Abstract
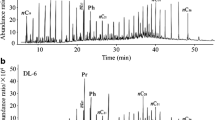
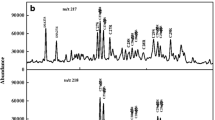
Bicyclic Sesquiterpanes (BSs) are ubiquitous components of crude oils and ancient sediments. BSs in crude oils and diesel oil were identified and characterized, the effects of moderate weathering on BS distributions were discussed, and a methodology using diagnostic indices of BSs was developed for oil correlation and differentiation. The results showed that crude oils and oil products had different abundances and distributions of BSs and, consequently, resulted in different diagnostic ratios. The selected diagnostic ratio indices of BSs, such as BS4/BS5 (ratio of 4,4,8,9,9-pentamethyl-decahydronaphthalene to 8β(H)-drimane), BS6/BS5 (ratio of 4,4,9,9,10-pentamethyl-decahydronaphthalene to 8β(H)-drimane), BS8/BS9 (ratio of the second peak to the third peak of C16 sequiterpane), and BS8/BS10 (ratio of C16 sequiterpane to 8β(H)-homodrimane), still maintained better stabilities (%RSD < 5%) after weathering for 30 d. The longer weathering process (150 d) had some effect on such ratios (5% < %RSD < 10%). The facts of the uniqueness, abundance in petroleum, and chemical stability of BSs enable them to be suitable as an effective diagnostic means for identifying spilled oil with moderate weathering, particularly for lighter refined product samples that are difficult to identify by current techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barakat A O, Mostafa A R, Qian Y, et al. 2002. Application of petroleum hydrocarbon chemical fingerprinting in oil spill investigations-gulf of Suez, Egypt. Spill Sci Technol Bull, 7(5-6): 229–231
D’Auria M, Emanuele L, Racioppi R, et al. 2009. Photochemical degradation of crude oil: Comparison between direct irradiation, photocatalysis, and photocatalysis on zeolite. J Hazard Mater, 164(1): 32–38
Garrett R M, Pickering I J, Haith C E, et al. 1998. Photooxidation of crude oils. Environ Sci Technol, 32(23): 3719–3723
Garcia OT, Grimalt J O. 2006. GC and GC-MS characterization of crude oil transformation in sediments and microbial mat samples after the 1991 oil spill in the Saudi Arabian Gulf coast. Environ Pollut, 139(3): 523–531
Hegazi AH, Anderson J T, Abu-Elgheit MA, et al. 2004. Source diagnostic and weathering indicators of tar-balls utilizing acyclic, polycyclic and S-heterocyclic components. Chemosphere, 55(7): 1051–1065
Li Yun, Xiong Yongqiang, Yang Wanying, et al. 2009. Compound-specific stable carbon isotopic composition of petroleum hydrocarbons as a tool for tracing the source of oil spills. Mar Pollut Bull, 58(1): 114–117
Peters K E, Moldowan J M. 1993. The Biomarker Guide. Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall
Prince R C, Owens E H, Sergy G A. 2002. Weathering of an Arctic oil spill over 20 years: the BIOS experiment revisited. Mar Pollut Bull, 44(1): 1236–1242
Stout S A, Uhler A D, McCarthy K J. 2001. A strategy and methodology for defensibly correlating spilled oil to source candidates. Environ Fore, 2: 87–98
Stout S A, Uhler A D, McCarthy K J. 2005. Middle distillate fuel fingerprinting using drimane-based bicyclic sesquiterpanes. Environ Forensics, 6(3): 241–251
Wang Zhendi, Fingas M F. 2003. Development of oil hydrocarbon fingerprinting and techniques. Mar Pollut Bull, 47(9-12): 423–452
Wang Zhendi, Yang Chun, Fingas M, et al. 2005. Characterization, weathering, and application of sesquiterpanes to source identification of spilled petroleum products. Environ Sci Technol, 39(22): 8700–8707
Wang Chuanyuan, Du Jianguo, Gao Xuelu, et al. 2011. Chemical characterization of naturally weathered oil residues in the sediment from Yellow River Delta, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(1): 2469–2475
Weston R J, Philp R P, Sheppard C M, et al. 1989. Sesquiterpanes, diterpanes, and other higher terpanes in oils from the Taranaki Basin of New Zealand. Org Geochem, 14(4): 405–421
Yang Chun, Wang Zhendi, Hollebone B P, et al. 2009. Characteristics of bicyclic sesquiterpanes in crude oils and petroleum products. J Chromatogr A, 1216(20): 4475–4484
Zhang Chunming, Guo Kangliang, Zhang Jun, et al. 2002. Distribution characteristics and their geochemical significance of bicyclic sesquiterpanes. J Jianghan Pet Inst, 24(2): 30–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Key Projects in the Yantai Science & Technology Pillar Program under contract No. 2011060; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 40806048 and 41206089; Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Hu, X., He, S. et al. Source diagnostic and weathering indicators of oil spills utilizing bicyclic sesquiterpanes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 32, 79–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0344-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0344-y