Abstract
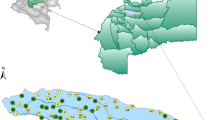
To provide a contribution to the Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection, here we present the results of a study focused on the potentially toxic elements (PTE) content in agricultural soils’ representative for the Mediterranean region. To reach this aim, samples of 22 Italian (NE Peloritani Mountains, Sicily) and 18 Turkish (Amik Plain, Hatay) soils were collected and analyzed to evaluate their PTE content. The Italian and Turkish sites have been selected because they represent very important cultivation zones. In Amik Plain (Turkey), the dominant crops consist of cotton, wheat, corn and olives, whereas in NE Peloritani Mountains, Sicily (Italy), an appreciate citrus variety, known as the “Interdonato lemon”, guaranteed by Protected Geographical Indication label, is produced. The collected results include: (1) the assessment of PTE levels in soils; (2) the identification of the PTE sources; (3) the relationships between PTE contents and soil properties (pH, electrical conductivity, organic matter, CaCO3, and clay). Several multivariate statistical methods such as correlation matrix, cluster analysis and main component analysis were applied to individuate the anthropogenic vs natural origin of the PTE sources. The detected PTE levels are in decreasing order Mn > Zn > V > Cr > Cu > Ni > As > Pb > Co > Sb > Se > Cd for the Italian soils, and Mn > Ni > V > Zn > Cr > Cu > Pb > Co > As > Se > Sb > Cd for the Turkish soils. The overall obtained results allowed to define: (a) a main lithogenic source for PTE detected in the Italian soils, except for Zn which origin is also associated to anthropogenic input; (b) a lithogenic origin for all of the PTE detected for the Turkish soils, with an associate anthropogenic contribution for Cr, Ni, V, Cu and V. The results obtained in this work enhance the knowledge in the individuation of PTE pollution sources in agricultural soils of the European Mediterranean region.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
(2020) http://www2.ct.ingv.it/it/banca-dati-delle-eruzioni/eruzioni-etna.html
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Sarzanini C, Petrella F (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils from Piedmont, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment. Chemosphere 49:545–557
Acosta JA, Faz A, Kalbitz K, Jansen B, Martínez-Martínez S (2014) Partitioning of heavy metals over different chemical fraction in street dust of Murcia (Spain) as a basis for risk assessment. J Geochem Explor 144:298–305
Ağca N, Özdel E (2013) Assessment of spatial distribution and possible sources of heavy metals in the soils of Sariseki-Dörtyol District in Hatay Province (Turkey). Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2507-8
Agricole I, Forestali E (1999) Decreto Ministeriale del 13/09/1999 Approvazione dei “Metodi ufficiali di analisi chimica del suolo”, emanato/a dal Ministro per le Politiche Agricole e pubblicato sulla Gazz. Uff. Suppl. Ordin. n° 248 del 21/10/1999
Almeida-Silva M, Almeida SM, Freitas MC, Pio CA, Nunes T, Cardoso J (2013) Impact of sahara dust transport on cape verde atmospheric element particles. J Toxicol Environ Health A 76(4–5):240–251
Andrejkovičová S, Sudagar A, Rocha J, Patinha C, Hajjaji W, da Silva EF, Velosa A, Rocha F (2016) The effect of natural zeolite on microstructure, mechanical and heavy metals adsorption properties of metakaolin based geopolymers. Appl Clay Sci 126:141–152
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Boersch J, Frohne T, Du Laing G, Rinklebe J (2017a) Bioavailability and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in garden edible vegetables and soils around a highly contaminated former mining area in Germany. J Environ Manag 186:192–200
Antoniadis V, Levizou E, Shaheen SM, Ok YS, Sebastian A, Baum C, Prasad MNV, Wenzel WW, Rinklebe J (2017b) Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation—a review. Earth Sci Rev 171:621–645
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Tsadilas CD, Selim M, Rinklebe J (2018) Zinc sorption by different soils as affected by selective removal of carbonates and hydrous oxides. Appl Geochem 88:49–58
Biasioli M, Grcman H, Kralj T, Madrid F, Dıaz-Barrientos E, Ajmone-Marsan F (2006) Potentially toxic elements contamination in urban soils: a comparison of three European cities. J Environ Qual 36(1):70–79
Blaha U, Sapkota B, Appel E, Stanjek H, Rösler W (2008) Micro-scale grain-size analysis and magnetic properties of coal-fired power plant fly ash and its relevance for environmental magnetic pollution studies. Atmos Environ 42(36):8359–8370
Bonardi G, Giunta G, Liguori V, Perrone V, Rosso M, Zuppetta A. Schema Geologico Dei Monti Peloritani ELORITANI. Boll Soc Geol Ital Ital.; DA. 1976 Paru 1977; Vol. 95; No 1-2; pp. 49–74; H.T. 1; BIBL. 2 P. 1/2; 4 ILL
Bonardi G, Compagnoni R, Del Moro A, Macaione E, Messina A (2008) Perrone V (2008) Rb-Sr age constraints on the Alpine metamorphic overprint in the Aspromonte Nappe (Calabria-Peloritani Composite Terrane, southern Italy). Boll Soc Geol Ital (Ital J Geosci) 127(2):173–190
Brussaard L, De Ruiter PC, Brown GG (2007) Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agric Ecosyst Environ 121:233–244
Carbone S, Messina A, Lentini F (2008) Note Illustrative della Carta Geologica d’Italia alla Scala 1:50.000. Foglio 601 Messina-Reggio di Calabria-Servizio Geologico d’Italia—APAT, 1–179. S.EL.CA., Florence
Carbone S, Messina A, Lentini F, Macaione E (2011) Note illustrative della Carta Geologica d’Italia alla scala 1:50,000. Foglio 587-600 Milazzo-Barcellona P.G. ISPRA, 1–262. S.EL.CA., Florence, Italy
Cosenza A, Lima A, Ayuso RA, Foley NK, Albanese S, Messina A, De Vivo B (2015) Soil geochemical survey of abandoned mining sites in the Eastern-Central Peloritani Mountains, Sicily, Italy. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 15:361–372. https://doi.org/10.1144/geochem2014-307
Dongarrà G, Manno E, Sabatino G, Varrica D (2009) Geochemical characteristics of waters in mineralised area of Peloritani Mountains (Sicily, Italy). Appl Geochem 24(2009):900–914
Doran JW, Zeiss MR (2000) Soil health and sustainability: managing the biotic component of soil quality. Appl Soil Ecol 15:3–11
Dragović S, Mihailović N, Gajić B (2008) Heavy metals in soils: distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and radionuclides and multivariate assessment of contamination sources. Chemosphere 72(3):491–495
Dung TTT, Cappuyns V, Swennen R, Phung NK (2013) From geochemical background determination to pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments and soils. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12:335–353
EC (2006) Communication of 16 April 2002 from the Commission to the Council, the European Parliament, the Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Towards a Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection. European Commission (EC), Brussels
Edelstein M, Ben-Hur M (2018) Heavy metals and metalloids: sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci Hortic 234:431–444
Franco-Uría A, López-Mateo C, Roca E, Fernández-Marcos ML (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):1008–1015
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Field A (2009) Discovering Statistics Using SPSS. Sage, Newcastle Upon Tyne
Gün M, Erdem AM (2003) Agricultural master plan of Hatay. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs-Agricultural Directorate of Hatay (in Turkish)
Gürel S, Başar H (2014) Metal status of olive trees grown in southeastern Marmara Region of Turkey. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45(11):1464–1479
Italiano F, Yuce G, Di Bella M, Rojay B, Sabatino G, Tripodo A, Martelli M, Rizzo A, Misseri M (2017) Noble gases and rock geochemistry of alkaline intraplate volcanics from the Amik and Ceyhan-Osmaniye areas, SE Turkey. Chem Geol 469:34–46
Ji Y, Feng Y, Wu J, Zhu T, Bai Z, Duan C (2008) Using geoaccumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. J Environ Sci 20(5):571–578
Jing Y, O’Connor D, Sik Ok Y, Tsang DCW, Loud LA, Hoya D (2019) Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Int 124:320–328
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Karaoğlan F, Parlak O, Klötzli U, Koller F, Rızaoğlu T (2013) Age and duration of intra-oceanic arc volcanism built on a suprasubduction zone type oceanic crust in southern Neotethys, SE Anatolia. Geosci Front 4(4):399–408
Kelepertzis E (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 221–222:82–90
Kibblewhite MG, Ritz K, Swift MJ (2008) Soil health in agricultural systems. Phil Trans R Soc B 363:685–701
Kılıç Ş (2011) Agroecological land use potential of Amik Plain, Turkey. Turk J Agric For 35(2011):433–442. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1007-940
Kozak M, Scaman CH (2008) Unsupervised classification methods in food sciences: discussion and outlook. J Sci Food Agric 88:1115–1127
Lado LR, Hengl Hannes T, Reutera I (2008) Heavy metals in European soils: a geostatistical analysis of the FOREGS geochemical database. Geoderma 148(15):189–199
Lim HS, Lee JS, Chon HT, Sager M (2008) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. J Geochem Explor 96(2–3):223–230
Mackintosh PW, Robertson AHF (2012) Sedimentary and structural evidence for two-phase Upper Cretaceous and Eocene emplacement of the Tauride thrust sheets in central southern Turkey. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 372:299–322
Micó C, Peris M, Sánchez J, Recatalá L (2006a) Heavy metal content of agricultural soils in a Mediterranean semiarid area: the Segura River Valley (Alicante, Spain). Span J Agric Res 4(4):363–372
Micó C, Peris M, Recatalá L, Sánchez J (2006b) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of a European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65(5):863–872
Micó C, Peris M, Sánchez J, Recatalá L (2008) Trace element analysis via open-vessel or microwave-assisted digestion in calcareous mediterranean soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39(5–6):890–904
Ministero delle politiche agricole alimentari e forestali DIPARTIMENTO DELLE POLITICHE COMPETITIVE, DELLA QUALITA’ AGROALIMENTARE, IPPICHE E DELLA PESCA DIREZIONE GENERALE PER LA PROMOZIONE DELLA QUALITÀ AGROALIMENTARE E DELL’IPPICA PQAI IV. Disciplinare di produzione della indicazione geografica protetta “Limone Interdonato Messina” (2013).
Odabasi M, Bayram A, Elbir T, Seyfioglu R, Dumanoglu Y, Ornektekin S (2010) Investigation of soil concentrations of persistent organic pollutants, trace elements, and anions due to iron-steel plant emissions in an industrial region in Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut 213:375–388
Özer E, Koç H, Özsayar TY (2004) Stratigraphical evidence for thedepression of the northern margin of the Menderes-Tauride Block (Turkey) during the Late Cretaceous. J Asian Earth Sci 22(5):401–412
Parlak O, Höck V, Kozlu H, Delaloye M (2004) Oceanic crust generation in an island arc tectonic setting, SE Anatolian orogenic belt (Turkey). Geol Mag 141(5):583–603
Parlak O, Rizaoglu T, Bagci U, Karaoglan F, Höck V (2009) Tectonic significance of the geochemistry and petrology of ophiolites in southeast Anatolia, Turkey. Tectonophysics 473:173–187
Pinto M, Silva E, Silva M, Melo-Gonçalves P, Candeias C (2014) Environmental risk assessment based on high-resolution spatial maps of potentially toxic elements sampled on stream sediments of Santiago. Cape Verde. Geosciences 4(4):297–315
Pinto MMSC, da Silva EF, Silva MMVG, Melo-Gonçalves P (2015) Heavy metals of Santiago Island (Cape Verde) top soils: estimated background value maps and environmental risk assessment. J Afr Earth Sci 101:162–176
Pinto MMSC, Silva MMVG, da Silva EAF, Dinis PA, Rocha F (2017) Transfer processes of potentially toxic elements (PTE) from rocks to soils and the origin of PTE in soils: a case study on the island of Santiago (Cape Verde). J Geochem Explor 183:140–151
Qu M, Chen J, Huang B, Zhao Y (2020) Enhancing apportionment of the point and diffuse sources of soil heavy metals using robust geostatistics and robust spatial receptor model with categorical soil-type data. Environ Pollut 265(A):114964
Ravindran J, Pankajshan M, Puthur S (2016) Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip Toxicol 9(3–4):90–100
Rinklebe J, Shaheen SM (2017) Redox chemistry of nickel in soils and sediment: a review. Chemosphere 179:265–278
Rinklebe J, Vasileios A, Shaheen SM, Rosche O, Altermann M (2019) Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Environ Int 126:76–88
Roozbahani M, Sobhanardakani S, Karimi H, Sorooshnia R (2015) Natural and anthropogenic source of heavy metals pollution in the soil samples of an industrial complex; a case study. Iran J Toxicol 9(29):1336–1341
Saccà C, Saccà D, Nucera P, Somma R (2003) Gold-bearing polymetallic ferous mineralization in the Central Peloritani Mts (NE Sicily, Italy). Boll Soc Geol Ital 122(2003):503–509
Sdiri A, Higashi T, Chaabouni R, Jamoussi F (2012) Competitive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by montmorillonitic and calcareous clays. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(3):1191–1204
Sengör AMC, Yilmaz Y (1981) Tethyan evolution of Turkey: a plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 75:181–241
Setälä H, Berg MP, Jones TH (2005) Trophic structure and functional redundancy in soil communities. In: Bardgett RD, Usher M, Hopkins D (eds) Biological diversity and function in soils. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 236–249
Shan Y, Tysklind M, Hao F, Ouyang W, Chen S, Lin C (2013) Identification of sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils using multivariate analysis and GIS. J Soils Sediments 13(4):720–729
Six L, Smolders E (2014) Future trends in soil cadmium concentration under current cadmium fluxes to European agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 485–486:319–328
Smolders E (2013) Revisiting and updating the effect of phosphorus fertilizers on cadmium accumulation in European agricultural soils. In: International Fertiliser Society. Leek, Windsor, UK on 23rd May. Volume 724 di proceedings (International Fertiliser Society), International Fertiliser Society, ISSN 1466-1314, pp 32
Tavazzi S, Locoro G, Comero S, Sobiecka E, Loos R, Gans O, Ghiani M, Umlauf G, Suurkuusk G, Paracchini B (2012) Occurrence and levels of selected compounds in European Sewage Sludge Samples. JRC Scientific and Policy report. Results of a Pan-European Screening Exercise (FATE SEES)
Ullah Z, Naz A, Saddique U, Khan A, Shah W, Muhammad S (2017) Potentially toxic elements concentrations and human health risk assessment of food crops in Bajaur Agency, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 76:482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6824-1
Varrica D, Tamburo E, Milia N, Vallascas E, Cortimiglia V, De Giudici G, Dongarrà G, Sanna E, Monna F, Losno R (2014) Metals and metalloids in hair samples of children living near the abandoned mine sites of Sulcis-Inglesiente (Sardinia, Italy). Environ Res 134(Suppl. C):366–374
Weissengruber L, Möller K, Puschenreiter M (2018) Long-term soil accumulation of potentially toxic elements and selected oranic pollutants through application of recycled phosphorus fertilizers for organic farming conditions. Nutr Cycle Agroecosyst 110:427–449
Wellnitz T, Poff NL (2001) Functional redundancy in heterogeneous environments: implications for conservation. Ecol Lett 4(3):177–179
World Health Organization (2001) Arsenic and arsenic compounds Environmental Health Criteria 224. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int Sch Res Netw ISRN Ecol 2011, Article ID 402647, 20. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/402647
Xu Z, Mi W, Mi N, Fan X, Zhou Y, Tian Y (2020) Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in desert steppe soil related to transportation and industrial activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09877-9
Yuce G (2018) Determination of fault activity and geothermal origin by soil and groundwater degassing: The extension of Dead Sea Fault Zone (DSFZ) in the Amik Basin (Hatay) and its relation with Karasu Fault Zone and origin of thermal waters in Amik Basin, Final report of the TUBITAK-COST Research Project in the frame of COST Action, Project No: 111Y090, 2012–2015
Yuce G, Pinarbasi A, Ozcelik S, Ugurluoglu D (2005) Soil and water pollution derived from anthropogenic activities in the Porsuk River Basin, Turkey. Environ Geol 49:359–375
Yuce G, Italiano F, D’Alessandro W, Yalcin TH, Yasin DU, Gulbay AH, Ozyurt NN, Rojay B, Karabacak V, Bellomo S, Brusca L, Yang T, Fu CC, Lai CW, Ozacar A, Walia V (2014) Origin and interactions of fluids circulating over the Amik Basin (Hatay-Turkey) and relationships with the hydrologic, geologic and tectonic settings. Chem Geol 38:23–39
Acknowledgements
Turkish side of this study was supported by TUBITAK project No 111Y090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mottese, A.F., Sabatino, G., Di Bella, M. et al. Environmental screening for the assessment of potentially toxic elements content in PGI soils from the Mediterranean region (Italy and Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 79, 499 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09245-3