Abstract
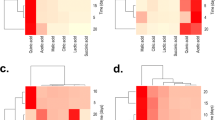
In recent years, numerous reports have characterized fungi not only to increase the efficiency of phosphate fertilizers but also to increase the availability of phosphorus from insoluble sources of phosphate. Aspergillus niger, as one of the ubiquitous organic acid-producing soil fungus, was screened for the ability to solubilize different concentrations of tricalcium phosphate (TCP) and zinc phosphate (ZP) ranging from 100 to 400 ppm. A. niger was able to solubilize TCP and ZP with solubilization index ranging from 2.10 to 3.5 and from 2.06 to 2.26, respectively. A drop in pH from 6.5 to 3.0 and 3.2 as one mechanism of phosphorus solubilization was observed in medium inoculated and supplemented with 400 ppm of TCP and ZP, respectively. A. niger released phosphorus from TCP (23.01 ppm) increasing its concentrations up to 400 ppm associated with increasing calcium releasing. Phosphorus releasing increased (42.16 ppm) with increasing ZP up to 200 ppm, and then decreased with increasing ZP up to 400 ppm associated with the releasing of zinc. HPLC results indicate that organic acids were released in high concentration when TCP and ZP were used with different concentrations compared with the control. For example, oxalic, malic, succinic, citric, and fumaric acid concentrations were 3.61, 3.13, 4.93, 3.17, and 2.11 at 100 ppm of TCP; and 3.09, 5.50, 5.08, 3.80, and 2.35 μg/ml at ZP compared with their concentrations 2.46, 1.83, 2.61, 3.16, and 1.37 μg/ml, respectively, in control.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Son, H. J., Park, G. T., Cha, M. S., & Hoe, M. S. (2006). Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphates by a novel salt- and pH tolerant Pantoea agglomerans R-42 isolated from soybean rhizosphere. Bioresource Technology, 97(2), 204–210.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2002). The nature and properties of soils (13th ed.p. 960). New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.
Song, O. R., Lee, S. J., Lee, Y. S., Lee, S. C., Kim, K. K., & Choi, Y. L. (2008). Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphate by Burkholderia cepacia DA23 isolated from cultivated soil. Baraz J Microbiol, 39, 151–156.
Sharma, S. B., Sayyed, R. Z., Trivedi, M. H., & Gobi, T. A. (2013). Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springerplus, 2, 587.
Abdel-Ghany, T. M., & Alawlaqi, M. M. (2018). Molecular identification of rhizospheric thermo-halotolerant Aspergillus terreus and its correlation to sustainable agriculture. BioResources, 13(4), 8012–8023.
Pradhan, N., & Sukla, L. B. (2005). Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by fungi isolated from agriculture soil. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(10), 850–854.
Abdel -Ghany, T. M., Alawlaqi, M. M., & Al Abboud, M. A. (2013). Role of biofertilizers in agriculture: a brief review. Mycopathologia, 11(2), 95–101.
Abdel-Ghany, T. M., Aisha, M., Al-Rajhi, H., Al Abboud, M. A., Alawlaqi, M. M., Magdah, G., Helmy, E. A. M., & Mabrouk, A. S. (2018a). Recent advances in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications: about future directions. A review. BioNanoScience, 8(1), 5–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-017-0413-3.
Abdel-Ghany, T. M., Ganash, M., Bakri, M. M., & Al-Rajhi, A. M. H. (2018b). Molecular characterization of Trichoderma asperellum and lignocellulolytic activity on barley straw treated with silver nanoparticles. BioResources, 13(1), 1729–1744. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.13.1.1729-1744.
Abdel-Ghany, T. M., Masrahi, Y. S., Mohamed, A., A, A., Alawlaqi, M. M., & Elhussien, N. I. (2015). Maize (Zea mays L.) growth and metabolic dynamics with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Journal of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, 6(9), 305. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7471.1000305.
Didiek, G. S., & Sugiarto, Y. (2000). Bioactivation of poorly soluble phosphate rocks with a phosphorus-solubilizing fungus. America Journal Soil Science & Biochemistry, 64, 927–932.
Helen, J. B. P., Graeme, K., Ritz, D., Fordyce, A., & Geoffrey, G. M. (2002). Solubilization of calcium phosphate as a consequence of carbon translocation by Rhizoctonia solani. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 40, 65–71.
Morales, A., Alvear, M., Valenzuela, E., Castillo, C. E., & Borie, F. (2011). Screening, evaluation and selection ofphosphate-solubilising fungi as potential biofertilizer. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 11(4), 89–103.
Gizaw, B., Tsegay, Z., Tefera, G., Aynalem, E., Wassie, M., & Abatneh, E. (2017). Phosphate solubilizing fungi isolated and characterized from Teff rhizosphere soil collected from North Showa zone, Ethiopia. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 11(17), 687–696. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2017.8525.
Nath, R., Sharma, G. D., & Madhumita, B. (2012). Efficiency of tri calcium phosphate solubilization by two different endophytic Penicillium sp. isolated from tea (Camellia sinensis L.). European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2(4), 1354–1358.
Padamavathi, T. (2015a). Optimization of phosphate solubilization by Aspergillus niger using plackett-burman and response surface methodology. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 15(3), 781–793.
El-Azouni, M. I. (2008). Effect of phosphate solubilizing fungi on growth and nutrient uptake of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 4(6), 592–598.
Venkateswarlu, B., Rao, A. V., Raina, P., & Ahmad, N. (1984). Evaluation of phosphorus solubilization by microorganisms isolated from arid soil. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 32, 273–277.
Kim, K. Y., McDonald, G. A., & Jordan, D. (1997). Solubilization of hydroxyapatite by Enterobacter agglomerans and cloned Escherichia coli in culture medium. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 24(4), 347–352.
Deubel, A., Granse, & Merbach, W. (2000). Transformation of organic rhizodeposits by rhizoplane bacteria and its influence on the availability of tertiary calcium phosphate. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 163, 387–392.
Baig, K. S., Arshad, M., Zahir, Z. A., & Cheema, M. A. (2010). Comparative efficacy of qualitative and quantitative methods for rock phosphate solubilization with phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria. Soil and Environment, 29, 82–86.
Patil, M. P., Kuligod, V. B., Hebsur, N. S., Patil, C. R., & Kulkarni, G. N. (2012). Effect of phosphate solubilizing fungi and phosphorus levels on growth, yield and nutrient content in maize (Zea mays). Karnataka. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 25(1), 58–62.
Illmer, P., & Schinner, F. (1992). Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by microorganisms isolated from forest soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 24, 389–395.
Chen, Y. P., Rekha, P. D., Arun, A. B., Shen, F. T., Lai, W. A., & Young, C. C. (2006). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Applied Soil Ecology, 34, 33–41.
Cunningham, J. E., & Kuiack, C. (1992). Production of citric and oxalic acids and solubilization of calcium phosphate by Penicillium bilaii. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 1451–1458.
Raper, K. B., & Fennell, D. I. (1973). The genus Aspergillus. New York: Robert E Krieger Publishing Company.
Samson, R. A., Visagie, C. M., Houbraken, J., Hong, S. B., Hubka, V., & Klaassen, C. H. W. (2014). Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus. Aspergillus. Studies in Mycology, 78, 141–173.
Padamavathi, T. (2015b). Solubilization of different inorganic phosphates by Aspergillus niger and Penicilium oxalicum. Advances in Bioresearch, 6(3), 113–119.
Iman, M. (2008). Effect of phosphate solubilizing fungi on growth and nutrient uptake of soyabean (Glycine max L.) plants. Journal of Applied Science Research, 4, 592–598.
Firew, E., Delelegn, W., & Diriba, M. (2016). Phosphate solubilization potential of rhizosphere fungi isolated from plants in Jimma Zone, Southwest Ethiopia. International Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 5472601, 11 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5472601.
Chuang, C. C., Kuo, Y. L., Chao, C. C., & Chao, W. L. (2007). Solubilization of inorganic phosphates and plant growth promotion by Aspergillus niger. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 43(5), 575–584.
Paul, S., & Sinha, N. (2017). Solubilizing bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa KUPSB12 with antibacterial potential from river Ganga, India Dipak. Annals of Agrarian Science, 15, 130–136.
Iyer, B., Mahendrapal, S. R., & Shalini, R. (2017). Effect of succinate on phosphate solubilization in nitrogen fixing bacteria harbouring chick pea and their effect on plant growth. Microbiological Research, 202(2017), 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.05.005.
Alam, S., Samina, K., Najma, A., & Maliha, R. (2002). In vitro solubilization of inorganic phosphate by phosphate solubilizing microorganisms (PSM) from maize rhizosphere. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology., 4(4), 444–458.
Fomina, M., Alexander, I. J., Hillier, S., & Gadd, G. M. (2004). Zinc phosphate and pyromorphite solubilization by soil plant-symbiotic fungi. Geomicrobial Journal, 21, 351–366.
Hruda, R. S., & Nibha, G. (2014). Evaluation of phosphate solubilising potential of some endophytic fungi under solid and liquid state. BMR Microbiology, 1(1), 1–6.
Akintokun, A. K., Akande, G. A., Akintokun, P. O., Popoola, T. O. S., & Babalola, A. O. (2007). Solubilization of insoluble phosphorus by organic acid-producing fungi isolated from the Nigerian soil. International Journal of Soil Science, 2(4), 301–307.
Omar, S. A. (1997). The role of rock-phosphate-solubilizing fungi and vesicular-arbusular-mycorrhiza (VAM) in growth of wheat plants fertilized with rock phosphate. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, 211–218.
Bar-Yosef, B., Rogers, R. D., Wolfram, J. H., & Richman, E. (1999). Pseudomonas cepacia-mediated rock phosphate solubilization in kaolinite and montmorillonite suspensions. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63, 1703–1708.
Narula, N., Kumar, V., Behl, R. K., Deubel, A. A., & Gransee, A. (2000). Effect of P solubilizing Azotobacter chroococcum on N, P, K uptake in P responsive wheat genotypes grown under greenhouse conditions. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 163, 393–398.
Banik, S., & Dey, B. K. (1983). Alluvial soil microorganisms capable of utilizing insoluble aluminium phosphate as a sole source of phosphorus. Zentralblatt fur Mikrobiologie, 138, 437–442.
Asea, P. E. A., Kucey, R. M. N., & Stewart, J. W. B. (1988). Inorganic phosphate solubilization by two Penicillium species in solution culture and soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 20, 459–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakri, M.M. Tri-Calcium and Zinc Phosphates Solubilization by Aspergillus niger and Its Relation to Organic Acids Production. BioNanoSci. 9, 238–244 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-0604-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-0604-1