Abstract
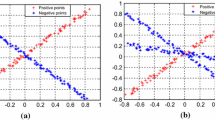
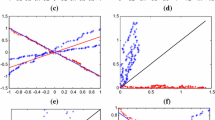
For multi-class classification problem, a novel multiple projection twin support vector machine (Multi-PTSVM) is proposed. Our Multi-PTSVM solves \(K\) quadratic programming problems (QPPs) to obtain \(K\) projection axes, which is similar to binary PTSVM, but the regularization terms and recursive procedure are introduced for each class, which improve the generalization ability greatly. Comparisons against the Multi-SVM, Multi-TWSVM, Multi-GEPSVM, and our Multi-PTSVM on both synthetic and benchmark datasets indicate that our Multi-PTSVM has its advantages.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S (2014) Fusing sequential minimal optimization and newtons method for support vector training. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-014-0265-x
Arun Kumar M, Gopal M (2009) Least squares twin support vector machines for pattern classification. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):7535–7543
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer, New York
Blake CL, Merz CJ (1998) UCI repository for machine learning databases. http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/MLRepository.html
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 2:1–27
Chen WJ, Shao YH, Hong N (2014) Laplacian smooth twin support vector machine for semi-supervised classification. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 5(3):459–468
Chen X, Yang J, Ye Q, Liang J (2011) Recursive projection twin support vector machine via within-class variance minimization. Pattern Recogn 44(10):2643–2655
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Deng NY, Tian YJ, Zhang CH (2012) Support vector machines: theory, algorithms, and extensions. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ding S, Hua X (2014) Recursive least squares projection twin support vector machines for nonlinear classification. Neurocomputing 130:3–9
Ghorai S, Mukherjee A, Dutta PK (2009) Nonparallel plane proximal classifier. Signal Process 89(4):510–522
Jayadeva R, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2009) Optimal kernel selection in twin support vector machines. Optim Lett 3(1):77–88
Lee Y, Lin Y, Wahba G (2004) Multicategory support vector machines: theory and application to the classification of microarray data and satellite radiance data. J Am Stat Assoc 99(465):67–81
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalize eigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Nene SA, Nayar SK, Murase H (1996) Columbia object image library (coil-20). In: Technical Report CUCS-005-96, Columbia University, New York
Qi Z, Tian Y, Shi Y (2013) Robust twin support vector machine for pattern classification. Pattern Recogn 46(1):305–316
Qi Z, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2012) Laplacian twin support vector machine for semi-supervised classification. Neural Netw 35:46–53
Qi Z, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2012) Twin support vector machine with universum data. Neural Netw 36:112–119
Scholkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with Kernels. MIT Press, MA Cambridge
Schwenker F (2000) Hierarchical support vector machines for multi-class pattern recognition. In: Knowledge-based intelligent engineering systems and allied technologies, pp 561–565
Shao YH, Chen WJ, Deng NY (2014) Nonparallel hyperplane support vector machine for binary classification problems. Inf Sci 263(1):22–35
Shao YH, Chen WJ, Zhang JJ, Wang Z, Deng NY (2014) An efficient weighted lagrangian twin support vector machine for imbalanced data classification. Pattern Recogn 47(9):3158–3167
Shao YH, Chen WJ, Zhang JJ, Wang Z, Deng NY (2014) An efficient weighted lagrangian twin support vector machine for imbalanced data classification. Pattern Recogn 47:3158–3167
Shao YH, Deng NY (2012) A coordinate descent margin based-twin support vector machine for classification. Neural Netw 25:114–121
Shao YH, Deng NY, Chen WJ (2013) A proximal classifier with consistency. Knowl Based Syst 49:171–178
Shao YH, Deng NY, Chen WJ, Wang Z (2013) Improved generalized eigenvalue proximal support vector machine. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(3):213–216
Shao YH, Deng NY, Yang ZM (2012) Least squares recursive projection twin support vector machine for classification. Pattern Recogn 45(6):2299–2307
Shao YH, Wang Z, Chen WJ, Deng NY (2013) A regularization for the projection twin support vector machine. Knowl Based Syst 37:203–210
Shao YH, Zhang CH, Wang XB, Deng NY (2011) Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):962–968
Sun L, Mu WS, Qi B, Zhou ZJ (2014) A new privacy-preserving proximal support vector machine for classification of vertically partitioned data. Int J Mach Learn Cybern doi:10.1007/s13042-014-0245-1
Tao Q, Chu D, Wang J (2008) Recursive support vector machines for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19(1):189–193
Tian YJ, Ju XC, Qi ZQ, Shi Y (2014) Improved twin support vector machine. Sci Chin Math 57(2):417–432
Tian YJ, Qi ZQ, Ju XC, Shi Y, Liu X (2013) Nonparallel support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(7):1067–1079
Wang XZ, He Q, Chen DG, Yeung D (2005) A genetic algorithm for solving the inverse problem of support vector machines. Neurocomputing 68:225–238
Wang XZ, Lu SX, Zhai JH (2008) Fast fuzzy multi-category svm based on support vector domain description. Int J Pattern Recogn Artif Intell 22(1):109–120
Weston J, Watkins C (1998) Multi-class support vector machines. In: Technical Report CSD-TR-98-04, Department of Computer Science, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham
Xiang C, Fan XA, Lee TH (2006) Face recognition using recursive fisher linear discriminant. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(8):2097–2105
Xue H, Chen S, Yang Q (2009) Discriminatively regularized least-squares classification. Pattern Recogn 42(1):93–104
Yang ZX, Shao YH, Zhang XS (2012) Multiple birth support vector machine for multi-class classification. Neural Comput Appl 1–9
Ye Q, Zhao C, Ye N, Chen, Y (2010) Multi-weight vector projection support vector machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 31(13):2006–2011
Ye QL, Zhao CX, Zhang HF, Chen XB (2012) Recursive “concave–convex” Fisher linear discriminant with applications to face, handwritten digit and terrain recognition. Pattern Recogn 45(1):54–65
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11201426 and 11371365), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LQ12A01020, LQ13F030010 and LQ14G010004), the Ministry of Education, Humanities and Social Sciences Research Project of China (No. 13YJC910011), and the Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (No. Y201432746).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CN., Huang, YF., Wu, HJ. et al. Multiple recursive projection twin support vector machine for multi-class classification. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 7, 729–740 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0289-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0289-2