Abstract
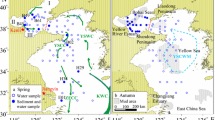
Biomarkers had been widely used to reconstruct phytoplankton productivity, and this method was applied in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea (Yellow Sea). In this study, Biologic Silicon (BSi) was used as productivity proxy to reconstruct productivity change of phytoplankton during last 200 years. The results show that the BSi contents of surficial sediments were in the range of 0.018%–2.516%, averaging 0.726%, and had a similar variation trend with phytoplankton biomass. The vertical distribution profiles revealed that BSi contents were relatively stable, in accordance with the variations of the contemporary phytoplankton standing crop index. According to the stability analysis of BSi in sediments, BSi was not degradaded for the past two hundred years and remained in sediments steadily. Thus, BSi in sediments had the potential to invert paleoproductivity. To conduct further survey, the linear regression equation between BSi contents and phytoplankton biomass index could be used to calculate the phytoplankton productivity by BSi, so that paleoproductivity may be reconstructed during last 200 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumgarter T R, Soutar A, Ferreira-Bartrina V. 1992. Reconstruction of the history of pacific sardine and northern anchovy populations over the past two millennia from sediments of the Santa Barbara Basin. California. CALCOFI Rep. 33: 24–40
Chen Meirong, Shi Shaohua, Shen Hongmei. 2005. The relationship between the sea surface temperature and elnino phenomenon of the Changjiang Estuary. Marine Forecasts (in Chinese), 2(1): 80–85
Chai Xinyu. 1986. The distribution of chlorophyll-a and its correlation with the water mass and spring layer in the area adjacent to the Changjiang River Estuary and Chejudo island. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 16(2): 1–26
Chen Jixin, Huang Bangqin, Liu Yuan, et al. 2006. Phytoplankton community structure in the transects across East China Sea and northern south China Sea determined by analysis of HPLC photosynthetic pigment signatures. Advances in Earth Science (in Chinese), 7: 738–746
Gu Xingen, Yuan Qi. 1995. An ecological study on phytoplankton in frontal region of Changjiang estuarine area. Marine Fisheries Research (in Chinese), 2(1): 1–15
Guo Yujie, Pan Youlian. 1992a. The study of primary productivity in the Changjiang River Estuary. Studia Marina Sinica (in Chinese), 33: 191–200
Guo Yujie, Pan Youlian. 1992b. The wave of phytoplankton and the analysis of ecological in the Changjiang River Estuary. Studia Marina Sinica (in Chinese), 33: 167–189
Jia Haibo. 2008. The use of sedimentary fish-scale for reconstruction of the last 150 years fish population fluctuations in the Yellow Sea (in Chinese) [dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China
Jiao Nianzhi, Wang Rong, Li Chaolun. 1998. Primary production and new production in spring in the east China Sea. Oceanologja et Limnologia Science (in Chinese), 29(2): 135–140
Kohfeld K E, Quere C L, Harrison S P, et al. 2005. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science, 74: 308
Liu Zilin, Ning Xiuren, Cai Yuming. 2001. Primary productivity and standing stock of the phytoplankton in the Hangzhou Bay to the Zhoushan fishing ground during autumn. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 23(2): 93–98
Long Qian. 2002. Magnetic and geochemical character of core samples from East China Sea and the Yellow Sea [dissertation]. Shanghai: East China Normal University
Lu Beiwei, Wang Rong. 1996. The distribution characteristic of surface chlorophyll-a in spring in the east China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Science (in Chinese), 27(5): 487–491
Ning Xiuren, Liu Zilin, Cai Yuming. 2000. A review on primary production studies for China seas in the past 20 years. Donghai Marine Science (in Chinese), 18(3): 13–19
Ning Xiuren, Liu Zilin, Hu Qinxian. 1985. The distribution characteristic of chlorophyll-a and productivity of phytoplankton in the coastal upwelling of chekiang, Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 7(6): 751–762
Ragueneau O, Treguer P, Leynaert A, et al. 2000. A review of the Si cycle in the modem ocean: Recent progress and missing gaps in the application of biogenic opal as a paleoproductivity proxy. Global Planet Change, 26(4): 317–365
Shen Zhiliang. 1991. A study on the effectes of the three gorge project on the distributions and changes of the nutrients in the Changjiang River estuary. Oceanologja et Limnologia Science (in Chinese), 22(6): 540–546
Shen Zhiliang. 1993. The effects of the physic-chemical environment on the primary productivity in the Changjiang River Estuary. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), 1: 42–51
Wang Baodong. 2000. Characteristics of variations and interrelations of biogenic elements in the Huanghai Sea cold water mass. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 22(6): 47–54
Wang Jun. 2001. Study on phytoplankton in the Yellow Sea in Spring. Marine Fisheries Research (in Chinese), 22(3): 56–61
Wang Jinhui. 2002. Phytoplankton communities in three distinct ecotypes of the Changjiang Estuary. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 32: 422–428
Wang Lisha, Shi Xiaoyong, Zhang Chuansong. 2008. Distribution of biogenic silica in the sediment of the East China Sea. Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 27(4): 117–120
Wang Yunlong, Yuan Qi, Shen Xinqiang. 2005. Ecological character of phytoplankton in spring in the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters. Marine Fisheries Research (in Chinese), 12(3): 300–306
Xing Lei, Zhao Meixun, Zhang Hailong, et al. 2008. Biomarker reconstruction of phytoplankton productivity and community structure changes in the middle Okinawa Trough during the last 15 ka. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(16): 2552–2559
Yang Qian, Sun Yao, Wang Didi, et al. 2010. Biogenic silica distributions in recent sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea and implications for productivity reconstructions. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 32(3): 1–9
Yang Hong, Yi Chaolu, Xie Ping. 2004. Records of human activities in the sediments of Lake Donghu, Wuhan. China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 24(3): 261–264
Ye Xiwen, Liu Sumei, Zhao Yingfei. 2004. The distribution of biogenic silica in the sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea and its environmental signification. China Environmental Science (in Chinese), 24(3): 265–269
Zhao Yingfei, Liu Sumei, Ye Xiwen, et al. 2005. The analysis of biogenic silica in core sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China (in Chinese), 35(3): 423–428
Zhao Baoren, Ren Guangfa, Cao Deming, et al. 2001. Characteristics of the ecological environment in up welling area adjacent to the Changjiang River Estuary. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), (3): 13–16
Zheng Yuanjia, Chen Xuezhong, Cheng Jiahua. 2003. The Living Resources and Environment of Continental Shelf of East China Sea (in Chinese). Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Education Publishing House
Zhou Weihua, Yuan Xiangcheng, Huo Weixi, et al. 2004. Distribution of chlorophylla and primary productivity in the adjacent sea area of Changjiang River Estuary. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 26(3): 143–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Key Basic Research Program of China under contract No. 2006CB400007; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 40876088.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Song, X., Sun, Y. et al. Application of biologic silicon in modern sedimentary section to reconstruction of phytoplankton changes in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea during last 200 years. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 31, 70–77 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0193-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0193-0