Abstract
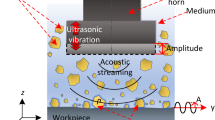
A recent and promising technique in advanced material processing techniques is the use of ultrasonic assistance in almost all cutting, forming and shaping processes. Optimizing manufacturing costs through reducing process forces and tool wears, improving machinability through enhancing surface finish and quality with minimal production time and energy, and delivering products with prolonged service life are some of the most important features of the vibration assisted manufacturing methods. To study the effect of ultrasonic vibrations on the milling process of the stainless steels, a series of experiments was designed and then implemented on a difficult-to-machine material. The result of the surface roughness and the cutting force tests has been comprised with and without processing by ultrasonic assistance. Experiments prove that under ultrasonic assistance, cutting forces are reduced, surface quality is improved and in all, a better machinability is achieved. It is concluded that dry aero-acoustical lubrication conditions and materials softening are of crucial importance in the machinability of difficult-to-cut AISI 304 materials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brehl D E, and Dow T A, Precis Eng 32 (2008) 153.
Abdullah A, Malaki M, and Baghizadeh E, Proc Inst Mech Eng C 226 (2012) 681.
Ashida Y, and Aoyamab H, J Mater Process Technol 187–188 (2007) 118.
Abdullah A, Malaki M, and Eskandari A, Mater Des 38 (2012) 7.
Puga H, Teixeira J C, and Prokic M, Mater Lett 63 (2009) 2089.
Liu C S, Zhao B, Gao G F, and Zhang X H, Key Eng Mater 291–292 (2005) 447.
Azarhoushang B, and Akbari J, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47 (2007) 1027.
Ostasevicius V, Gaidys R, Rimkeviciene J, and Dauksevicius R, J Sound Vib 329 (2010) 4866.
Babitsky V I, Mitrofanov A V, and Silberschmidt V V, Ultrasonics 42 (2004) 81.
Tawakoli T, and Azarhoushang B, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48, (2008) 1585.
Zhong Z W, and Lin G, Mater Manuf Process 20 (2005) 27.
Babitsky V I, Kalashnikov A N, Meadows A, and Wijesundara A A P, J Mater Process Technol 132 (2003) 157.
Nath C, and Rahman M, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48 (2008) 965.
Moriwaki T, and Shamoto E, CIRP Ann 40, (1991) 59.
Babitsky V I, Astashev V K, and Meadows A, J Sound Vib 308, (2007) 805.
Zhang Z, and Babitsky V I, J Sound Vib 330 (2011) 2124.
Aurich J C, Dornfeld D, Arrazola P J, Franke V, Leitz L, and Min S, CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58 (2009) 519.
ASTM Handbook, Tests for Chemical, Physical, and Optical Properties, Vol 6, ASTM, Materials Park (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarvi Hampa, P., Razfar, M.R., Malaki, M. et al. The Role of Dry Aero-acoustical Lubrication and Material Softening in Ultrasonically Assisted Milling of Difficult-to-Cut AISI 304 Steels. Trans Indian Inst Met 68, 43–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0429-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-014-0429-0