Abstract
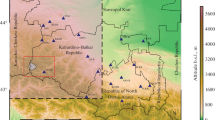
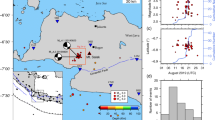
South Gujarat, a part of the northwestern Deccan Volcanic Province of India has been experiencing episodic swarm activity with reports of sounds, whose association remains unclear. After the Indian monsoon period, during the month of September 2016, a swarm activity occurred around the Keliya dam in the Navsari district of South Gujarat and nearby villages in the Dadra and Nagar Haveli (DNH), which continued for about 4 months. Again, the swarm activity recurred during the month of August 2017 and continued for about 5 months till January 2018. Many of these events were accompanied by audible sounds, like blasting, that caused severe panic among local occupants. A local network of four stations was installed to monitor the swarm activity, in addition to the Gujarat state seismic network. A total of 1048 earthquakes were located around the Keliya dam and 229 events in the DNH region from September 2016 to June 2018. In the present study, we performed a spectrogram analysis of the events with associated sounds. The analysis revealed significant energy at frequencies ≥ 20 Hz, in the audible frequency range. The relocated earthquake distribution shows that seismicity in the Navsari district follows a ~ NW–SE trend, confined to an area of 13 km × 2 km with a depth extent of 3 km. The trend is similar in the DNH region, confined to an area of 15 km × 2 km, down to a depth of 6 km. The determined focal mechanism in DNH region shows strike-slip faulting. The seismicity patterns seem to corroborate with the trends of the lineaments/dykes in the region. In general, the swarm-type earthquake sequences seem to occur when the annual rainfall exceeds the mean annual rainfall. We speculate that the present swarm activity, noticed with some delay after the Indian summer monsoon season, may be due to the phenomenon of hydro-seismicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya SN, Dattatrayam RS (2003) Some characteristics of recent earthquake sequences in peninsular India. Gondwana Geol Magz Spl 5:67–85
Bhattacharya SN, Karanth KV, Dattatrayam RS, Sohoni PS (2004) Earthquake sequence in and around Bhavnagar, Saurashtra, western India during August–December 2000 and associated tectonic features. Curr Sci 86(8):1165–1170
Biswas SK (1987) Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India. Tectonophysics 135:307–327
Biswas SK (2005) A review of structure and tectonics of Kachchh basin, western India, with special reference to earthquake. Curr Sci 88:1592–1600
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) (2002) Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structures (fifth revision, 39 pp
Chopra S, Rao KM, Sairam B, Kumar S, Gupta AK, Patel H, Gadhavi MS, Rastogi BK (2008) Earthquake swarm activities after rains in Peninsular India and a case study from Jamnagar. J Geol Soc India 72:245–252
Christiansen L, Hurwitz B, Ingebritsen SE (2007) Annual modulation of seismicity along the San Andreas Fault near Parkfield, CA. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL028634
Costain JK, Bollinger GA, Speer JA (1987) Hydroseismicity: a hypothesis for the role of water in the generation of intraplate seismicity. Seismol Res Lett 58:41–64
Ellsworth WL (2013) Injection-induced earthquakes. Science 341:1225942
Gahalaut K, Hassoup A (2012) Role of fluids in the earthquake occurrence around Aswan reservoir. Egypt J Geophys Res 117:B02303. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008796
Got JL, Fréchet J, Klein FW (1994) Deep fault plane geometry inferred from multiple relative relocation beneath the south flank of Kilauea. J Geophys Res 99:15375–15386
Griggs D (1967) Hydrolytic weakening of quartz and other silicates. Geophys J R Astron Soc 14:19–31
Hainzl S, Kraft T, Wassermann J, Igel H, Schemdes E (2006) Evidence for rainfall triggered earthquake activity. Geophys Res Lett 33:L19303
Hainzl S, Ben-Zion Y, Cattania C, Wassermann J (2013) Testing atmospheric and tidal earthquake triggering at Mt. Hochstaufen, Germany. J Geophys Res 118:5442–5452
Hainzl S, Aggarwal SK, Khan PK, Rastogi BK (2015) Monsoon-induced earthquake activity in Talala, Gujarat, India. Geophys J Int 200:627–637
Havskov J, Ottemoller L (2003) SEISAN: the earthquake analysis software for Windows, Solaris and Linux, version 8.0. Institute of Solid Earth Physics, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, pp 1–400
Heinicke J, Woith H, Alexandrakis CE, Buske S, Telesca L (2018) Can hydroseismicity explain recurring earthquake swarms in NW-Bohemia? Geophys J Int 212:p211–228
Joshi V, Chopra S, Mahesh P, Kumar S (2017) Joint modeling of velocity structure and hypocentral locations in the seismically active Kachchh, Saurashtra, and Narmada regions of Western India: an active intraplate region. Res Lett, Seismol. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220160203
Kanasewich ER (1981) Time sequence analysis in geophysics. The University of Alberta Press, Ed-monton
Kayal JR, Ram S, De R, Srirama BV, Gaonkar SG (2002) Aftershocks of the 26 January, 2001 Bhuj earthquake in western India and its seismotectonic implications. J Geol Soc India 59:395–417
Kolvankar VG (2001) Earthquake sequence of 1991 form Valsad region, Gujarat. Technical report, BARC/2001/E/006, BARC, Mumbai
Lacoss RT (1971) Data adaptive spectral analysis methods. Geophysics 36:661–675
Lienert BRE, Havskov J (1995) A computer program for locating earthquakes both locally and globally. Seismol Res Lett 66:26–36
Lin G, Shearer PM (2009) Evidence for water-filled cracks in earthquake source regions. Geophys Res Lett 36, L17315
Mahesh P, Gupta S (2016) The role of crystallized magma and crustal fluids in intraplate seismic activity in Talala region Saurashtra, Western India: an insight from local earthquake tomography. Tectonophysics 690:131–141
Merh SS (1995) Geology of Gujarat. J Geol Soc, India, p. 222
Muco B (1995) The seasonality of Albanian earthquakes and cross-correlation with rainfall. Phys Earth Planet Inter 88:285–291
Paige CC, Saunders MA (1982) LSQR: an algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least squares. ACM Trans Math Softw 8:43–71
Parotidis M, Rothert E, Shapiro SA (2003) Pore-pressure diffusion: a possible triggering mechanism for the earthquake swarms 2000 in Vogtland/NW-Bohemia, Central Europe. Geophys Res Lett 30:2075
Rajendran CP, Rajendran K (2001) Characteristics of deformation and past seismicity associated with the 1819 Kutch earthquake, north western India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 91:407–426
Rao DT, Jambusaria BB, Srivastava S, Srivastava NP, Hamid A, Desai BN, Srivastava HN (1991) Earthquake swarm activity in south Gujarat. Mausam 42:89–98
Rastogi BK (1992) Seismotectonics inferred from earthquakes and earthquake sequences in India during the 1980s. Curr Sci 62:101–108
Rastogi BK, Santosh K, Aggrawal SK (2012) Seismicity of Gujarat. Nat Hazards 65:1027–1044
Roberts RG, Christofferson A, Cassedy F (1989) Real time event detection, phase identification and source location using single station 3 component seismic data and a small PC. Geophys J Int 97:471–480
Saar MO, Manga M (2003) Seismicity induces by seasonal groundwater recharge at Mt. Hood, Oregon. Earth Planet Sci Lett 214:605–618
Singh AP, Mishra OP (2015) Seismological evidence for monsoon induced micro to moderate earthquake sequence beneath the 2011Talala, Saurashtra earthquake, Gujarat, India. Tectonophysics 661:38–48
Singh AP, Kumar MR, Kumar S, Sateesh A, Mahesh P, Shukla A, Talukdar R (2017) Seismicity and subterranean sounds in the northwest Deccan volcanic province of India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 107(3):1129–1135
Špičák A, Horálek J (2001) Possible role of fluids in the process of earthquake swarm generation in the West Bohemia/Vogtland seismoactive region. Tectonophysics 336(1/4):151–161
Srinagesh D, Chadha RK, Raju SP, Suresh G, Vijayaraghavan R, Sarma ANS, Shekhar M, Murty YVVBSN (2015) Seismicity studies in eastern Dharwar craton and neighbouring tectonic regions. Geol Soc India 85:419–430
Srivastava S and Rao DT (1997) Present status of seismicity of Gujarat. Vayu Mandal Jan–Jun, 27, 32–39
Stuart WD, Johnston MJS (1975) Intrusive origin of the Matsushiro earthquake swarm. Geology 3(2):63–67
Talwani P (1997) On the nature of reservoir-induced seismicity. Pure Appl Geophys 150:473–492
Talwani P (2014) Intraplate earthquakes. Cambridge University Press, New York. ISBN 9781139628921
Waldhauser F (2001) hypoDD-A program to compute double-difference hypocenter locations. U.S. Geol. Surv. Open File Rep. 01-113, 25 p
Waldhauser F, Ellsworth WL (2000) A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: method and application to the Northern Hayward fault, California. Bull Seismiol Soc Am 90:1353–1368
Zhao LS, Helmberger DV (1994) Source estimation from broadband regional seismograms. Bull Seismiol Soc Am 84:92–104
Zhu L, Helmberger DV (1996) Advancement in source estimation techniques using broadband regional seismograms. Bull Seismol Soc Am 86(5):1634–1641
Zoback MD, Harjes HP (1997) Injection-induced earthquakes and crustal stress at 9 km depth at the KTB deep drilling site, Germany. J Geophys Res 102:18477–18492
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the help of Ganpat Parmar, Mahesh Valekar and Bharat Mevada in the installation of seismic stations in South Gujarat and data analysis. The authors wish to thank Department of Science and Technology, Government of Gujarat for supporting the GSNet. All the figures were generated using Generic Mapping Tools v.4.5.0 (www.soest.hawaii.edu/gmt, last accessed December 2014). We are very thankful to the Editor-in-chief James W. LaMoreaux and two anonymous reviewers for constructive remarks, which greatly improved the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sateesh, A., Mahesh, P., Singh, A.P. et al. Are earthquake swarms in South Gujarat, northwestern Deccan Volcanic Province of India monsoon induced?. Environ Earth Sci 78, 381 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8382-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8382-1