virus (NNV), in the grouper. The whole process was completed within 3.5 h from the RNA extraction to PCR product visualization. The detection limit of this method was 200 copies of NNV RNA standard, which corresponded to 200 copies of virus particles. This RT-PCR method was specific to the NNV detection with no cross-reactivity to other fish viral disease pathogens, such as infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV), infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV), spring viraemia of carp virus (SVCV), epizootic haematopoietic necrosis virus (EHNV), and large yellow croaker iridovirus (LYCIV). With this method, the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) fry from hatcheries with or without incidence of the VNN epidemic in Fujian Province were detected. The results showed that all or 93% of the fry from the two hatcheries with incidence of the epidemic were diagnosed as positive, while 40% or 25% of fry from the two hatcheries without the VNN epidemic were also detected as NNV positive, indicating that this RT-PCR method can be used for rapid, sensitive detection of NNV infection and applied in the VNN epidemic alert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breton A L, Grisez L, Sweetman J, et al. 1997. Viral nervous necrosis (VNN) associated with mass mortalities in cage-reared sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Journal of Fish Diseases, 20: 145–151
Chi Shau-Chi, Lin Su-Ching, Su Huei-Meei, et al. 1999. Temperature effect on nervous necrosis virus infection in grouper cell line and in grouper larvae. Virus Res, 63: 107–114
Coeurdacier J L, Laporte F, Pepin J F. 2003. Preliminary approach to find synthetic peptides from nodavirus capsid potentially protective against sea bass viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 14: 435–447
Comps M, Trindade M, Delsert C. 1996. Investigation of fish encephalitis viruses (FEV) expression in marine fishes using DIGlabelled probes. Aquaculture, 143: 113–121
Dalla Valle L, Toffolo V, Lamprecht M, et al. 2005. Development of a sensitive and quantitative diagnostic assay for fish nervous necrosis virus based on two-target real-time PCR. Vet Microbiol, 110: 167–79
Guillou J P, Merle G, Henault S, et al. 1999. Detection of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by reverse transcription followed by polymerase chain reaction. Diagnostic validation. Vet Res, 30: 49–60
Kai Yu-Hsuan, Chi Shau-Chi. 2008. Efficacies of inactivated vaccines against betanodavirus in grouper larvae (Epinephelus coioides) by bath immunization. Vaccine, 26: 1450–7
Lai Yu-Shen, John J A C, Guo Ing-Cherng, et al. 2002. In vitro efficiency of intra- and extracellular immunization with mouse anti-YGNNV antibody against yellow grouper nervous necrosis virus. Vaccine, 20: 3221–3229
Lin Chin-Chiu, Lin John Han-You, Chen Ming-Shyan, et al. 2007. An oral nervous necrosis virus vaccine that induces protective immunity in larvae of grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Aquaculture, 268: 265–273
Liu Hong, Shi Xiujie, Gao Longying, et al. 2004. Establishment of discriminating method of various genotypes of viral nervous necrosis virus (VNNV) and application in quarantine and surveillance of VNNV. Journal of fisheries of China (in Chinese), 28: 695–702
Liu Wangta, Hsu Chi-Hsin, Chang Chiung-Yin, et al. 2006. Immune response against grouper nervous necrosis virus by vaccination of virus-like particles. Vaccine, 24: 6282–6287
Mikalsen A B, Teig A, Helleman A L, et al. 2001. Detection of infectious salmon anaemia virus (ISAV) by RT-PCR after cohabitant exposure in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Dis Aquat Organ, 47: 175–181
Mori K, Nakai T, Muroga K, et al. 1992. Properties of a new virus belonging to nodaviridae found in larval striped jack (Pseudocaranx dentex) with nervous necrosis. Virology, 187: 368–371
Munday B L, Kwang J, Moody N. 2002. Betanodavirus infections of teleostsh: a review. Journal of Fish Diseases, 25: 127–142
Nishizawa T M, Furuhashi T, Nagai T, et al. 1997. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl Environ Microbiol, 63: 1633–1636
Nishizawa T, Mori K, Nakai T, et al. 1994. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of RNA of striped jack nervous necrosis virus (SJNNV). Diseases of aquatic organisms, 18: 103–107
Popova A G, Oreshkova S F, Zhchelkunov I S, et al. 2008. RT-PCR-based methods for identification and typing of infectious hemopoietic necrosis virus in salmons. Vopr Virusol, 53: 39–43
Seng E K, Fang Q, Lam T J, et al. 2004. Development of a rapid, sensitive and specific diagnostic assay for fish Aquareovirus based on RT-PCR. J Virol Methods, 118: 111–122
Shieh J R, Chi S C. 2005. Production of monoclonal antibodies against grouper nervous necrosis virus (GNNV) and development of an antigen capture ELISA. Dis Aquat Organ, 63: 53–60
Starkey W G, Millar R M, Jenkins ME, et al. 2004. Detection of piscine nodaviruses by real-time nucleic acid sequence based amplification (NASBA). Dis Aquat Organ, 59: 93–100
Villoing S, Castric J, Jeffroy J, et al. 2000. An RT-PCR-based method for the diagnosis of the sleeping disease virus in experimentally and naturally infected salmonids. Dis Aquat Organ, 40: 19–27
Wang Xiaowen, Ao Jingqun, Li Qingge, et al. 2006. Quantitative detection of a marine fish iridovirus isolated from large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea, using a molecular beacon. Journal of Virological Methods, 133: 76–81
Wang Yi-Da, Kung Chun-Wei, Chen Jyh-Yih. 2010. Antiviral activity by fish antimicrobial peptides of epinecidin-1 and hepcidin 1-5 against nervous necrosis virus in medaka. Peptides, 31: 1026–1033
World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). 2001. Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals (in Chinese). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 80–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Basic Research Program under contract No. 2012CB114402; the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) under contract No. 2012AA092202; Scientific Research Project of Marine Public Welfare Industry of China under contract No. 200905020-07.
Contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, Y., Lin, K., Chen, X. et al. Diagnosis of nervous necrosis virus in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, by a rapid and convenient RT-PCR method. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 32, 88–92 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0370-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0370-9