Abstract
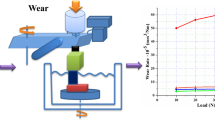
Titanium alloys are extensively used in various fields of engineering, medicine, aerospace, marine due to their excellent mechanical properties. Their usage is more pronounced today in the field of biomedical implants due to superior biocompatibility, corrosive resistance and high strength. However, titanium alloys have poor wear resistance due to high coefficient of friction. Poor abrasive wear resistance results in the formation of wear debris at the implant area causing toxicity, inflammation and pain. Surface treatment of the implant alloy through heat treatment, application of protective coatings and introduction of compressive residual stresses by shotpeening are some of the methods to mitigate wear of the implant alloy. In this work Ti–6Al–4V implant alloy is treated under various conditions of heat treatment and shotpeening operations on a pin on disc wear testing machine. Scanning electron micrograph along with energy dispersive spectrometry analysis is done to authenticate the experimental results obtained during the wear testing procedure.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Chu P K, and Ding C, Mater Sci Eng (R) 47 (2004) 49.
Boehlart C J, Cowen C J, Quast J P, Akahori T, and Niinomi M, Mater Sci Eng (C) 28 (2008) 323.
Thomann U I, and Uggowitzer P J, J Wear 239 (2000) 48.
Niinomi M, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 1 (2008) 30.
Balazic M, Kopac J, Jackson M J, and Ahmed W, Int J Nano Biomater 1 (2007) 3.
Rack H J, and Qazi J I, Mater Sci Eng C 26 (2006) 1277.
Yongqing F, Loh N l, and Batchelor A W, J Surf Coat Technol 106 (1998) 193.
Molinari A, Straffelini G, Tesi B, and Bacci T, J Wear 208 (1997) 105.
Alam M O, and Haseeb A S M A, J Tribol Int 35 (2002) 357.
Li S J, Yang R, and Li S, J Wear 257 (2004) 869.
Majumdar P, Singh S B, and Chakraborty M, J Wear 264 (2008) 1015.
Gispert M P, Serro A P, Colaco R, and Botelho Do Rego AM, J Wear 262 (2007) 1337.
Leyens C, and Peters M, Titanium and Titanium alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, Wiley, New York (2003), Chap. 1, p 13.
Guleryuz H, and Cimenglu H. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.04.024 (in press).
Jha A K, Singh S K, and Kiranmayee M S, J Eng Fail Anal 17 (2010) 1457.
Mohammadi Z, Ziaei-Moayyed A A, and Shekh-Mehdi Mesgar A, J Mater Process Technol 194 (2007) 15.
Aparicio C, Gil F J, Fonseca C, Barbosa M, and Planell J A, Biomaterials 24 (2003) 263.
Lee B-H, Lee C, Kim D-G, Choi K, Lee K H, and Kim Y D, Mater Sci Eng C 28 (2008) 1448.
Suh N P, J wear 25 (1974) 111.
Wang S Q, Wei M X, Wang F, and Zhao Y T, Tribol Int, 43 (2010) 577.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesh, B.K.C., Ramanaih, N. & Chandrasekhar Rao, P.V. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Ti–6Al–4V Implant Alloy Subjected to Various Surface Treatments. Trans Indian Inst Met 65, 425–434 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-012-0147-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-012-0147-4