Abstract
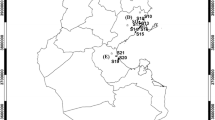
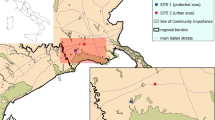
To evaluate the influence of soil contamination on the distribution of terrestrial isopods, species richness, relative abundance, and diversity, various indices were studied in 20 sampling sites from five industrial areas located in Sfax (SE Tunisia). The following hypotheses were tested: (1) is isopod diversity affected by soil properties? (2) What are the environmental factors that influence the isopod distribution? A total of 445 individuals were sampled and eight species of terrestrial isopods were identified. Porcellionides pruinosus was the most abundant species (38%); however, the highest specific richness per area was equal to four species. To evaluate the impact of metal contamination on isopod distribution, cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and iron (Fe) concentrations were measured in soils and terrestrial isopods. Moreover, multivariate analyses revealed a negative correlation between heavy metal concentrations and ecological parameters suggesting an impact of the contamination degree on biodiversity. In addition, to characterize the heavy metal accumulation in isopods, the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) was determined and revealed that Cu and Zn were the most accumulated elements. Results showed that for all species, the order of the BAF values is as follows: Cu ≫ Zn ≫ Cd > Pb > Fe. On the contrary, all species seemed to be deconcentrators of Fe and Cd, with some exceptions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andre J, Stürzenbaum SR, Kille P, Morgan AJ, Hodson ME (2010) Metal bioaccumulation and cellular fractionation in an epigeic earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus): the interactive influences of population exposure histories, sitespecific geochemistry and mitochondrial genotype. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1566–1573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.05.029
Arnold RE, Hodson ME, Langdon CJ (2008) A Cu tolerant population of the earthworm Dendrodrilus rubidus (Savigny, 1862) at Coniston Copper Mines, UK. Environ Pollut 152:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.048
Becquer T, Dai J, Quantin C, Lavelle P (2005) Sources of bioavailable heavy metals for earthworms from a Zn-, Pb- and Cd-contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1564–1568
Ben Ouaghrem S (2014) Impact des rejets industriels sur la biodiversité de l’isopodofaune dans la région de Sfax. Université de Tunis El Manar, Mastère
Bonaventura J, Bonaventura C (1980) Haemocyanins: relationships in their structure, function and assembly. Amer Zool 20:7–17
Cao X, Ma LQ, Chen M, Hardison DW, Harris WG (2003) Lead transformation and distribution in the soils of shooting ranges in Florida, USA. Sci Total Environ 307:179–189
Chandrasekaran A, Ravisankar R, Harikrishnan N, Satapathy KK, Prasad MVR, Kanagasabapathy KV (2015) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metal concentration in soils of Yelagiri Hills, Tamilnadu, India-Spectroscopical approach, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A J Mol Biomol Spectrosc 137:589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.08.093
Charfi-Cheikhrouha F (2003) Genetic diversity in the mitochondrial 16S rDNA among five populations of Armadillidium pelagicum (Isopoda, Oniscidea). In: Sfenthourakis S, Araujo PB, Hornung E, Schmalfuss H, Taiti S, Szlávecz K (eds) The biology of terrestrial isopods, V. Crustaceana monographs. Brill, Leiden, pp 365–380
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1994) Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, Plymouth
Cortet J, Vaufleury AG, Balanguer NP, Gomot L, Texier C, Cluzeau D (1999) The use of invertebrate soil fauna in monitoring pollutants effects. Eur J Soil Biol 35:115–34
Dallinger R (1993) Strategies of metal detoxification in terrestrial invertebrate. In: Dallinger RAR, Rainbow PS (eds) Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 245–290
Dallinger R, Berger B, Birkel S (1992) Terrestrial isopods: Useful biological indicators of urban metal pollution. Oecologia 89:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319012
De Matos AT, Fontes MPF, Da Costa LM, Martinez MA (2001) Mobility of heavy metals as related to soil chemical and mineralogical characteristics of Brazilian soils. Environ Pollut 111:420–435
Dong JH, Yu M, Bian ZF, Wang Y, Di C (2011) Geostatistical analyses of heavy metal distribution in reclaimed mine land in Xuzhou, China. Environ Earth Sci 62:127–37
Eijsackers H (1987) The impact of heavy metals on terrestrial ecosystems: biological adaptation through behavioural and physiological avoidance. In: Ravera O (ed) Ecological assessment of environmental degradation, pollution and recovery. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, Amsterdam, pp 245–259
El Zrelli R, Courjault-Radé P, Rabaoui L, Castet S, Michel S, Bejaoui N (2015) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of the coastal area surrounding the industrial complex of Gabes City, Gulf of Gabes, SE Tunisia. Mar Pollut Bull 101:922–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.047
El Zrelli R, Courjault-Radé P, Rabaoui L, Daghbouj N, Mansour L, Balti R, Castet S, Attia F, Michel S, Bejaoui N (2017) Biomonitoring of coastal pollution in the Gulf of Gabes (SE, Tunisia): use of Posidonia oceanica seagrass as a bioindicator and its mat as an archive of coastal metallic contamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:22214–22225
Ferreira NGC, Cardoso DN, Morgado R, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2015) Long-term exposure of the isopod Porcellionides pruinosus to nickel: costs in the energy budget and detoxification enzymes. Chemosphere 135:354–362
Gàl J, Markiewicz PJ, Hursthouse A, Tatner P (2008) Metal uptake by woodlice in urban soils. Ecotox Environ Safe 69:139–149
Gasmi M (2006) La répartition des établissements industriels a` Sfax: un schéma radio-concentrique. Les partis politiques dans les pays arabes, Tome 2, le Maghreb, pp 245–278. http://remmm.revues.org/2879
Ghannem S, Khazri A, Sellami B, Boumaiza M (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and Chlaenius (Chlaeniellus) olivieri (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the vicinity of a textile factory near Ras Jbel (Bizerte, Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 75:442
Ghannem S, Touaylia S, Bejaoui M (2018) Assessment of trace metals contamination in soil, leaf litter and leaf beetles (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) in the vicinity of a metallurgical factory near Menzel Bourguiba (Tunisia). Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1405338
Ghemari C, Waterlot C, Leclercq J, Douay F, Nasri-Ammar K (2014) Metal bioaccumulation in Porcellio laevis and Porcellionides pruinosus from Tunisian contaminated sites. In: Proceeding of the 9th ISTIB (International Symposium in Terrestrial Isopods Biology, Poitiers, 26–30 June)
Ghemari C, Waterlot C, Ayari A, Leclercq J, Douay F, Nasri-Ammar K (2017) Assessment of heavy metals in soil and terrestrial isopod Porcellio laevis in Tunisian industrialized areas. Environ Earth Sci 76:6–23
Harmsen J (2007) Measuring bioavailability: from a scientific approach to standard methods. J Environ Qual 36:1420–1428. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2006.0492
Heikens A, Peijnenburg WJGM, Hendriks AJ (2001) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Pollut 113:385–393
Henin S (1983) Les éléments traces dans le sol. Science du Sol 2:67–71
Hobbelen PHF, Koolhaas JE, van Gestel CAM (2006) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa in relation to total and available metal concentrations in field soils. Environ Pollut 144:639–646
Hoese B (1981) Morphologie und Funktion des Wasserleitungs systems der terrestrischen Isopoden [Crustacea, Isopoda, Oniscoidea]. Zoomorphology 98:135–167
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Elsevier Applied Science, Barking
Hopkin S, Martin MH (1982a) The distribution of zinc, cadmium, lead and cooper within the woodlouse Oniscus asellus (Crustacea, Isopoda). Oecologia 54:227–232
Hopkin S, Martin MH (1982b) The distribution of zinc, cadmium, lead and cooper within the hepatopancreas of woodlouse. Tissue Cell 17:703–715
Hopkin SP, Martin MH (1984) Heavy metals in woodlice. Symp Zool Soc Lond 53:143–166
Hopkin SP, Martin MH (1985) Assimilation of zinc, cadmium, lead, copper, and iron by the spider Dysdera crocata, a predator of woodlice. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 34:183–187
Hopkin SP, Hardisty GN, Martin MH (1986) The woodlouse Porcellio scaber as a ‘biological indicator’ of zinc, cadmium, lead and copper pollution. Environ Pollut B 11:271–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0143-148X(86)90045-5
Hussein MA, Obuid-Allah AH, Mohammad AH, Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Abd El-Wakeil KF (2006) Seasonal variation in heavy metal accumulation in subtropical population of the terrestrial isopod, Porcellio laevis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:168–174
Janssen RPT, Peijnenburg WJGM, Posthuma L, Van Den Hoop AGT (1997) Equilibrium partitioning of heavy metals in Dutch field soils. I. Relationship between metal partition coefficients and soil characteristics. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:2470–2478
Khemaissia H, Jelassi R, Touihri M, Souty-Grosset C, Nasri-Ammar K (2016) Diversity of terrestrial isopods in the Northern Tunisian Wetlands. Afr J Ecol 55(2):176–187
Kontas A (2007) Trace metals (Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn, Fe) contamination in marine sediment and zooplankton samples from Izmir Bay (Aegean Sea, Turkey). Water Air Soil Pollut 188:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9547-1
Krásný J, Sharp JM (2007) Groundwater in fractured rocks: IAH selected paper series, vol 9, ISBN 9780415414425
Khlifi R, Olmedo P, Fernando G, Feki-Tounsi M, Hammami B, Rebai A, Hamza-Chaffai A (2014) Biomonitoring of cadmium, chromium, nickel and arsenic in general population living near mining and active industrial areas in Southern Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 186:761–779
Laskowski R (1991) Are the top carnivores endangered by heavy metal biomagnification? Oikos 60:387–390
Liao D, Zheng W, Li X, Yang Q, Yue X, Guo L, Zeng G (2010) Removal of lead (II) from aqueous solutions using carbonate hydroxyapatite extracted from eggshell waste. J Hazard Mater 177:126–130
Loureiro S, Amorim MJB, Campos B, Rodrigues SMG, Soares AMVM (2009) Assessing joint toxicity of chemicals in Enchytraeus albidus (Enchytraeidae) and Porcellionides pruinosus (Isopoda) using avoidance behaviour as an endpoint. Environ Pollut 157:625–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.08.010
Loureiro S, Sampaio A, Brandão A, Nogueira AJ, Soares AM (2006) Feeding behaviour of the terrestrial isopod Porcellionides pruinosus Brandt, 1833 (Crustacea, Isopoda) in response to changes in food quality and contamination. Sci Total Environ 369:119–128
Maerz JC, Karuzas JM, Madison DM, Blossey B (2005) Introduced invertebrates are important prey for a generalist predator. Divers Distrib 11:83–90
Mazzei V, Longo G, Brundo MV, Copat C, Oliveri Conti G, Ferrante M (2014) Bioaccumulation of cadmium and lead and its effects on hepatopancreas morphology in three terrestrial isopod Crustacean species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:269–279
Nahmani J, Lavelle P (2002) Effects of heavy metal pollution on soil macrofauna in a grassland of Northern France. Eur J Soil Biol 38:297–300
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:402–424
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. American Soc. of Agronomy, Wisconsin, pp 539–579
Nico MVS, Ruslan OB, Andrei DP, Andrei SZ, Verhoef SC (2001) Metal concentrations in soil and invertebrates in the vicinity of a metallurgical factory near Tula (Russia). Pedobiologia 45:451–466
Ouni A (2015) Impacts des métaux lourds sur les réponses physiologiques et comportementales de deux Oniscoïdes: Armadillo officinalis et Porcellionides pruinosus. Université de Tunis El Manar, Mastère
Peijnenburg WJGM, Posthuma L, Eijsackers HJP, Allen HE (1997) A conceptual framework for implementation of bioavailability of metals for environmental management purposes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 37:163–172
Petra DBF, David JS, Gabriele B, Claus S, Peter KH, Nisha P, Hege ES, Jason MW (2004) Metal effects on soil invertebrate feeding: measurements using the bait lamina method. Ecotoxicology 13:807–816
Rabaoui L, Balti R, El Zrelli R, Tlig-Zouari S (2014) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the gulf of Gabes (Tunisia) using four mollusc species. Mediterr Mar Sci 15(1):45–58
Raczuk J, Pokora A (2008) Influence of traffic pollution on heavy metal contentin soil and earthworms (Lumbricidae). Ecol Chem Engineer A 15:265–274
Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA, Musibono DE, Chapman A (2000) The transfer of lead (Pb) from earthworms to shrews (Myosorex varius). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:392–397
Richard AF, Dennis JT (2011) Copper: an essential metal in biology. Curr Biol 21:877–883
Sallaku F, Fortuzi S, Tota O, Huji B, Chachalis D D, Darawsheh M (2009) Heavy metal soil contamination around the metallurgical plant of Elbasani in Albania. J Food Agric Environ 7(3–4):878–881
Sandifer RD (1996) The effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc contamination on arthropod communities in the vicinity of a primary smelting works. PhD thesis, University of Reading
Sipos P, Németh T, Mohai I (2005) Distribution and possible immobilization of lead in a forest soil (Luvisol) profile. Environ Geochem Health 27:1–10
Smit CE, Van Gestel CAM (1998) Effects of soil type, prepercolation, and ageing on bioaccumulation and toxicity of zinc for the springtail Folsomia candida. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1132–1141
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1996) Risk assessment of the threat of secondary poisoning by metals to predators of earthworms in the vicinity of a primary smelting works. Sci Total Environ 187:167–183
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1999) Seasonal variation in the abundance, biomass and biodiversity of earthworms in soils contaminated with metal emissions from a primary smelting works. J Appl Ecol 36:173–183
Stonard MD, Webb M (1976) Influence of dietary cadmium on the distribution of the essential metals copper, zinc and iron in tissues of the rat. Chem Biol Interact 15:349–366
Ter Meulen-Smidt GRB (1995) Regional differences in potentials for delayed mobilization of chemicals in Europe. In: Salomons W, Stigliani WN (eds) Biogeodynamics of pollutants in soils and sediments. Springer, Berlin, pp 135–169
Thakali S, Allen HE, Di-Toro DM, Ponizovsky AA, Rooney CP, Zhao FJ (2006) Terrestrial biotic ligand model. 2. Application to Ni and Cu toxicities to plants, invertebrates, and microbes in soil. Environ Sci Technol 40:7094–7100. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061173c
Tourinho PS, Van Gestel CAM, Jurkschat K, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2015) Effects of soil and dietary exposures to Ag nanoparticles and AgNO3 in the terrestrial isopod Porcellionides pruinosus. Environ Pollut 205:170–177
Tranvik L, Eijsackers H (1989) On the advantage of Folsomia fimetarioides over Isotomiella minor (Collembola) in a metal polluted soil. Oecologia 80:195–200
Van Gestel CAM, Rademaker MCJ, Van Straalen NM (1995) Capacity controlling parameters and their impact on metal toxicity in soil invertebrates. In: Salomons W, Stigliani WM (eds) Biogeodynamics of pollutants in soils and sediments. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–192
Vijver MG, van Gestel CA, Lanno RP, van Straalen NM, Peijnenburg JGM (2004) Internal metal sequestration and its ecotoxicological relevance, a review. Environ Sci Technol 38:4705–4712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es040354g
Waterlot C, Bidar G, Peldrêne A, Roussel H, Fourrier H, Douay F (2013) Contamination, fractionation and availability of metals in urban soils in the vicinity of former lead and zinc smelters, France. Pedosphere 23:143–159
Witzel B (2000) The influence of zinc on the uptake and loss of cadmium and lead in the woodlouse, Porcellio scaber (Isopoda, Oniscidea). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:43–53
Wolters V (2001) Biodiversity of animals its function. Eur J Soil Biol 37:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1164-5563(01)01088-3
Zaghden H, Kallel M, Louati A, Elleuch B, Oudot J, Saliot A (2005) Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Sfax coastal zone (Tunisia), Mediterranean Sea. Mar Pollut Bullet 50(11):1287–1294
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Research Laboratory of Biodiversity, Management and Conservation of Biological systems, University of Tunis El Manar, Faculty of Science of Tunis. We gratefully acknowledge the support of all members of the LGCgE (Yncréa Lille) regarding their considerable assistance in chemical analyses. The authors are grateful to Mrs. Abdelkefi Najoua (Translator/Interpreter) for proofreading the English of the manuscript and Mrs. Chebaane Sahar (Ph.D.) for designing the map.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouni, A., Ghemari, C., Ben Said, A. et al. Monitoring of heavy metal contamination in soils and terrestrial isopods sampled from the industrialized areas of Sfax (southeastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 78, 440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8432-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8432-8