Abstract
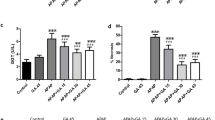
The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of the new formyl peptide receptor 2/lipoxin A4 receptor agonist BML-111 on acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury in mice and explore its possible mechanism(s). Male Swiss albino mice were intraperitoneally injected with BML-111 (1 mg/kg) twice daily for five consecutive days prior to a single intraperitoneal injection of APAP (500 mg/kg). Results have shown that APAP injection caused liver damage as indicated by significant increase in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Liver histopathological examination revealed marked necrosis and inflammation. Additionally, APAP decreased activities of hepatic glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) with significant increase in the hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Furthermore, APAP increased serum nitrite/nitrate (NO2 −/NO3 − ) level and hepatic tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). Pretreatment with BML-111 significantly reversed all APAP-induced pathological changes. BML-111 prevented the increase of AST, ALT, and ALP. Also, BML-111 markedly attenuated APAP-induced necrosis and inflammation. It decreased MDA with increase in SOD and GSH. Importantly, BML-111 decreased NO2 −/NO3 − level and TNF-α. These findings suggest that BML-111 has hepatoprotective effects against APAP-induced liver injury in mice. Its protective effect may be attributed to its ability to counteract the inflammatory ROS generation and regulate cytokine effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APAP:
-
Acetaminophen
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- FPR2/ALX:
-
Formyl peptide receptor 2/lipoxin A4 receptor
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- LX:
-
Lipoxin
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NO2 −/NO3 − :
-
Nitrite/nitrate
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Hady RH, Mahmoud MM, Farrag MM (2008) The potential protective role of alpha-lipoic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology 243:261–170
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Rahman MM, Hafez MM, Omran FM (2007) Role of nitric oxide and reduced glutathione in the protective effects of aminoguanidine, gadolinium chloride and oleanolic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology 234:124–134
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Nafees S, Seth A, Ali N, Rashid S, Sultana S (2012) Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Toxicol Lett 208:149–161
Ariel A, Chiang N, Arita M, Petasis NA, Serhan CN (2003) Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 and B4 analogs block extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent TNF-alpha secretion from human T cells. J Immunol 170:6266–6272
Ariel A, Fredman G, Sun YP, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE, Luster AD, Serhan CN (2006) Apoptotic neutrophils and T cells sequester chemokines during immune response resolution through modulation of CCR5 expression. Nat Immunol 7:1209–1216
Chen Y, Hao H, He S, Cai L, Li Y, Hu S, Ye D, Hoidal J, Wu P, Chen X (2010) Lipoxin A4 and its analogue suppress the tumor growth of transplanted H22 in mice: the role of antiangiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther 9:2164–2174
Coles B, Wilson I, Wardman P, Hinson JA, Nelson SD, Ketterer B (1988) The spontaneous and enzymatic reaction of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinonimine with glutathione: a stopped-flow kinetic study. Arch Biochem Biophys 264:253–260
Conte FP, Menezes-de-Lima O, Verri WA, Cunha FQ, Penido C, Henriques MG (2010) Lipoxin A4 attenuates zymosan-induced arthritis by modulating endothelin-1 and its effects. Br J Pharmacol 161:911–924
Dahlin DC, Miwa GT, Lu AY, Nelson SD (1984) N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine: a cytochrome P-450-mediated oxidation product of acetaminophen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1327–1331
Dai Y, Cederbaum AI (1995) Cytotoxicity of acetaminophen in human cytochrome P4502E1-transfected HepG2 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:1497–1505
Devchand PR, Arita M, Hong S, Moussignac RL, Gronert K, Serhan CN (2003) Human ALX receptor regulates neutrophil recruitment in transgenic mice: roles in inflammation and host defense. FASEB J 17:652–659
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Fierro IM, Colgan SP, Bernasconi G, Petasis NA, Clish CB, Arita M, Serhan CN (2003) Lipoxin A4 and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin A4 inhibit human neutrophil migration: comparisons between synthetic 15 epimers in chemotaxis and transmigration with microvessel endothelial cells and epithelial cells. J Immunol 170:2688–2694
Folco G, Murphy RC (2006) Eicosanoid transcellular biosynthesis: from cell-cell interactions to in vivo tissue responses. Pharmacol Rev 58:375–388
Gardner CR, Gray JP, Joseph LB, Cervelli J, Bremer N, Kim Y, Mishin V, Laskin JD, Laskin DL (2010) Potential role of caveolin-1 in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245:36–46
Goh J, Baird AW, O'Keane C, Watson RW, Cottell D, Bernasconi G, Petasis NA, Godson C, Brady HR, MacMathuna P (2001) Lipoxin A (4) and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin A (4) antagonize TNF-alpha-stimulated neutrophil–enterocyte interactions in vitro and attenuate TNF-alpha-induced chemokine release and colonocyte apoptosis in human intestinal mucosa ex vivo. J Immunol 167:2772–2780
Gong J, Guo S, Li HB, Yuan SY, Shang Y, Yao SL (2012) BML-111, a lipoxin receptor agonist, protects haemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury in rats. Resuscitation 83:907–912
Hachicha M, Pouliot M, Petasis NA, Serhan CN (1999) Lipoxin (LX) A4 and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-LXA4 inhibit tumor necrosis factor 1alpha-initiated neutrophil responses and trafficking: regulators of a cytokine-chemokine axis. J Exp Med 189:1923–1930
Harizi H, Corcuff JB, Gualde N (2008) Arachidonic-acid-derived eicosanoids: roles in biology and immunopathology. Trends Mol Med 14:461–469
He M, Zhang S, Jiao Y, Lin X, Huang J, Chen C, Chen Z, Huang R (2012) Effects and mechanisms of rifampin on hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 50:3142–3149
James LP, McCollough SS, Lamps LW, Hinson JA (2003) Effect of N-acetylcysteine on acetaminophen toxicity in mice: relationship to reactive nitrogen and cytokine formation. Toxicol Sci 75:458–467
Jin SW, Zhang L, Lian QQ, Liu D, Wu P, Yao SL, Ye DY (2007) Post treatment with aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 analog attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice: the role of heme oxygenase-1. Anesth Analg 104:369–377
Kelava T, Cavar I, Culo F (2010) Influence of small doses of various drug vehicles on acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88:960–967
Kieran NE, Maderna P, Godson C (2004) Lipoxins: potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution, and antifibrotic mediators in renal disease. Kidney Int 65:1145–1154
Laskin DL (2009) Macrophages and inflammatory mediators in chemical toxicity: a battle of forces. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1376–1385
Laskin DL, Gardner CR (2007) Nonparenchymal cells, inflammatory macrophages, and hepatotoxicity. In: Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD (eds) Drug-induced liver disease. Informa Healthcare, New York, pp 159–184
Lin F, Zeng P, Xu Z, Ye D, Yu X, Wang N, Tang J, Zhou Y, Huang Y (2012) Treatment of lipoxin A(4) and its analogue on low-dose endotoxin induced preeclampsia in rat and possible mechanisms. Reprod Toxicol 34:677–685
Maderna P, Godson C (2009) Lipoxins: resolutionary road. Br J Pharmacol 158:947–959
Medeiros R, Rodrigues GB, Figueiredo CP, Rodrigues EB, Grumman A Jr, Menezes-de-Lima O Jr, Passos GF, Calixto JB (2008) Molecular mechanisms of topical anti-inflammatory effects of lipoxin A(4) in endotoxin induced uveitis. Mol Pharmacol 74:154–161
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Gillette JR, Brodie BB (1973) Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. IV. Protective role of glutathione. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187:211–217
Nelson SD (1990) Molecular mechanisms of the hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen. Semin Liver Dis 10:267–278
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Rajesh MG, Letha MS (2004) Preliminary evaluation of the antihepatotoxic activity of Kamilari, a polyherbal formulation. J Ethnopharmacol 91:99–104
Serhan CN, Savill J (2005) Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol 6:1191–1197
Serhan CN, Yacoubian S, Yang R (2008) Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators. Annu Rev Pathol 3:279–312
Shi Y, Zhang L, Jiang R, Chen W, Zheng W, Chen L, Tang L, Li L, Li L, Tang W, Wang Y, Yu Y (2012) Protective effects of nicotinamide against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Int Immunopharmacol 14:530–537
Spite M, Serhan CN (2010) Novel lipid mediators promote resolution of acute inflammation: impact of aspirin and statins. Circ Res 107:1170–1184
Srinivasan C, Williams WM, Ray MB, Chen TS (2001) Prevention of acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity by 2(R, S)-n-propylthiazolidine-4(R)-carboxylic acid in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 61:245–252
Takano T, Fiore S, Maddox JF, Brady HR, Petasis NA, Serhan CN (1997) Aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and LXA4 stable analogues are potent inhibitors of acute inflammation: evidence for anti-inflammatory receptors. J Exp Med 185:1693–1704
Tracey WR, Tse J, Carter G (1995) Lipopolysaccharide-induced changes in plasma nitrite and nitrate concentrations in rats and mice: pharmacological evaluation of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:1011–1015
Wu J, Wang A, Min Z, Xiong Y, Yan Q, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhang S (2011) Lipoxin A4 inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines induced by β-amyloid in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 408:382–387
Yuan L, Kaplowitz N (2009) Glutathione in liver disease and hepatotoxicity. Mol Aspects Med 30:29–41
Zhang L, Wan J, Li H, Wu P, Jin S, Zhou X, Yuan P, Xiong W, Li Y, Ye D (2007) Protective effects of BML-111, a lipoxin A4 receptor agonist, on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatol Res 37:948–956
Zhou M, Chen B, Sun H, Deng Z, Andersson R, Zhang Q (2011) The protective effects of lipoxin A4 during the early phase of severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 46:211–219
Zhou XY, Wu P, Zhang L, Xiong W, Li YS, Feng YM, Ye DY (2007) Effects of lipoxin A(4) on lipopolysaccharide induced proliferation and reactive oxygen species production in RAW264.7 macrophages through modulation of G-CSF secretion. Inflamm Res 56:324–333
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr. Abdelhadi M. Shebl, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, for providing assistance.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Agamy, D.S., Makled, M.N. & Gamil, N.M. Protective effects of BML-111 against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. J Physiol Biochem 70, 141–149 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0288-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0288-x