Abstract
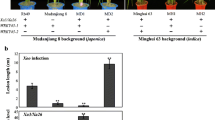
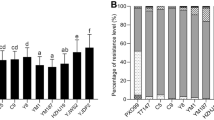
Bacterial blight, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is a destructive disease of rice in the major rice growing countries of Asia. In 2003, a serious bacterial blight epidemic occurred in the southwestern coastal areas in Korea, causing significant yield loss due to the emergence of a new race, K3a. IR24 near-isogenic lines containing Xa4, xa5, Xa7 and Xa21 genes conferred different degrees of resistance to the most virulent K3a isolate, HB01009 in an inoculation experiment in the greenhouse. Expression levels of the resistance genes, Xa4, xa5 and Xa21 were studied in two F2 populations derived from the crosses between elite japonica cultivars and an advanced backcross breeding line possessing Xa4, xa5 and Xa21 genes. F2 progenies segregated for K3a resistance (R) and susceptible (S) phenotypes in a ratio of 3(R):1(S) indicated that K3a resistance was controlled by a major dominant gene. Three PCR markers tightly linked to the resistance genes Xa4, xa5 and Xa21 confirmed the presence of the genes and their interaction with each gene. This study demonstrated that the Xa21 gene dominantly contributed to K3a resistance. However, the Xa4 gene also contributed to the full expression of resistance. The level of expression of strong resistance to K3a race was attributed to the presence of Xa21 and Xa4 genes irrespective of the presence of xa5 gene. Our results suggest that the R-gene combinations of Xa4+Xa21 could be a useful and effective strategy toward improving resistance to K3a race of Korean japonica cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheema K, Grewal N, Vikal Y, Sharma R, Lore JS, Das A, Bhatia D, Mahajan R, Gupta V, Bharaj TS, Singh K. 2008. A novel bacterial blight resistance gene from Oryza nivara maped to 38kb region on chromosome 4L and transferred to Oryza sativa L. Genet. Res., Camb. 90: 397–407
Garris AJ, McCouch SR, Kresovich S. 2003. Population structure and its effect on haplotype diversity and linkage disequilibrium surrounding the xa5 locus of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 165: 759–769
Gu K, Yang B, Tian D, Wu L, Wang D, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu Z, Wang GL, White FF, Yin Z. 2005. R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435: 1122–1125
Huang N, Angeles ER, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh S, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush GS. 1997. Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker-aided selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 313–320
Jena KK, Mackill DJ. 2008. Molecular markers and their use in marker-assisted selection in rice. Crop Sci. 48:1266–1276
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Noh TH, Heu S, Suh JP, Kim KY, Shin MS, Reveche MY, Pamplona A, Vera Cruz CM, Kim YG, Brar DS. 2007. Molecular breeding for bacterial blight resistance in japonica rice. The 2nd International Conference on Bacterial Blight of Rice. Nanjing, China. pp 71–76
Jeung JU, Heu SG, Shin MS, Vera Cruz CM, Jena KK. 2006. Dynamics of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae populations in Korea and their relationship to known bacterial blight resistance genes. Phytopathology 96: 867–875
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsien SPY, Merca SD. 1973. An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep 57: 537–541
Khush GS. 2001. Green revolution: The way forward. Nature Rev Genet 2: 815–822
Khush GS, Bacalangco E, Ogawa T. 1990. A new gene for resistance to bacterial blight from O. longistaminata. Rice Genet. Newsl. 7: 121–122
Khush GS, Mackill DJ, Sidhu GS. 1989. Breeding rice for resistance to bacterial blight. In: Bacterial blight of rice. International Rice Research Institute, Los, Banos, Manila, Philippines, pp207–217
Korinsak S, Sriprakhon S, Sirithanya P, Jairin J, Korinsak S, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T. 2009. Identification of microsatellite markers (SSR) linked to a new bacterial blight resistance gene xa33(t) in rice cultivar ‘Ba7’. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 3: 235–247
Lee KS, Rasabandith S, Angeles ER, Khush GS. 2003. Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight in 21 cultivars of rice. Phytopathology 93: 147–152
Lee SW, Choi SH, Han SS, Lee DG, Lee BY. 1999. Distribution of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strain virulent to Xa21 in Korea. Phytopathology 89: 928–933
Liu DO, Ronald PC, Bogdanove AJ. 2006. Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7: 303–324
Mew TW, Alvarez AM, Leach JE, Swings J. 1993. Focus on bacterial blight of rice. Plant Dis. 77: 5–12
Mew TW, Vera Cruz CM, Medalla ES. 1992. Changes in race frequency of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in response to rice cultivars planted in Philippines. Plant Dis. 76: 1029–1032
Murray MG, Thompson WF. 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8: 4321–4325
Noh TH, Lee DK, Kang MH, Shin MS, Na SY. 2003. Identification of new race of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) in Korea. (Abstr.) Phytopathology 93(suppl.):S66
Petpisit V, Khush GS, Kauffman HE. 1977. Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight in rice. Crop Sci. 17: 551–554
Singh S, Sidhu JS, Huang N, Vikal Y, Li Z, Brar DS, Dhaliwal HS, Khush GS. 2001. Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes (xa5, xa13 and Xa21) using marker-assisted selection into india rice cultivar PR106. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102: 1011–1015
Song WY, Pi LY, Wang GL, Gardner J, Holston T, Ronald PC. 1997. Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 9: 1279–1287
Sun X, Cao Y, Yang Z, Xu C, Li X, Wang S, Zhang Q. 2004. Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J. 37: 517–527
Sun X, Yang Z, Wang S, Zhang Q. 2003. Identification of a 47kb DNA fragment containing Xa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106: 683–687
Wang GL, Song WY, Ruan DL, Sideris S, Ronald PC. 1996. The cloned gene, Xa21, confers resistance to multiple Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains in transgenic plants. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 9: 850–855
Yang D, Sanchez A, Khush GS, Zhu Y, Huang N. 1998. Construction of a BAC contig containing the xa5 locus in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 1120–1124
Yang Z, Sun X, Wang S, Zhang Q. 2003. Genetic and physical mapping of a new gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106: 1467–1472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suh, JP., Noh, TH., Kim, KY. et al. Expression levels of three bacterial blight resistance genes against K3a race of Korea by molecular and phenotype analysis in japonica rice (O. sativa L.). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 12, 103–108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-009-0103-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-009-0103-y