Abstract
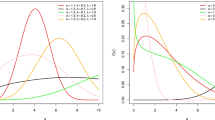
Information diffusion techniques and Monte Carlo methods have been widely used in solving all kinds of problems of small samples with incomplete data in the field of natural disaster risk assessment such as environmental resource rating, flood monitoring and temperature changing. Data are not the only thing that matters for natural disaster risk assessment, but with enough data, we can accurately predict the time, place, scale and loss of future disasters. It is important to simulate the complete data scene when there is a minimum sample size. In this paper, we collect temperature data from 3050 meteorological stations in China and use the Monte Carlo simulation method to investigate the effect of sample size on estimating the normal information diffusion. The results show that (1) for the same sample, the information diffusion method is significantly better than the traditional histogram method. (2) Using the hard histogram estimation method, the recommended sample size is 85 or more, which is slightly larger than the traditional threshold value (i.e., 30), while using the information diffusion estimation method, the recommended sample size decreases to 45 or more. (3) Simulation experiments show that, with insufficient samples, both estimation methods, i.e., the information diffusion and the traditional histogram methods become invalid because of its poor correlation, low robustness, high RMSE and variance values. These results indicate that the Monte Carlo simulation method and information diffusion technique have certain practical reference value in the research of natural disaster risk assessment in the case of a small sample.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ableidinger M, Buckwar E, Thalhammer A (2017) An importance sampling technique in Monte Carlo methods for SDEs with a.s. stable and mean-square unstable equilibrium. J Comput Appl Math 316:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2016.08.043. (Accepted 9 August 2016)
Andreotti E, Hult M, Marissens G, Lutter G, Garfagnini A, Hemmer S, von Sturm K (2014) Determination of dead-layer variation in HPGe detectors. Applied radiation isotopes 87:331–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.11.046. (Accepted 18 November 2013)
Bai C-Z, Zhang R, Hong M, Qian L-x, Wang Z (2015) A new information diffusion modelling technique based on vibrating string equation and its application in natural disaster risk assessment. Int J Gen Syst 44:601–614
Baio G, Copas A, Ambler G, Hargreaves J, Beard E, Omar RZ (2015) Sample size calculation for a stepped wedge trial. Trials 16:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081079.2014.980242. (Accepted 21 Oct 2014)
Bekker-Grob EWD, Donkers B, Jonker MF, Stolk EA (2015) Sample size requirements for discrete-choice experiments in healthcare: a practical guide. The patient. Patient Cent Outcomes Res 8:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40271-015-0118-z
Dehghani M, Saghafian B, Nasiri Saleh F, Farokhnia A, Noori R (2014) Uncertainty analysis of streamflow drought forecast using artificial neural networks and Monte-Carlo simulation. Int J Climatol 34:1169–1180, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258395784
Del Moral P, Doucet A, Jasra A (2011) An adaptive sequential Monte Carlo method for approximate Bayesian computation. Stat Comput 22:1009–1020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-011-9271-y. (Accepted 7 July 2017)
Dembkowski DJ, Willis DW, Wuellner MR (2012) Comparison of four types of sampling gears for estimating age-0 yellow perch density. J Freshw Ecol 27:587–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.2012.680932
Dornheim T, Groth S, Filinov A, Bonitz M (2015) Permutation blocking path integral Monte Carlo: a highly efficient approach to the simulation of strongly degenerate non-ideal fermions. New J Phys arXiv:1504.03859
Elanique A, Marzocchi O, Leone D, Hegenbart L, Breustedt B, Oufni L (2012) Dead layer thickness characterization of an HPGe detector by measurements and Monte Carlo simulations. Applied radiation and isotopes: including data, instrumentation and methods for use in agriculture. Ind Med 70:538–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.11.014. (Accepted 4 November 2011)
Engblom H, Heiberg E, Erlinge D, Jensen SE, Nordrehaug JE, Dubois-Rande JL, Halvorsen S, Hoffmann P, Koul S, Carlsson M et al (2016) Sample size in clinical cardioprotection trials using myocardial salvage index, infarct size, or biochemical markers as endpoint. J Am Heart Assoc 5:e002708. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.115.002708
Feng L, Luo G (2008) Flood risk analysis based on information diffusion theory. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 14:1330–1337. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030802494691. (Accepted 02 Feb 2008)
Gamboa F, Janon A, Klein T, Lagnoux A, Prieur C (2015) Statistical inference for Sobol pick-freeze Monte Carlo method. Statistics 50:881–902. https://doi.org/10.1080/02331888.2015.1105803. (Accepted 05 Oct 2015)
Gregory A, Graves (2004) A Monte Carlo simulation of biotic metrices as a function of subsample size. J Freshw Ecol 19(2):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.2004.9664532. (Accepted 12 Nov 2003)
Haar T, Kamleh W, Zanotti J, Nakamura Y (2017) Applying polynomial filtering to mass preconditioned hybrid Monte Carlo. Comput Phys Commun 215:113–127, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2017.02.020 (Get rights and content. Accepted 19 February 2017)
Hao L, Yang LZ, Gao JM (2014) The application of information diffusion technique in probabilistic analysis to grassland biological disasters risk. Ecol Model 272:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.10.014. Accepted 13 October 2013
Huang CF (2005) Risk assessment of natural disaster (theory and practice). Science Press, Beijing
Kazama K, Imada M, Kashiwagi K (2012) Characteristics of information diffusion in blogs, in relation to information source type. Neurocomputing 76:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.04.036
Kong LY, Tao YC, Liu J, Wu AH (2015) Study on integrated spatial database for composite urban disaster risk assessment. Appl Mech Mater 738–739:285–288. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.738-739.285
Levitan L, Wronski J (2013) Risk prediction model of LNG terminal station based on information diffusion theory. Procedia Engineering 52:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.02.106
Li Q, Zhou JZ, Liu DH, Jiang XW (2012) Research on flood risk analysis and evaluation method based on variable fuzzy sets and information diffusion. Saf Sci 50:1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2012.01.007. (Accepted 14 January 2012)
Li ZR, Lu TJ, Shi WH, Zhang XH (2013) Predicting the scale of information diffusion in social network services. J China Univ Posts Telecommun 20:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-8885(13)60239-3
Liang Z, Xu BY, Jia Y, Zhou B (2012) Mining evolutionary link strength for information diffusion modeling in online social networks. Appl Mech Mater 157–158:567–572
Lin S (2015) information diffusion and momentum in laboratory markets. J Behav Finance 16:357–372. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427560.2015.1095757
Maillé M-È, Saint-Charles J (2014) Fuelling an environmental conflict through information diffusion strategies. Environ Commun 8:305–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/17524032.2013.851099
Malterud K, Siersma VD, Guassora AD (2015) Sample size in qualitative interview studies: guided by information power. Qual Health Res 26:1753–1760, https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732315617444
Medhat ME, Abdel-hafiez A, Singh VP (2017) Optimization of fast neutron flux in an irradiator assembly using Monte Carlo simulations. Vacuum 138:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.01.026. (Accepted 24 January 2017)
Mundahl ND, Hunt AM (2011) Recovery of stream invertebrates after catastrophic flooding in southeastern Minnesota, USA. J Freshw Ecol 26:445–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.2011.596657. (Accepted 12 May 2011)
Myint SW, Yuan M, Cerveny RS, Giri4 C (2008) Categorizing natural disaster damage assessment using satellite-based geospatial techniques. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 8:707–719. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-8-707-2008
Nagata K, Shirayama S (2012) Method of analyzing the influence of network structure on information diffusion. Phys A 391:3783–3791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2012.02.031
Newhauser W, Fontenot J, Zheng Y, Polf J, Titt U, Koch N, Zhang X, Mohan R (2007) Monte Carlo simulations for configuring and testing an analytical proton dose-calculation algorithm. Phys Med Biol 52:4569–4584, https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/52/15/014/meta
Parsons M, Glavac S, Hastings P, Marshall G, McGregor J, McNeill J, Morley P, Reeve I, Stayner R (2016) Top-down assessment of disaster resilience: a conceptual framework using coping and adaptive capacities. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 19:1–11,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2016.07.005. (Accepted 19 July 2016)
Perneger TV, Courvoisier DS, Hudelson PM, Gayet-Ageron A (2015) Sample size for pre-tests of questionnaires. Qual Life Res 24:147–151, https://doi.org/10.1007/2Fs11136-014-0752-2
Schorr RA, Ellison LE, Lukacs PM (2014) Estimating sample size for landscape-scale mark-recapture studies of North American migratory tree bats. Acta Chiropterologica 16:231–239. https://doi.org/10.3161/150811014X683426
Shin JK (2009) Information accumulation system by inheritance and diffusion. Phys A 388:3593–3599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2009.05.032
Sun CZ, Zhang X (2008) Risk assessment of agricultural drought in Liaoning Province based on information diffusion. Syst Sci Compr Stud 24:507–510
Tang D-S, Hua Y-C, Cao B-Y (2016) Thermal wave propagation through nanofilms in ballistic-diffusive regime by Monte Carlo simulations. Int J Therm Sci 109:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2016.05.030. (Accepted 28 May 2016)
Vadapalli U, Srivastava RP, Vedanti N, Dimri VP (2014) Estimation of permeability of a sandstone reservoir by a fractal and Monte Carlo simulation approach: a case study. Nonlinear Process Geophys 21:9–18. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-21-9-2014. (Accepted: 12 Nov 2013)
Wang D, Sun S, Tse PW (2015a) A general sequential Monte Carlo method based optimal wavelet filter: a Bayesian approach for extracting bearing fault features. Mech Syst Signal Process 52–53:293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.07.005. (Accepted 7 July 2014)
Wang Y, Zhang J, Guo E, Sun Z (2015b) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation-based disaster risk assessment of desertification in Horqin Sand Land, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:1703–1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120201703. (Accepted: 22 January 2015)
Xu LF, Xu XG, Meng XW (2013) Risk assessment of soil erosion in different rainfall scenarios by RUSLE model coupled with information diffusion model: a case study of Bohai Rim. China Catena 100:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2012.08.012. (Accepted 24 August 2012)
Xue Y, Gencay R (2012) Hierarchical information and the rate of information diffusion. J Econ Dyn Control 36:1372–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jedc.2012.03.001. (Accepted 1 March 2012)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams; the key deployment project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant no. KZZD-EW-08-02); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41471148, 41771383, 41371495, 41501559); the key science and technology research of Jilin Province (20150204047SF); Science & Technology project for universities and for ‘twelfth five-year’ of Jilin province in 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that this study has no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, S., Wu, J. et al. Research of influence of sample size on normal information diffusion based on the Monte Carlo method: risk assessment for natural disasters. Environ Earth Sci 77, 480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7612-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7612-2