Abstract
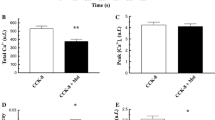
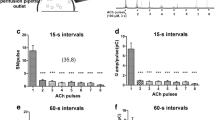
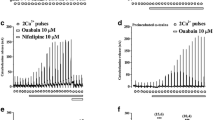
In the present work, we have evaluated the effect of an acute addition of melatonin on cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8)-evoked Ca2+ signals and amylase secretion in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. For this purpose, freshly isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells were loaded with fura-2 to study intracellular free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c). Amylase release and cell viability were studied employing colorimetric methods. Our results show that CCK-8 evoked a biphasic effect on amylase secretion, finding a maximum at a concentration of 0.1 nM and a reduction of secretion at higher concentrations. Pre-incubation of cells with melatonin (1 μM–1 mM) significantly attenuated enzyme secretion in response to high concentrations of CCK-8. Stimulation of cells with 1 nM CCK-8 led to a transient increase in [Ca2+]c, followed by a decrease towards a constant level. In the presence of 1 mM melatonin, stimulation of cells with CCK-8 resulted in a smaller [Ca2+]c peak response, a faster rate of decay of [Ca2+]c and lower values for the steady state of [Ca2+]c, compared with the effect of CCK-8 alone. Melatonin also reduced the oscillatory pattern of Ca2+ mobilization evoked by a physiological concentration of CCK-8 (20 pM), and completely inhibited Ca2+ mobilization induced by 10 pM CCK-8. On the other hand, Ca2+ entry from the extracellular space was not affected in the presence of melatonin. Finally, melatonin alone did not change cell viability. We conclude that melatonin, at concentrations higher than those found in blood, might regulate exocrine pancreatic function via modulation of Ca2+ signals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]c :
-
Cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration
- CCK-8:
-
Cholecystokinin octapeptide
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′N′-tetraacetic acid
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- Fura-2/AM:
-
Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester
References
Aust S, Jäger W, Kirschner H, Klimpfinger M, Thalhammer T (2008) Pancreatic stellate/myofibroblast cells express G-protein-coupled melatonin receptor 1. Wien Med Wochenschr 158:575–578
Bähr I, Mühlbauer E, Albrecht E, Peschke E (2012) Evidence of the receptor-mediated influence of melatonin on pancreatic glucagon secretion via the Gαq protein-coupled and PI3K signaling pathways. J Pineal Res 53:390–398
Carafoli E (1991) Calcium pump of the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev 71:129–153
Çöl C, Dınler K, Hasdemır O, Büyükaşik O, Firat T, Kükner A (2010) Evaluation of the effects of melatonin administration intraperitoneally on rats with acute pancreatitis induced by ductal ligation. Turk J Gastroenterol 21:433–438
Cuesta S, Kireev R, García C, Forman K, Escames G, Vara E, Tresguerres JA (2011) Beneficial effect of melatonin treatment on inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress on pancreas of a senescence accelerated mice model. Mech Ageing Dev 132:573–582
Del Castillo-Vaquero A, Salido GM, González A (2010) Melatonin induces calcium release from CCK-8- and thapsigargin-sensitive cytosolic stores in pancreatic AR42J cells. J Pineal Res 49:256–263
Fernández-Sánchez M, del Castillo-Vaquero A, Salido GM, González A (2009) Ethanol exerts dual effects on calcium homeostasis in CCK-8-stimulated mouse pancreatic acinar cells. BMC Cell Biol 10:77
González A, Camello PJ, Pariente JA, Salido GM (1997) Free cytosolic calcium levels modify intracellular pH in rat pancreatic acini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:652–656
González A, del Castillo-Vaquero A, Miró-Morán A, Tapia JA, Salido GM (2011) Melatonin reduces pancreatic tumor cell viability by altering mitochondrial physiology. J Pineal Res 50:250–560
González A, Salido GM (2010) Participation of mitochondria in calcium signalling in the exocrine pancreas. J Physiol Biochem 57:331–339
González A, Schmid A, Sternfeld L, Krause E, Salido GM, Schulz I (1999) Cholecystokinin-evoked Ca2+ waves in isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells are modulated by activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2, phospholipase D, and protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261:726–733
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatily improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Gülben K, Ozdemir H, Berberoğlu U, Mersin H, Yrkin F, Cakýr E, Aksaray S (2010) Melatonin modulates the severity of taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 55:941–946
Habara Y, Kanno T (1994) Stimulus-secretion coupling and Ca2+ dynamics in pancreatic acinar cells. Gen Pharmacol 25:843–850
Huai J, Shao Y, Sun X, Jin Y, Wu J, Huang Z (2012) Melatonin ameliorates acute necrotizing pancreatitis by the regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis. Pancreatology 12:257–263
Jaworek J (2006) Ghrelin and melatonin in the regulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion and maintaining of integrity. J Physiol Pharmacol 57:83–96
Jaworek J, Nawrot K, Konturek SJ, Leja-Szpak A, Thor P, Pawlik WW (2004) Melatonin and its precursor, L-tryptophan: influence on pancreatic amylase secretion in vivo and in vitro. J Pineal Res 36:155–164
Jaworek J, Nawrot-Porabka K, Leja-Szpak A, Bonior J, Szklarczyk J, Kot M, Konturek SJ, Pawlik WW (2007) Melatonin as modulator of pancreatic enzyme secretion and pancreatoprotector. J Physiol Pharmacol 58:65–80
Jaworek J, Nawrot-Porabka K, Leja-Szpak A, Konturek SJ (2010) Brain-gut axis in the modulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion. J Physiol Pharmacol 61:523–531
Jaworek J, Leja-Szpak A, Bonior J, Nawrot K, Tomaszewska R, Stachura J, Sendur R, Pawlik W, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ (2003) Protective effect of melatonin and its precursor L-tryptophan on acute pancreatitis induced by caerulein overstimulation or ischemia/reperfusion. J Pineal Res 34:40–52
Jaworek J, Zwirska-Korczala K, Szklarczyk J, Nawrot-Porąbka K, Leja-Szpak A, Jaworek AK, Tomaszewska R (2010) Pinealectomy aggravates acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pharmacol Rep 62:864–873
Jensen RT, Lemp GF, Gardner JD (1982) Interactions of COOH-terminal fragments of cholecystokinin with receptors on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem 257:5554–5559
Leja-Szpak A, Jaworek J, Pierzchalski P, Reiter RJ (2010) Melatonin induces pro-apoptotic signaling pathway in human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC-1). J Pineal Res 49:248–255
Muñoz-Casares FC, Padillo FJ, Briceño J, Collado JA, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Ortega R, Cruz A, Túnez I, Montilla P, Pera C, Muntané J (2006) Melatonin reduces apoptosis and necrosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury of the pancreas. J Pineal Res 40:195–203
Putney JW (1988) A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium 7:1–12
Qi W, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Kim SJ, Manchester LC, Cabrera J, Sainz RM, Mayo JC (1999) Melatonin reduces lipid peroxidation and tissue edema in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 44:2257–2262
Rivera-Barreno R, del Castillo-Vaquero A, Salido GM, González A (2010) Effect of cinnamtannin B-1 on cholecystokinin-8-evoked responses in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:980–988
Ruiz-Rabelo J, Vázquez R, Arjona A, Perea D, Montilla P, Túnez I, Muntané J, Padillo J (2011) Improvement of capecitabine antitumoral activity by melatonin in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 40:410–414
Stehle JH, Saade A, Rawashdeh O, Ackermann K, Jilg A, Sebestény T, Maronde E (2011) A survey of molecular details in the human pineal gland in the light of phylogeny, structure, function and chronobiological diseases. J Pineal Res 51:17–43
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I (1983) Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 306:67–69
Stumpf I, Mühlbauer E, Peschke E (2008) Involvement of the cGMP pathway in mediating the insulin-inhibitory effect of melatonin in pancreatic beta-cells. J Pineal Res 45:318–327
Thomas RP, Hellmich MR, Townsend CM Jr, Evers BM (2003) Role of gastrointestinal hormones in the proliferation of normal and neoplastic tissues. Endocr Rev 24:571–599
Williams JA (2006) Regulation of pancreatic acinar cell function. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 22:498–504
Williams JA (2010) Regulation of acinar cell function in the pancreas. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26:478–483
Williams JA, Burnham DB, Hootman SR (1989) The gastrointestinal system. Salivary, gastric, pancreatic and hepatobiliary secretion. In: Schultz SG, Forte JG, Rauner BB (eds) Handbook of physiology, Vol. III, Section 6. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, pp 419–441
Yule DI (2010) Pancreatic acinar cells: molecular insight from studies of signal-transduction using transgenic animals. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:1757–1761
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. This work was supported by Junta de Extremadura-FEDER (GR10010). Patricia Santofimia-Castaño was granted a fellowship from Junta de Extremadura (Consejería de Economía, Comercio e Innovación) and European Social Fund. The authors would like to thank Mrs. Mercedes Gomez Blázquez for her excellent technical support.
Author contributions
Patricia Santofimia-Castaño performed data acquisition and analysis. Deborah Clea Ruy is responsible for acquisition of data. Ginés M. Salido performed data interpretation and critical revision of the manuscript. Antonio González is responsible for concept/design of the research, data analysis/interpretation, drafting and approval of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santofimia-Castaño, P., Ruy, D.C., Salido, G.M. et al. Melatonin modulates Ca2+ mobilization and amylase release in response to cholecystokinin octapeptide in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol Biochem 69, 897–908 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0267-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0267-2