Abstract
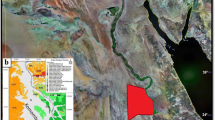
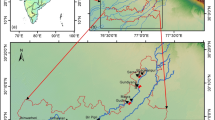
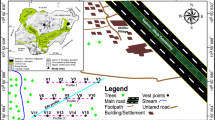
Aquifer overexploitation is a common problem in drinking water management. This will become more and more important given the general reduction of water resources. To overcome overexploitation, one of the most adopted solutions is the relocation of extraction wells. To establish the positions of new wells, a precise knowledge of the hydrogeological setting is required. Specific surveys are therefore necessary to obtain information over wide investigation zones. Geophysical methods, particularly electromagnetic and electrical, can be useful with this aim. In the present paper a case history on the combined use of Electric Resistivity Tomography and Time Domain Electromagnetic soundings is reported. Surveys have been performed within the Maggiore and Traversola Valleys, to investigate the uppermost part of the Quaternary deposits, hosting the near surface aquifer. The electromagnetic data have been inverted with a spatially constrained approach by assuming a quasi 1D model of the subsurface. Geophysical surveys allowed for depicting the depth and lateral continuity of the supposed aquifer level in the surveyed area up to a depth of about 200 m and proposing potential positions for well relocation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Nassir SS, Loke MH, Lee CH, Nawawi MNM (2000) Saltwater intrusion mapping by geoelectrical imaging surveys. Geophys Prospect 48:647–661
Ajassa R, Bove A, Castellaro M, Caviglia C, De Luca DA, Destefanis E, Forno MG, Gregorio L, Lasagna M, Masciocco L (2011) Convenzione tra il Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra dell’Università degli Studi di Torino e l’Autorità d’Ambito n°5 Astigiano Monferrato “Aggiornamento ed approfondimento dello studio delle falde idriche sotterranee di Valle Maggiore (di Cantarana) e di Valle Traversola (San Paolo Solbrito) per la razionalizzazione dei prelievi idropotabili e per la definizione delle aree di salvaguardia”. Unpublished report
Archie GE (1942) The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans AIME 146(01):54–62
ATO5 (2015). Valutazione ambientale strategica. Rapporto ambientale. http://www.regione.piemonte.it/ambiente/valutazioni_ambientali/dwd/vas/pianoAmbito5/1_RapportoAmbientale.pdf. Accessed 03 Oct 2017
Auken E, Christiansen AV (2004) Layered and laterally constrained 2D inversion of resistivity data. Geophysics 69:752–761
Batte A, Muwanga A, Sigrist PW, Owor M (2008) VES as an exploration technique to improve on the certainty of groundwater yield in the fractured crystalline basement of eastern Uganda. Hydrogeol J 16(8):1683–1693
Beretta GP, De Luca DA, Masciocco L, Novo M (1999) Conoscenza e protezione dell’acquifero plio-pleistocenico di interesse strategico dell’Astigiano occidentale e tutela del campo acquifero della valle Maggiore di Cantarana. Atti del 3_ convegno nazionale sulla protezione e gestione delle acque sotterranee per il millennio. Quaderni di geologia applicata, Pitagora Ed. Bologna
Boano P, Forno MG (1996) Carta geologica dell’area-tipo della successione villafranchiana. Litografia GEDA—Torino
Bortolami GC, Braga G, Colombetti A, Dal Pra` A, Francani V, Francavilla F, Giuliano G, Manfredini M, Pellegrini M, Petrucci F, Pozzi R, Stefanini S (1978) Hydrogeological features of the Po Valley (Northern Italy). In: Proceedings of the IAHS conference on hydrogeology of great sedimentary basins, Budapest, pp 304–321
Bove A, Casaccio D, Destefanis E, De Luca DA, Lasagna M, Masciocco L, Ossella L, Tonussi M (2005) Idrogeologia della pianura piemontese. Regione Piemonte Direzione Pianificazione delle Risorse Idriche, Mariogros Industrie Grafiche S.p.A., Torino, pp 17 (with CD-Rom)
Carothers JE (1968) A statistical study of the formation factor relation. Log Anal 9:13–20
Carraro F (1996) Revisione del Villafranchiano nell’area-tipo di Villafranca d’Asti (The Villafranchian in the Villafranca d’Asti type-area: a revision). Il Quaternario It Journ Quatern Sc 9(1):5–120
Cimino A, Cosentino C, Oieni A, Tranchina L (2007) A geophysical and geochemical approach for seawater intrusion assessment in the Acquedolci coastal aquifer (Northern Sicily). Environ Geol 55:1473–1482
Comina C, Socco LV, Manzella A (2012) Pseudo-3D characterization of a geothermal field through magneto telluric. In: Near surface geoscience 2012
Dahlin T (1996) 2D resistivity surveying for environmental and engineering applications. First Break 14:275–283
De Luca DA, Dell’Orto V, Forno MG, Gregorio L, Lasagna M, Masciocco L (2009). Assetto idrogeologico della Pianura Piemontese in un’area caratterizzata dalla presenza di un sito nucleare e di un importante campo acquifero (Hydrogeological structure in Piedmont Plain in an area characterized by the presence of a nuclear site and an important aquifer field). Rend. Online Soc. Geol. It, pp. 201–202
De Luca DA, Destefanis E, Forno MG, Lasagna M, Masciocco L (2014) The genesis and the hydrogeological features of the Turin Po Plain fontanili, typical lowland springs in Northern Italy. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73:409–427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0527-y
Debernardi L, De Luca DA, Lasagna M (2008) Correlation between nitrate concentration in groundwater and parameter affecting aquifer intrinsic vulnerability. Environ Geol 55:539–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1006-1
Demanet D, Renardy F, Vanneste K, Jongmans D, Camelbeeck T, Megrahoui M (2001) The use of geophysical prospecting for imaging active faults in the Roer Graben, Belgium. Geophysics 66:78–89
Ezersky M, Legchenko A, Al-Zoubi A, Levi E, Akkawi E, Chalikakis K (2011) Tem study of the geoelectrical structure and groundwater salinity of the nahal hever sinkhole site, dead sea shore. Israel J Appl Geophys 75(1):99–112
Ingeman-Nielsen T, Baumgartner F (2006) CR1Dmod: a Matlab program to model 1D complex resistivity effects in electrical and electromagnetic survey. Comput Geosci 32:1411–1419
Kafri U, Goldman M (2005) The use of the time domain electromagnetic method to delineate saline groundwater in granular and carbonate aquifers and to evaluate their porosity. J Appl Geophys 57:167–178
Lasagna M, Caviglia C, De Luca DA (2014) Simulation modeling for groundwater safety in an overexploitation situation: the Maggiore Valley context (Piedmont, Italy). Bull Eng Geol Environ 2014(73):341–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0500-9
Lasagna M, De Luca DA, Franchino E (2016) Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the western Po Plain (Italy): the effects of groundwater and surface water interactions. Environ Earth Sci 75:240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5039-6
McNeill JD (1990) Use of electromagnetic methods for groundwater studies. In: Ward SH (ed) Geotechnical and environmental geophysics, vol 1. SEG, Tulsa, pp 191–218
Nicaise Y, Descloitres M, Alassane A, Mama D, Boukari M (2012) Environmental geophysical study of the groundwater mineralization in a plot of the cotonou Littoral zone (South Benin). Int J Geophys 2012. Article ID 329827
Parsekian A, Grombacher D, Davis A, Flinchum B, Munday T, Cahill K (2017) Near-surface geophysics for informed water-management decisions in the Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara (APY) lands of South Australia. Lead Edge 33(12):1342–1347
Porter CR, Carothers JE (1970) Formation factor-porosity relation derived from well log data. Society of professional well log analysts, transactions, 11th annual logging symposium, Los Angeles, 3−6 May, pp A1−A19
Reynolds JM (2011) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics, 2nd edn. Wiley Blackwell, Hoboken
Sacco F (1924) Geoidrologia dei pozzi profondi della Valle Padana. Min. LL. PP., Serv. Idr., Uff. Idr. Po, pp 180
Seaton WJ, Burbery TJ (2000) Aquifer characterization in the Blue Ridge physiographic province using resistivity profiling and borehole geophysics: geologic analysis. J Environ Eng Geophys 5:45–58
Sirhan A, Hamidi MO (2012) Characterization by electrical and electromagnetic geophysical methods of the shallow hydrogeological system at Hebron (West Bank, Palestine) in a semi-arid zone. Comptes Rendus Geosci 344(9):449–460
Socco LV, Boiero D, Foti S, Wisén R (2010) Laterally constrained inversion of ground roll from seismic reflection records. Geophysics 74(6):G35–G45
Soupios P, Kouli M, Vallianatos F, Vafidis A, Stavroulakis G (2010) Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: a case study of Keritis basin in Chania (Crete–Greece). J Hydrol (Amst) 338:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.02.028
Tixier MP, Morris RL, Connell JG (1968) Log evaluation of low-resistivity pay sands in the Gulf Coast. Log Anal 9(6):3–20
Viezzoli A, Christiansen AV, Auken E, Sorensen K (2008) Quasi-3D modelling of airborne TEM data by spatially constrained inversion. Geophysics 73:F105–F113. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2895521
Vigna B, Fiorucci A, Ghielmi M (2010) Relations between stratigraphy, groundwater flow and hydrogeochemistry in Poirino Plateau and Roero areas of the Tertiary Piedmont Basin, Italy. Mem Descr Carta Geol d’It XC:267–292
Winsauer WO, Shearing HM, Masson PH, Williams M (1952) Resistivity of brine saturated sands in relation to pore geometry. AAPG Bull 36:253–277
Young M, Macumber P, Watts D, Toqy N (2004) Electromagnetic detection of deep freshwater lenses in a hyper-arid limestone terrain. J Appl Geophys 57:43–61
Acknowledgements
Authors are indebted with the management authorities (ATO 5–Ambito Territoriale Ottimale n.5 Astigiano Monferrato) for funding the surveys object of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Luca, D.A., Comina, C., Lasagna, M. et al. Effectiveness of geophysical surveys for water wells relocation in overexploited aquifers (the example of Maggiore and Traversola Valleys, Northwestern Italy). Environ Earth Sci 77, 19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7218-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7218-0