Abstract
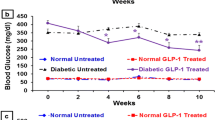
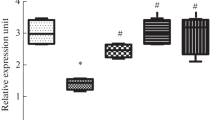
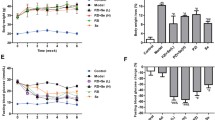
The mechanisms by which exendin-4 and selenium exert their antidiabetic actions are still unclear. Here, we investigated the effects of exendin-4 or selenium administration on the expression of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), and preproinsulin in the pancreas of diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced by streptozotocin administration. Diabetic rats were injected intraperitoneally with 0.03 μg exendin-4/kg body weight/daily or treated with 5 ppm selenium in drinking water for a period of 4 weeks. GLP-1R and IRS-1 levels were decreased while the level of preproinsulin messenger RNA (mRNA) was increased in the pancreas of diabetic untreated rats, as compared to that in control rats. Treatment of diabetic rats with exendin-4 increased protein and mRNA levels of GLP-1R, and IRS-1, and the mRNA level of preproinsulin in the pancreas, as compared to their levels in diabetic untreated rats. Selenium treatment of diabetic rats increased the pancreatic mRNA levels of GLP-1R, IRS-1, and preproinsulin. Exendin-4 or selenium treatment of diabetic rats also increased the numbers of pancreatic islets and GLP-1R molecules in the pancreas. Therefore, exendin-4 and selenium may exert their antidiabetic effects by increasing GLP-1R, IRS-1, and preproinsulin expression in the pancreas and by increasing the number of pancreatic islets.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 October 2017
Volume 73 issue 3 was published with an incorrect cover date. Correct is August 2017. The Publisher apologizes for this mistake and all related inconveniences caused by this.
References
Barakat GM, Moustafa ME, Bikhazi AB (2012) Effects of selenium and exendin-4 on glucagon-like peptide receptor, IRS-1, and Raf-1 in the liver of diabetic rats. Biochem Genet 50(11–12):922–935
Becker DJ, Reul B, Ozcelikay AT, Buchet JP, Henquin JC, Brichard SM (1996) Oral selenate improves glucose homeostasis and partly reverses abnormal expression of liver glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes in diabetic rats. Diabetologia 39:3–11
Bleys J, Navas-Acien A, Guallar E (2007) Serum selenium and diabetes in U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 30:829–834
Blonde L, Klein EJ, Han J, Zhang B, Mac SM, Poon TH et al (2006) Interim analysis of the effects of exenatide treatment on A1C, weight and cardiovascular risk factors over 82 weeks in 314 overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 8:436–447
Colagiuri S (2010) Diabesity: therapeutic options. Diabetes Obes Metab 12:463–473
Doyle ME, Egan JM (2007) Mechanisms of action of GLP-1 in the pancreas. Pharmacol Ther 113:546–593
Drucker DJ, Philippe J, Mojsov S, Chick WL, Habener JF (1987) Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S a 84:3434–3438
Fehmann HC, Habener JF (1992) Insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-I [7-37] stimulation of proinsulin gene expression and proinsulin biosynthesis in insulinoma beta TC-1 cells. Endocrinol 130:159–166
Forstermann U (2008) Oxidative stress in vascular disease: causes, defense mechanisms and potential therapies. Nat Clin Pract Card 5:338–349
Gebhard B, Holst JJ, Biegelmayer C, Miholic J (2001) Postprandial GLP-1, norepinephrine, and reactive hypoglycemia in dumping syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 46:1915–1923
Gutniak M, Ørkov C, Holst JJ, Ahrén B, Efendić S (1992) Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1[7-36] amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 326:1316–1322
Harkavyi A, Whitton PS (2010) Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection. Br J Pharmacol 159:495–501
Hay CW, Sinclair EM, Bermano G, Durward E, Tadayyon M, Docherty K (2005) Glucagon-like peptide-1stimulates human insulin promoter activity in part through cAMP-responsive elements that lie upstream and downstream of the transcription start site. J Endocrinol 186:353–365
Hwang D, Seo S, Kim Y, Kim C, Shim S, Jee S, Lee S, Jang M, Kim M, Yim S, Lee SK, Kang B, Jang I, Cho J (2007) Selenium acts as an insulin-like molecule for the down-regulation of diabetic symptoms via endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin signalling proteins in diabetes-induced non-obese diabetic mice. J Biosci 32:723–735
Kelleher AR, Fairchild TJ, Keslacy S (2010) STZ-induced skeletal muscle atrophy is associated with increased p65 content and downregulation of insulin pathway without NF-κB canonical cascade activation. Acta Diabetol 47:315–323
Kornhauser C, Garcia-Ramirez JR, Wrobel K, Pérez-Luque EL, Garay-Sevilla ME, Wrobel K (2008) Serum selenium and glutathione peroxidase concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Primary Care Diabetes 2:81–85
Kwon DY, Kim YS, Ahn IS, Kimda S, Kang S, Hong SM, Park S (2009) Exendin-4 potentiates insulinotropic action partly via increasing beta-cell proliferation and neogenesis and decreasing apoptosis in association with the attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in islets of diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Sci 111:361–371
Laybutt DR, Sharma A, Sgroi DC, Gaudet J, Susan Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC (2002) Genetic regulation of metabolic pathways in β-cells disrupted by hyperglycemia. J Biol Chem 277:10912–10921
Li Y, Hansotia T, Yusta B, Ris F, Halban PA, Drucker DJ (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling modulates beta cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:471–478
Lippman SM, Klein EA, Goodman PJ, Lucia MS, Thompson IM, Ford LG, Parnes HL, Minasian LM, Gaziano JM, Hartline JA, Parsons JK, Bearden JD, Crawford ED, Goodman GE, Claudio J, Winquist E, Cook ED, Karp DD, Walther P, Lieber MM, Kristal AR, Darke AK, Arnold KB, Ganz PA, Santella RM, Albanes D, Taylor PR, Probstfield JL, Jagpal TJ, Crowley JJ, Meyskens FL, Baker LH, Coltman CA (2009) Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of prostate cancer and other cancers: the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial [SELECT]. Jama 301:39–51
Marcason W (2008) What is the latest research on the connection between selenium and diabetes? J Am Diet Assoc 108:188
McNeill JH, Delgatty HL, Battell ML (1991) Insulin like effects of sodium selenate in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 40:1675–1678
Mojsov S, Heinrich G, Wilson IB, Ravazzola M, Orci L, Habener JF (1986) Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-translational processing. J Biol Chem 261:11880–11889
Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Yang H, Rodgers BD, Beday A, Pritchette LA, Eng J (1997) High potency antagonists of the pancreatic glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J Biol Chem 272:21201–21206
Ogawa W, Matozaki T, Kasuga M (1998) Role of binding proteins to IRS-1 in insulin signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 182:13–22
Okerson T, Chilton RJ (2010) The cardiovascular effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Cardiovasc Ther 30:e146–e155
Orskov C, Holst JJ, Knuhtsen S, Baldissera FG, Poulsen SS, Nielsen OV (1986) Glucagon-like peptides GLP-1 and GLP-2, predicted products of the glucagon gene, are secreted separately from pig small intestine but not pancreas. Endocrinol 119:1467–1475
Perfetti R, Merkel P (2000) Glucagon-like peptide-1: a major regulator of pancreatic β-cell function. Eur J Endocrinol 143:717–725
Ruíz C, Alegría A, Barberá R, Farré R, Lagarda J (1998) Selenium, zinc and copper in plasma of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in different metabolic control states. J Trace Elem Med Biol 12:91–95
Scaglia L, Cahill CJ, Finegood DT, Bonner-Weir S (1997) Apoptosis participates in the remodeling of the endocrine pancreas in the neonatal rat. Endocrinol 138:1736–1741
Stranges S, Marshall JR, Natarajan R, Donahue RP, Trevisan M, Combs GF, Cappuccio FP, Ceriello A, Reid ME (2007) Effects of long-term selenium supplementation on the incidence of type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern med 147:217–223
Wang X, Cahill CM, Pineyro MA, Zhou J, Doyle ME, Egan JM (1999) Glucagon-like peptide-1 regulates the beta cell transcription factor, PDX-1, in insulinoma cells. Endocrinol 140:4904–4907
Wootten D, Simms J, Koole C, Woodman OL, Summers RJ, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM (2011) Modulation of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling by naturally occurring and synthetic flavonoids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:540–550
Xu G, Stoffers DA, Habener JF, Bonner-Weir S (1999) Exendin-4 stimulates both β-cell replication and neogenesis, resulting in increased β-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes 48:2270–2276
Xu G, Kaneto H, Laybutt DR, Duvivier-Kali VF, Trivedi N, Suzuma K, King GL, Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S (2007) Downregulation of GLP-1 and GIP receptor expression by hyperglycemia. Diabetes 56:1551–1558
Yeo JE, Kang SK (2007) Selenium effectively inhibits ROS-mediated apoptotic neural precursor cell death in vitro and in vivo in traumatic brain injury. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:1199–1210
Young-Sun L, Seungjin S, Toshikatsu S, Eunsil H, Meng-Ju L, Jaeseok H, Ji-Won Y, Hee-Sook J (2007) Glucagon-like peptide-1 gene therapy in obese diabetic mice results in long-term cure of diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 56:1671–1679
Yusta B, Baggio LL, Estall JL, Koehler JA, Holland DP, Li H, Pipeleers D, Ling Z, Drucker DJ (2006) GLP-1 receptor activation improves beta cell function and survival following induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Metab 4:391–406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR, MEM, and AB conceived, designed the study, and oversaw the analysis and interpretation of data. GB performed all animal experiments and drafted the manuscript. GB and MH designed and carried out western blots and PCR experiments. IK performed the immunofluorescence experiments and the hematoxylin/eosin staining. MEM and SR secured the funding for the project. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the research fund from the National Council for Scientific Research (CNRS), Lebanon to M.E.M. (grant number 01-11-08) and by the School Research and Development Council, Lebanese American University (SRDC-t-2016-4).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0593-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barakat, G., Moustafa, M.E., Khalifeh, I. et al. Effects of exendin-4 and selenium on the expression of GLP-1R, IRS-1, and preproinsulin in the pancreas of diabetic rats. J Physiol Biochem 73, 387–394 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0565-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0565-1