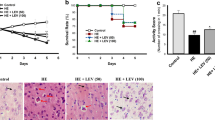
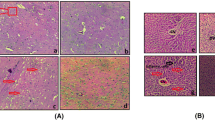
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a devastating neuropsychiatric presentation of the advanced hepatic insufficiency. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Aquaporin-4 (AQP4), the principal astrocyte water channel, is primarily involved in brain edema development. Ulinastatin (ULI) is a potent protease inhibitor, extracted from fresh human urine. We hypothesized that ULI could be neuroprotective in acute HE through molecular targeting of brain AQP4, which is known to be upregulated in HE. To induce acute liver failure (ALF), the rats were acutely intoxicated with thioacetamide (TAA). Animals were randomized into HE- and ULI-treated HE groups, with control normal group. Total bilirubin, albumin, serum aminotransferases, and serum/brain ammonia/proinflammatory cytokines, blood–brain barrier (BBB) integrity/tight junction proteins, brain water content, and neurological scores were assessed. Additionally, brain AQP4 and α-Syntrophin mRNA expression and protein levels were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. Brain and liver tissues were stripped and processed for further microscopic and histological analyses. ULI exerted potent dual neuro/hepato protective potential, improved neurological score, animals’ survival, ameliorated brain edema, probably via anti-inflammatory activity, preserved BBB integrity, down-regulated AQP4 expression, and membrane polarization by decreased α-syntrophin level, with rescued brain bioenergetics. ULI could be tooled as a possible therapeutic option in HE in ALF.
Graphical abstract

The possible ULI mediated protection in TAA-induced HE rat model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeva MM, Souto G, Blanco N, Donapetry C (2012) Ammonium metabolism in humans. Metabolism 61:1495–1511
Anderova M, Benesova J, Mikesova M, Dzamba D, Honsa P, Kriska J, Butenko O, Novosadova V, Valihrach L, Kubista M, Dmytrenko L, Cicanic M, Vargova L (2014) Altered astrocytic swelling in the cortex of α-syntrophin-negative GFAP/EGFP mice. PLoS One 9:e113444
Assentoft M, Kaptan S, Schneider HP, Deitmer JW, de Groot BL, MacAulay N (2016) Aquaporin 4 as a NH3 channel. J Biol Chem 291:19184–19195
Avraham Y, Grigoriadis N, Poutahidis T, Vorobiev L, Magen I, Ilan Y, Mechoulam R, Berry E (2011) Cannabidiol improves brain and liver function in a fulminant hepatic failure-induced model of hepatic encephalopathy in mice. Br J Pharmacol 162:1650–1658
Benarroch EE (2007) Aquaporin-4, homeostasis, and neurologic disease. Neurology 69:2266–2268
Bobermin LD, Hansel G, Scherer EB, Wyse AT, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A, Gonçalves CA (2015) Ammonia impairs glutamatergic communication in astroglial cells: protective role of resveratrol. Toxicol in Vitro 29:2022–2029
Bodega G, Suárez I, López-Fernández LA, García MI, Köber M, Penedo M, Luna M, Juárez S, Ciordia S, Oria M, Córdoba J, Fernández B (2012) Ammonia induces aquaporin-4 rearrangement in the plasma membrane of cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Int 61:1314–1324
Butterworth RF (2010) Altered glial-neuronal crosstalk: cornerstone in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int 57:383–388
Butterworth RF (2015) Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and brain edema in acute liver failure. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5:S96–S103
Chen HM, Huang HS, Ruan L, He YB, Li XJ (2014) Ulinastatin attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:1483–1489
Chu H, Huang C, Ding H, Dong J, Gao Z, Yang X, Tang Y, Dong Q (2016) Aquaporin-4 and cerebrovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci 17
Cui T, Zhu G (2015) Ulinastatin attenuates brain edema after traumatic brain injury in rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 71:595–600
Dai H, Song D, Xu J, Li B, Hertz L, Peng L (2013) Ammonia-induced Na,K-ATPase/ouabain-mediated EGF receptor transactivation, MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling and ROS formation cause astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Int 63:610–625
Esmann M (1988) ATPase and phosphatase activity of Na+,K+-ATPase: molar and specific activity, protein determination. Methods Enzymol 156:105–115
Fang M, Zhong WH, Song WL, Deng YY, Yang DM, Xiong B, Zeng HK, Wang HD (2018) Ulinastatin ameliorates pulmonary capillary endothelial permeability induced by sepsis through protection of tight junctions via inhibition of TNF-α and related pathways. Front Pharmacol 9:823
Farjam M, Dehdab P, Abbassnia F, Mehrabani D, Tanideh N, Pakbaz S, Imanieh MH (2012) Thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rat: behavioral, biochemical and histological changes. Iran Red Crescent Med J 14:164–170
Fukuda AM, Badaut J (2012) Aquaporin 4: a player in cerebral edema and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 9:279
He W, Liu Y, Geng H, Li Y (2015) The regulation effect of ulinastatin on the expression of SSAT2 and AQP4 in myocardial tissue of rats after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:10792–10799
Heidari R (2019) Brain mitochondria as potential therapeutic targets for managing hepatic encephalopathy. Life Sci 218:65–80
Heidari R, Jamshidzadeh A, Ghanbarinejad V, Ommati MM, Niknahad H (2018) Taurine supplementation abates cirrhosis-associated locomotor dysfunction. Clin Exp Hepatol 4:72–82
Huang Y, Li SN, Zhou XY, Zhang LX, Chen GX, Wang TH, Xia QJ, Liang N, Zhang X (2019) The dual role of AQP4 in cytotoxic and vasogenic edema following spinal cord contusion and its possible association with energy metabolism via COX5A. Front Neurosci 13:584
Inoue K, Takano H (2010) Urinary trypsin inhibitor as a therapeutic option for endotoxin-related inflammatory disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:513–520
Ito H, Yamamoto N, Arima H, Hirate H, Morishima T, Umenishi F, Tada T, Asai K, Katsuya H, Sobue K (2006) Interleukin-1beta induces the expression of aquaporin-4 through a nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 99:107–118
Jamshidzadeh A, Heidari R, Abasvali M, Zarei M, Ommati MM, Abdoli N, Khodaei F, Yeganeh Y, Jafari F, Zarei A, Latifpour Z, Mardani E, Azarpira N, Asadi B, Najibi A (2017) Taurine treatment preserves brain and liver mitochondrial function in a rat model of fulminant hepatic failure and hyperammonemia. Biomed Pharmacother 86:514–520
Ju M, He H, Chen S, Liu Y, Liu Y, Pan S, Zheng Y, Xuan L, Zhu D, Luo Z (2019) Ulinastatin ameliorates LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury by blocking the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in rats. Mol Med Rep 20:3347–3354
Karnad DR, Bhadade R, Verma PK, Moulick ND, Daga MK, Chafekar ND, Iyer S (2014) Intravenous administration of ulinastatin (human urinary trypsin inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a multicenter randomized controlled study. Intensive Care Med 40:830–838
Kelly T, Rose CR (2010) Ammonium influx pathways into astrocytes and neurones of hippocampal slices. J Neurochem 115:1123–1136
Liere V, Sandhu G, DeMorrow S (2017) Recent advances in hepatic encephalopathy. F1000Res 6:1637
Lippi U, Guidi G (1970) A new colorimetric ultramicromethod for serum glutamic-oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminase determination. Clin Chim Acta 28:431–437
Llansola M, Montoliu C, Agusti A, Hernandez-Rabaza V, Cabrera-Pastor A, Gomez-Gimenez B, Malaguarnera M, Dadsetan S, Belghiti M, Garcia-Garcia R, Balzano T, Taoro L, Felipo V (2015) Interplay between glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission alterations in cognitive and motor impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int 88:15–19
Lu J, Chen YP, Wan R, Guo CY, Wang XP (2012) Protective effects of ulinastatin on acute liver failure induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine. Dig Dis Sci 57:399–404
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6:159–163
Mao J, Zhang L, Song AL, Chen X, Zhang YC (2011) Effect of ulinastatin donor-pretreatment on liver graft during cold preservation in rats. Chin Med J 124:574–580
Masuda T, Sato K, Noda C, Ikeda KM, Matsunaga A, Ogura MN, Shimizu K, Nagasawa H, Matsuyama N, Izumi T (2003) Protective effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor on myocardial mitochondria during hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion. Crit Care Med 31:1987–1992
Niknahad H, Jamshidzadeh A, Heidari R, Zarei M, Ommati MM (2017) Ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and energy metabolism disturbances in isolated brain and liver mitochondria, and the effect of taurine administration: relevance to hepatic encephalopathy treatment. Clin Exp Hepatol 3:141–151
Pardridge WM, Connor JD, Crawford IL (1975) Permeability changes in the blood-brain barrier: causes and consequences. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol 3:159–199
Rama Rao KV, Verkman AS, Curtis KM, Norenberg MD (2014) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces encephalopathy and brain edema in experimental acute liver failure. Neurobiol Dis 63:222–228
Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL (2013) Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 19:9240–9255
Turner PV, Brabb T, Pekow C, Vasbinder MA (2011) Administration of substances to laboratory animals: routes of administration and factors to consider. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 50:600–613
Xu B, Li KP, Shen F, Xiao HQ, Cai WS, Li JL, Liu QC, Jia L (2013) Ulinastatin reduces cancer recurrence after resection of hepatic metastases from colon cancer by inhibiting MMP-9 activation via the antifibrinolytic pathway. Biomed Res Int 2013:437950
Zhao Y, Cai H, Zhou P, Lin S, Pan Y, Liang X (2019) Protective effect of ulinastatin on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury through autophagy activation in Chang liver cells. J Cell Biochem 120:14960–14970
Zhou LW, Wang YL, Yan XT, He XH (2008) Urinary trypsin inhibitor treatment ameliorates acute lung and liver injury resulting from sepsis in a rat model. Saudi Med J 29:368–373
Zhou J, Lian J, Li HX, Hong GL, Zhao GJ, Zhi SC, Qiu QM, Li MF, Lu ZQ (2016) Mechanism research and effect of ulinastatin in the brain tissue injury of acute hydrogen sulfide intoxicated rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 34:166–172
Funding
This work did not receive funding from any organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to research design, conception, data collection and analysis interpretation and shared in the critically revised process of the manuscript. All authors have approved the final manuscript version, submitted for journal publication and agree to be accountable for research aspects.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
• Targeting AQP4 might be an appropriate focal point to combat brain edema in fulminant ALF.
• ULI neuroprotective effects with improved neurological outcome could be designed as a novel mechanism-based therapeutic modality to control brain edema.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abo El gheit, R.E., Atef, M.M., Badawi, G.A. et al. Role of serine protease inhibitor, ulinastatin, in rat model of hepatic encephalopathy: aquaporin 4 molecular targeting and therapeutic implication. J Physiol Biochem 76, 573–586 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00762-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00762-0