Abstract
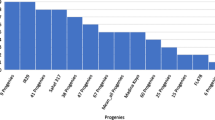
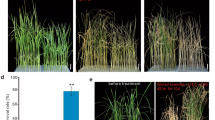
QTL analysis of physiological traits related to salt tolerance was carried out using 117 BC3F5 lines derived from a cross between “Ilpumbyeo” as a recurrent parent and “Moroberekan” as a donor parent. The 117 introgression lines with the parents were evaluated for five traits; dry weight, fresh weight, leaf area, seedling height, and survival rate under control and salinity conditions (55 mM) at the seedling stage. To identify QTLs related to salt tolerance, 125 SSR markers showing polymorphisms between the parents were genotyped for the 117 BC3F5 lines. A total of eight QTLs were detected on chromosomes 1, 6, and 7. These include two QTLs on chromosomes 6 and 7 for reduction rate of dry weight (R2 = 10.2∼13.6%), three QTLs on chromosomes 1, 6, and 7 for reduction rate of fresh weight (R2 = 10.9∼13.9 %), two QTLs on chromosomes 1 and 7 for reduction rate of leaf area (R2 = 12.1%), and one QTL on chromosome 7 for reduction rate of seedling height (R2 = 10.5%). The Moroberekan alleles contributed the positive effect at these eight QTL loci. Although the parents, Ilpumbyeo and Moroberekan, were not salt tolerant as the salt tolerant check variety, Pokkali, some lines displayed a similar level of tolerance as Pokkali. The effect of the QTL on chromosome 7 was further confirmed by evaluating four lines containing the target QTL for fresh and dry weight, turgid weight, and relative water content (RWC). Significant differences between each line and Ilpumbyeo were detected for dry and fresh weight, and RWC values, and these results seem to indicate the beneficial effect of the Moroberekam alleles for salt tolerance. A set of introgression lines are being developed containing only few chromosomal segments from Moroberekan in the Ilpumbyeo background. These would be useful in developing salt tolerant lines in the breeding program.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M, Harris PJC. 2004. Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plant. Plant Sci 166: 3–16
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB. 1997. QTL Cartographer: a refer ence manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. Raleigh, NC, Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwonse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PC, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD. 1994. Satutated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcreoss pop ulation. Genetics 138: 1251–1274
Cho YG, McCouch SR, Kuiper M, Kang MR, Pot J, Groenen JTM, Eun MY. 1998. Integrated map of AFLP, SSLP and RFLP markers using a recombinant inbred population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 370–380
Ebitani T, Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi K, Yano M. 2005. Construction and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of indica rice cultivar ‘Kasalath’ in a genetic back ground of japonica elite cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed. Sci. 55: 65–73
Gong JM, He P, Qian Q, Shen LS, Zhu LH, Chen SY. 1999. Identification of salt-tolerance QTL in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin. Sci. Bull. 44: 68–71
Ju HG, Yoon DB, Xie XB, SAhn SN, Jeong OY, Jeong EG, Choi KJ. 2004. Evaluation of agronomic traits of an Ilpumbyeo×Moroberekan BC3F2 population. Korean J. Breed. 36(5): 338–344
Juliano B. 1971. A simplified assay for milled-rice amylose. Cereal Sci. Today 16: 334–360
Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner RMD, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR. 2001. Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 125: 406–422
Kubo T, Aida Y, Nakamura K, Tsunematsu H, Doi K, Yoshimura A. 2002. Reciprocal chromosome segment substitution series derived from japonica and indica cross of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 52: 319–325
Lee KS. 1995. Variability and genetics of salt tolerance in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis. 1–112. University of the Philippines, Los Banos
Lee SY, Ahn JH, Cha YS, Yun DW, Lee MC, Ko JC, Lee KS, Eun MY. 2007. Mapping QTLs related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage. Plant Breed. 126: 43–46
Lin HX, Yanagihara S, Zhuang JY, Senboku T, Zheng KL, Yashima S. 1998. Identification of QTL for salt tolerance in rice via molecular markers. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 12: 72–78
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY. 2004. QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 108: 253–260
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD. 1988. Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 76: 815–829
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein D. 2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res. 9: 199–207
Nelson JC. 1997. QGENE: software for marker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol. Breed. 3:239–245
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR. 1996. Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Gen. Genet. 252: 597–607
Prasad SR, Bagali PG, Hittalmani S, Shashidhar HE. 2000. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with seedling tolerance to salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr. Sci. 78:162–164
Ren AH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX. 2005. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 37: 1141–1146
Temnykh S, Park W, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich N, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR. 2000. Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 100: 697–712
Temnykh S, DeClerk G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch SR. 2001. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequen cy, length, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res. 11: 1141–1452
Tian F, Li DJ, Fu Q, Zhu Z, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ. 2005. Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112: 570–580
Yano M, Sasaki T. 1997. Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 35: 145–153
Yano M, Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Lin HX, Sasaki T. 2001. Genetic control of flowering time in rice, a short-day plant. Plant Physiol. 127: 1425–1429
Yeo AR, Yeo ME, Flower SA, Flowers TJ. 1990. Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for physiological characters contributing to salinity resistance, and their relationship to overall performance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 79: 377–384
Yoon DB, Kang KH, Kim HJ, Ju HG, Kwon SJ, Suh JP, Jeong OY, Ahn SN. 2006. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield components and morphological traits in an advanced back cross population between Oryza grandiglumis and the O. sativa japonica cultivar Hwaseongbyeo. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112: 1052–1062
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA. 1976. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. 3rd edn. IRRI, Manila
Zhang GY, Guo Y, Chen SL, Chen SY. 1995. RFLP tagging of a salt tolerance gene in rice. Plant Sci. 110: 227–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DM., Ju, HG., Kwon, TR. et al. Mapping QTLs for salt tolerance in an introgression line population between Japonica cultivars in rice. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 12, 121–128 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-009-0108-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-009-0108-6