Abstract
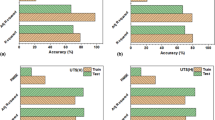
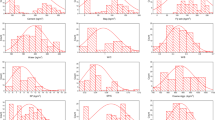
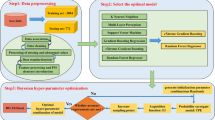
Mechanical property prediction for X70 pipeline steels attracts people’s attention because of maintaining high process stability and controlling production quality. Data-driven model is widely used and has the advantage of little professional knowledge requirement compared with phenomenological model. This paper introduced two new modeling techniques, namely ridge regression (RR) and random forest (RF). As a case, tensile strength prediction model of X70 pipeline steels was established and comparisons of different data-driven models, including the two new techniques and the already extensively used stepwise regression (SR), Bayesian regularization neural network (BRNN), radial-basis function neural network (RBFNN) and support vector machine (SVM), were made. The results show that all the models have reached good accuracies with relative error of ± 7%. On account of the excellent nonlinear fitting capability, models established by using intelligent algorithms (BRNN, RBFNN, SVM and RF) obtain better performance than multiple linear regression (SR and RR). Among the six models, RR provides a visualizing approach of the variable selection for multiple linear regression and RF achieves the best performance (R = 0.95 and MSE = 278.7 MPa2) on this data set.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu L, Xiao H, Li Q, Liu Y, Li P, Yang Z, and Yu H, Mater Sci Eng A 688 (2017) 388.
Qian D and Peng Y, J Mater Eng Perform 24 (2015) 1906.
Eser A, Broeckmann C, and Simsir C, Comput Mater Sci 113 (2016) 280.
Pouraliakbar H, Khalaj M J, Nazerfakhari M, and Khalaj G, J Iron Steel Res, Int 22 (2015) 446.
Powar A and Date P, Mat Sci Eng A 628 (2015) 89.
Abraham S, Raisee M, Ghorbaniasl G, Contino F, and Lacor C, J Comput Phys 332 (2017) 461.
Jovic O, Smrecki N, and Popovic Z, Talanta 150 (2016) 37.
[8] Rakhshkhorshid M, and Teimouri Sendesi S A, J Iron Steel Res, Int 21 (2014) 246.
Kappatos V, Chamos A N, and Pantelakis S G, Mater Des 31 (2010) 336.
Yang Z, Gu X S, Liang X Y, and Ling L C, Mater Des 31 (2010) 1042.
Zhao Y H, Weng Y, Peng N Q, Tang G B, and Liu Z D, J Iron Steel Res, Int 20 (2013) 9.
Zhi J, Zhang G, Yang F, Yang R, Liu F, Song X, Zhao Y, and Li D, Geoderma Regional 10 (2017) 1.
Zhao D, Wang Y, Liang D, and Zhang P, Mater Des 110 (2016) 676.
Cevik A, J Constr Steel Res 63 (2007) 1305.
Ahn J J, Byun H W, Oh K J, and Kim T Y, Expert Syst Appl 39 (2012) 8369.
Chen F F, Breedon M, White P, Chu C, Mallick D, Thomas S, Sapper E, and Cole I, Mater Des 112 (2016) 410.
He C L, Zong W J, Cao Z M, and Sun T, Mater Des 82 (2015) 216.
Yang R, Er P V, Wang Z, and Tan K K, Neurocomputing 199 (2016) 31.
Fathi A and Aghakouchak A A. Int J Fatigue 29 (2007) 261.
Zhang Y Z, Dong J H, and Zhang Y F, Trans China Weld Inst 29 (2008) 81.
Shi D Y, Xiong G J, Chen J F, and Li Y H, Proc CSEE 34 (2014) 562.
Zhang H R, Zhang Y, Dai D B, Cao M, and Shen W F, Mater Des 92 (2016) 371.
Lu W Z and Wang W J, Chemosphere 59 (2005) 693.
Yeganeh B, Motlagh M S P, Rashidi Y, and Kamalan H, Atmos Environ 55 (2012) 357.
Wang J F, Zhang L, Chen G X, and He X W, Appl Sci Technol 39 (2012) 28.
González Costa J J, Reigosa M J, Matías J M, and Covelo E F, Sci Total Environ 593–594 (2017) 508.
Shen X R, Study on the methods of fault detection and prediction in non-linear industrial processes based on support vector machine, Master Thesis, Bohai University, China (2017).
Zhou Y S, Research on combination forecasting model based on attribute selection algorithm and support vector machine, Master Thesis, Lanzhou University, China (2017).
Breiman L, Mach Learn 45 (2001) 5.
Adusumilli S, Bhatt D, Wang H, Devabhaktuni V, and Bhattacharya P, Neurocomputing 166 (2015) 185.
Cottrell G A, Kemp R, Bhadeshia H K D H, Odette G R, and Yamamoto T, J Nucl Mater 367–370 (2007) 603.
Ndez-Delgado M, Cernadas E, Barro S, and Amorim D, J Mach Learn Res 15 (2014) 3133.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB0304900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Ren, J., Zhou, X. et al. Comparisons of Different Data-Driven Modeling Techniques for Predicting Tensile Strength of X70 Pipeline Steels. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 1277–1288 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01624-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01624-0