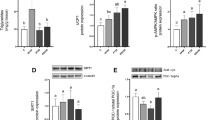
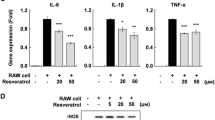
Abstract
Resveratrol is a naturally occurring polyphenol found in many dietary sources and red wine. Recognized as a cancer chemoprevention agent, an anti-inflammatory factor and an antioxidant molecule, resveratrol has been proposed as a potential anti-obesity compound and to be beneficial in diabetes. Most of the studies demonstrating the anti-adipogenic action of resveratrol were performed as long-term treatments on cultured preadipocytes. The aim of this study was to analyse the acute effects of resveratrol on glucose uptake and lipolysis in human mature adipocytes. Samples of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue were obtained from overweight humans and immediately digested by liberase. Fat cells were incubated (from 45 min to 4 h) with resveratrol 1 μM–1 mM. Then, glycerol release or hexose uptake was determined. Regarding lipolysis, the significant effects of resveratrol were found at 100 μM, consisting in a facilitation of isoprenaline stimulation and an impairment of insulin antilipolytic action. At 1 and 10 μM, resveratrol only tended to limit glucose uptake. Resveratrol 100 μM did not change basal glucose uptake but impaired its activation by insulin or by benzylamine. This inhibition was not found with other antioxidants. Such impairment of glucose uptake activation in fat cells may led to a reduced availability of glycerol phosphate and then to a decreased triacylglycerol assembly. Therefore, resveratrol increased triacylglycerol breakdown triggered by β-adrenergic activation and impaired lipogenesis. Consequently, our data indicate that resveratrol can be considered as limiting fat accumulation in human fat cells and further support its use for the mitigation of obesity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmo JM, Liang X, Rogers CQ, Pennock B, You M (2008) Resveratrol alleviates alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G833–G842
Akagawa M, Suyama K (2001) Amine oxidase-like activity of polyphenols. Mechanism and properties. Eur J Biochem 268:1953–1963
Alberdi G, Rodríguez VM, Miranda J, Macarulla MT, Arias N, Andrés-Lacueva C, Portillo MP (2011) Changes in white adipose tissue metabolism induced by resveratrol in rats. Nutr Metab (Lond) 8:29
Arias N, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Martínez-Castaño MG, Gómez-Zorita S, Miranda J, Martínez JA, Portillo MP (2011) The combination of resveratrol and conjugated linoleic acid is not useful in preventing obesity. J Physiol Biochem 67:471–477
Atgié C, Hadj-Sassi L, Bukowiecki L, Mauriège P (2009) High lipolytic activity and dyslipidemia in a spontaneous hypertensive/NIH corpulent (SHR/N-cp) rat: a genetic model of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Biochem 65:33–42
Atgié C, Sauvant P, Ambid L, Carpéné C (2009) Possible mechanisms of weight loss of Siberian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus sungorus) exposed to short photoperiod. J Physiol Biochem 65:377–386
Baile CA, Yang JY, Rayalam S, Hartzell DL, Lai CY, Andersen C, Della-Fera MA (2011) Effect of resveratrol on fat mobilization. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:40–47
Breen DM, Sanli T, Giacca A, Tsiani E (2008) Stimulation of muscle cell glucose uptake by resveratrol through sirtuins and AMPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:117–122
Brown VA, Patel KR, Viskaduraki M, Crowell JA, Perloff M, Booth TD, Vasilinin G, Sen A, Schinas AM, Piccirilli G, Brown K, Steward WP, Gescher A, Brenner DE (2010) Repeat dose study of the cancer chemopreventive agent resveratrol in healthy volunteers: safety, pharmacokinetics, and effect on the insulin-like growth factor axis. Cancer Res 70:9003–9011
Costa CS, Rohden F, Hammes TO, Margis R, Bortolotto JW, Padoin AV, Mottin CC, Guaragna RM (2011) Resveratrol upregulated SIRT1, FOXO1, and adiponectin and downregulated PPARγ1-3 mRNA expression in human visceral adipocytes. Obes Surg 21:356–361
Fischer-Posovszky P, Kukulus V, Tews D, Unterkircher T, Debatin KM, Fulda S, Wabitsch M (2010) Resveratrol regulates human adipocyte number and function in a Sirt1-dependent manner. Am J Clin Nutr 92:5–15
Floyd ZE, Wang ZQ, Kilroy G, Cefalu WT (2008) Modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma stability and transcriptional activity in adipocytes by resveratrol. Metabolism 57:S32–S38
Gómez-Zorita S, Fernández-Quintela A, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Hijona E, Bujanda L, Milagro F, Martínez JA, Portillo MP (2012) Resveratrol attenuates steatosis in obese Zucker rats by decreasing fatty acid availability and reducing oxidative stress. Br J Nutr 107:202–210
Grès S, Bour S, Valet P, Carpéné C (2012) Benzylamine antihyperglycemic effect is abolished by AOC3 gene invalidation in mice but not rescued by semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase expression under the control of aP2 promoter. J Physiol Biochem 68:651–662
Iffiú-Soltész Z, Mercader J, Daviaud D, Boucher J, Carpéné C (2011) Increased primary amine oxidase expression and activity in white adipose tissue of obese and diabetic db−/− mice. J Neural Transm 118:1071–1077
Iglesias-Osma MC, Bour S, Garcia-Barrado MJ, Visentin V, Pastor MF, Testar X, Marti L, Enrique-Tarancon G, Valet P, Moratinos J, Carpéné C (2005) Methylamine but not mafenide mimics insulin-like actvity of the semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase-substrate benzylamine on glucose tolerance and on human adipocyte metabolism. Pharmacol Res 52:475–484
Kang W, Hong HJ, Guan J, Kim DG, Yang EJ, Koh G, Park D, Han CH, Lee YJ, Lee DH (2012) Resveratrol improves insulin signaling in a tissue-specific manner under insulin-resistant conditions only: in vitro and in vivo experiments in rodents. Metabolism 61:424–433
Kennedy A, Overman A, Lapoint K, Hopkins R, West T, Chuang CC, Martinez K, Bell D, McIntosh M (2009) Conjugated linoleic acid-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in human adipocytes are attenuated by resveratrol. J Lipid Res 50:225–232
Krawczyk SA, Haller JF, Ferrante T, Zoeller RA, Corkey BE (2012) Reactive oxygen species facilitate translocation of hormone sensitive lipase to the lipid droplet during lipolysis in human differentiated adipocytes. PLoS One 7:e34904
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, Geny B, Laakso M, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127:1109–1122
Lasa A, Churruca I, Eseberri I, Andrés-Lacueva C, Portillo MP (2012) Delipidating effect of resveratrol metabolites in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:1559–1568
Lasa A, Schweiger M, Kotzbeck P, Churruca I, Simón E, Zechner R, Del Puy PM (2012) Resveratrol regulates lipolysis via adipose triglyceride lipase. J Nutr Biochem 23:379–384
Maraculla MT, Alberdi G, Gomez S, Tueros I, Bald C, Rodriguez VM, Martinez JA, Portillo MP (2009) Effects of different doses of resveratrol on body fat and serum parameters in rats fed a hypercaloric diet. J Physiol Biochem 65:369–376
Mercader J, Iffiú-Soltesz Z, Brenachot X, Földi A, Dunkel P, Balogh B, Attané C, Valet P, Mátyus P, Carpéné C (2010) SSAO substrates exhibiting insulin-like effects in adipocytes as a promising treatment option for metabolic disorders. Future Med Chem 2:1735–1749
Mercader J, Palou A, Bonet ML (2011) Resveratrol enhances fatty acid oxidation capacity and reduces resistin and retinol-binding protein 4 expression in white adipocytes. J Nutr Biochem 22:828–834
Mercader J, Wanecq E, Chen J, Carpéné C (2011) Isopropylnorsynephrine is a stronger lipolytic agent in human adipocytes than synephrine and other amines present in Citrus aurantium. J Physiol Biochem 67:443–452
Olholm J, Paulsen SK, Cullberg KB, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB (2010) Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol on adipokine expression and secretion in human adipose tissue explants. Int J Obes (Lond) 34:1546–1553
Park HJ, Yang JY, Ambati S, Della-Fera MA, Hausman DB, Rayalam S, Baile CA (2008) Combined effects of genistein, quercetin, and resveratrol in human and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Med Food 11:773–783
Pedersen SB, Ølholm J, Paulsen SK, Bennetzen MF, Richelsen B (2008) Low Sirt1 expression, which is upregulated by fasting, in human adipose tissue from obese women. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:1250–1255
Rayalam S, Yang J-Y, Ambati S, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA (2008) Resveratrol induces apoptosis and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytother Res 22:1367–1371
Rivera L, Moron R, Zarzuelo A, Galisteo M (2009) Long-term resveratrol administration reduces metabolic disturbances and lowers blood pressure in obese Zucker rats. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1053–1063
Serrano J, Jové M, Boada J, Bellmunt MJ, Pamplona R, Portero-Otín M (2009) Dietary antioxidants interfere with Amplex Red-coupled-fluorescence assays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:443–449
Su HC, Hung LM, Chen JK (2006) Resveratrol, a red wine antioxidant, possesses an insulin-like effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1339–E1346
Szkudelska K, Nogowski L, Szkudelski T (2009) Resveratrol, a naturally occurring diphenolic compound, affects lipogenesis, lipolysis and antilipolytic action of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 113:17–24
Szkudelska K, Nogowski L, Szkudelski T (2011) Resveratrol and genistein as adenosine triphosphate-depleting agents in fat cells. Metabolism 60:720–729
Szkudelski T, Szkudelska K (2011) Anti-diabetic effects of resveratrol. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1215:34–39
Timmers S, Konings E, Bilet L, Houtkooper RH, van de Weijer T, Goossens G, Hoeks J, van der Krieken S, Ryu D, Kersten S, Moonen-Kornips E, Hesselink M, Kunz I, Schrauwen-Hinderling V, Blaak E, Auwerx J, Schrauwen P (2011) Calorie restriction-like effects of 30 days of resveratrol supplementation on energy metabolism and metabolic profile in obese humans. Cell Metab 14:612–622
Wanecq E, Prévot D, Carpéné C (2009) Lack of direct insulin-like action of visfatin/Nampt/PBEF1 in human adipocytes. J Physiol Biochem 65:351–360
Yang JY, Della-Fera MA, Rayalam S, Ambati S, Hartzell DL, Park HJ, Baile CA (2008) Enhanced inhibition of adipogenesis and induction of apoptosis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes with combinations of resveratrol and quercetin. Life Sci 82:1032–1039
Yoshino J, Conte C, Fontana L, Mittendorfer B, Imai SI, Schechtman KB, Gu C, Kunz I, Fanelli FR, Patterson BW, Klein S (2012) Resveratrol supplementation does not improve metabolic function in nonobese women with normal glucose tolerance. Cell Metab 16:658–664
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Communauté de Travail des Pyrénées and the DIOMED project (INTERREG IVB-SUDOE-FEDER, SOE1/P1/E178). The authors express gratitude to Simon Rascalou, Sarah Canteiro and Sandra Grès for their help. They also acknowledge Philippe Valet (Univ. Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France) and Maria P. Portillo (Univ. of Pais Vasco, Vitoria, Spain) for their respective knowledge on human adipocyte biology and dietary diphenolic compounds and the staff of Plastic Surgery Dpt. of Rangueil Hospital for facilitating access to their post-surgical wastes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Submitted to Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry in 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez-Zorita, S., Tréguer, K., Mercader, J. et al. Resveratrol directly affects in vitro lipolysis and glucose transport in human fat cells. J Physiol Biochem 69, 585–593 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0229-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-012-0229-0