Abstract
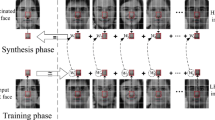
Face super-resolution is to synthesize a high resolution facial image from a low resolution input, which can significantly improve the recognition for computer and human. Regularization plays a vital role in ill-posed problems. The use of examples becomes much more effective when handling narrow family of images, such as face images. A properly chosen regularization can direct the solution toward a better quality outcome. An emerging powerful regularization is one that leans on image examples. This paper proposed a face hallucination method using example-based regularization. The work is specially targeted at improving the quality of high magnification. Our work follows the pyramid framework and assigns several high-quality candidate patches for each location in the degraded image. All problematic examples are rejected by defining an error function which embodies the example-based regularization. After repeated pruning, the reconstruction is done when there is only one candidate patch left in each location. The encouraging experimental results provide some hints that our approach is effective.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park S-C, Park M-K, Kang M-G (2003) Super-resolution image reconstruction: a technical overview (J). IEEE Signal Process Mag 20(3):21–36
Hertzmann A, Jacobs C-E, Oliver N et al. (2001) Image analogies. In: Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH. Los Angeles, USA, ACM Press, New York, pp 327–340
Elad M, Feuer A (1999) Super-resolution restoration of an image sequence: adaptive filtering approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 8(3):387–395
Tian J, Ma K (2011) A survey on super-resolution imaging. SIViP 5(3):1–14
Stark H, Oskoui P (1989) High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays, using convex projections. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 6(11):1715–1726
Nguyen N, Milanfar P (2000) A wavelet-based interpolation-restoration method for super-resolution. Circuits Syst Signal Process 19(4):321–338
Jian Sun, Zong-ben Xu, Heung-Yeung Shum (2008) Image super-resolution using gradient profile prior. In: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, anchorage, Alaska, USA, 24–26 June 2008, pp 1–8
Glasner D, Bagon S, Irani M (2009) Super-resolution from a single image. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on computer vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 Sept–2 Oct 2009, pp 349–356
Lyndsey C-P, David P-C, Stephen J-R, Andrew Z (2009) Bayesian methods for image super-resolution. Comput J 52(1):101–113
Yang Jianchao, Wright J, Huang T-S, Ma Yi (2010) Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(11):2861–2873
Farsiu S, Robinson M-D, Elad M et al (2004) Fast and robust multiframe super resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(10):1327–1344
Tsai R-Y, Huang T-S (1984) Multiple frame image restoration and registration. Adv Comput Vis Image Process 1:317–339
Ur H, Gross D (1992) Improved resolution from sub-pixel shifted pictures. IEEE Trans Graph Models Image Process 54(2):181–186
Nguyen N, Milanfar P (2000) An efficient wavelet-based algorithm for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of international conference on image processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–13 Sept 2000, pp 351–354
Irani M, Peleg S (1991) Improving resolution by image registration. IEEE Trans Graph Models Image Process 53(3):231–239
Schulz R-R, Stevenson R-L (1996) Extraction of high-resolution frames from video sequences. IEEE Trans Image Process 5:996–1011
Elad M, Feuer A (1997) Restoration of a single super-resolution image from several blurred, noisy, and under-sampled measured images. IEEE Trans Image Process 6(12):1646–1658
Hardie R-C, Barnard K-J, Armstrong E–E (1997) Joint MAP registration 245 and high-resolution image estimation using a sequence of under-sampled images. IEEE Trans Image Process 6:1621–1633
Baker S, Kanade T (2002) Limits on super-resolution and how to break them. IEEE Trans PAMI 24(9):1167–1183
Baker S, Kanade T (2000) Hallucinating faces. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition, Grenoble, France, 28–30 Mar 2000, pp 83–88
Freeman W-T, Pasztor E-C (1999) Learning low-level vision. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on computer vision, Kerkyra, Corfu, 20–25 Sept 1999, pp 1182–1189
Freeman W-T, Rjones T, Pasztor E-C (2002) Example-based super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 10th international conference on computer graphics and applications, Beijing, China, 9–11 Oct 2002, pp 56–65
Suresh K-V, Rajagopalan A-N (2007) Robust and computationally efficient super-resolution algorithm. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 24(4):984–992
Li X, Hu Y, Gao X et al (2010) A multi-frame image super-resolution method. IEEE Signal Process Mag 90(2):405–414
Shen H, Zhang L, Huang B et al (2007) A MAP approach for joint motion estimation, segmentation, and super resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(2):479–490
El-Khamy S-E, Hadhoud M-M, Dessouky M-I et al (2006) Wavelet fusion: a tool to break the limits on LMMSE image super-resolution. Int J Wavelets Multiresolut Inf Process 4(1):105–118
Farsiu S, Robinson D, Elad M et al (2004) Advances and challenges in super-resolution. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 16(2):47–57
Mohammad-Djafari A (2009) Super-resolution: a short review, a new method based on hidden Markov modeling of HR image and future challenges. Comput J 52(1):126–141
Sun J, Zhang N, Tao H, Shum H (2003) Image hallucination with primal sketch priors. In: Proceedings of international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Madison, Wisconsin, 16–22 June 2003, pp 729–736
Hong C, Dit-Yan Y, Yimin X (2004) Super-resolution through neighbor embedding. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Washington DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004, pp 275–282
Yi T, Pingkun Y, Yuan Y, Xue-long L (2011) Single-image super-resolution via local learning. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2(1):15–23
Chakrabarti A, Rajagopalan A-N, Chellappa R (2007) Super-resolution of face images using kernel PCA-based prior. IEEE Trans Multimedia 9(4):888–892
Bruce P, Ashraful A-M, Hong Y (2011) Performance evaluation and comparison of PCA based human face recognition methods for distorted images. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2(4):245–259
Xiang X, Wanquan L, Svetha V (2011) An innovative face image enhancement based on principle component analysis. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi: 10.1007/s13042-011-0060-x
Chacko Binu P, Vimal Krishnan VR, Raju G, Babu Anto P (2012) Handwritten character recognition using wavelet energy and extreme learning machine. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 3(2):149–161
Malay KK, Manish Ch, Minakshi B (2011) Interactive image retrieval using M-band wavelet, earth mover’s distance and fuzzy relevance feedback. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi: 10.1007/s13042-011-0062-8
Wang J, Zhu S, Gong Y (2010) Resolution enhancement based on learning the sparse association of image patches. Pattern Recogn Lett 31(1):1–10
Kim K, Kwon Y (2010) Single-image super-resolution using sparse regression and natural image prior. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(6):1127–1133
Yang J, Wright J, Huang T-S et al (2010) Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(11):2861–2873
Liu L, YiDing W (2008) Face super-resolution using a hybrid model. In: Proceedings of international conference on signal processing, Beijing, China, 26–29 Oct 2008, pp 1153–1156
Liu C, Shum H, Freeman W (2007) Face hallucination: theory and practice. Int J Comput Vis 75:115–134
Wang X, Tang X (2005) Hallucinating face by eigen-transformation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 35(3):425–434
Cong-yong S, Yue-ting Z, Li H, Fei W (2005) Steerable pyramid-based face hallucination. IEEE Trans Pattern Recogn 38:813–824
Dsenko D, Elad M (2007) Example-based single document image super-resolution: a global MAP approach with outlier rejection. Int J Multidimens Syst Signal Process 18(2):103–121
Lagendijk R-L, Biemond J (1991) Iterative identification and restoration of images. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Roth S, Black M-J (2005) Fields of experts: a framework for learning image priors. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), San-Diego, California, 20–25 June 2005, pp 860–867
Efros A-A, Leung T-K (1999) Texture synthesis by non-parametric sampling. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society conference on computer vision (ICCV), Corfu, Greece, 20–25 Sept 1999, pp 1033–1038
Nakagaki R, Katsaggelos A-K (2003) VQ-based blind image restoration algorithm. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(9):1044–1053
Criminisi A, Perez P, Toyama K (2004) Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image in painting. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(9):1200–1212
Philips P-J, Moon H, Rauss P, Rizvi S-A (1997) The FERET evaluation methodology for face-recognition algorithms. In: Proceedings of international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 17–19 June 1997, pp 137–143
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (61273273), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (4112050) and Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China. The authors would like to thank Zhen gang Zhai, Zi ye Yan and Yao zu An for the insightful discussions. This work is also supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (F2012201023) and Shenzhen Key Laboratory for High Performance Data Mining with Shenzhen New Industry Development Fund (CXB201005250021A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Lu, Y. Face hallucination using example-based regularization. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 4, 693–701 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-012-0149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-012-0149-x