Abstract
Airborne imaging spectrometer (also known as hyperspectral) remote sensing has been widely used to characterize mineralogy on mine waste surfaces, which is useful for predicting potential sources of acidity and metal leaching. The most successful applications employ fine spatial resolution—20-m pixels or smaller. Future satellite imaging spectrometer sensors are proposed to provide coarser spatial resolution—30- to 60-m pixels. This study examined the ability to map minerals related to acid mine drainage with visible to shortwave infrared hyperspectral imagery at varying spatial scales (2-, 15-, 30-, 60-m pixels) at the Leviathan mine Superfund site, located in the Eastern Sierra Nevada. Mineral maps were produced using spectral angle mapper and matched filtering algorithms. The 15-m images provided comparable maps to the 2-m images. The 30- and 60-m images lost the ability to identify smaller features; however, they were still able to identify high- and low-priority remediation zones at least 75 m in width. Based on our results, we believe 30-m spatial resolution on a satellite hyperspectral sensor will be sufficient for identifying hazardous surfaces at larger mine waste sites and provide important reconnaissance information that can help prioritize detailed ground-based studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers CN, Blowes DW, Nordstrom DK, Jambor JL (1994) Secondary minerals and acid mine-water chemistry. In: Jambor JL, Blowes DW (eds) Environmental geochemistry of sulfide mine-wastes, vol 22. Mineral. Assoc. Can. Short Course, pp 247–270
Bigham JM (1994) Mineralogy of ochre deposits formed by sulfide oxidation. In: Jambor JL, Blowes DW (eds) Environmental Geochemistry of Sulfide Mine-Wastes, Mineral. Assoc. Can. Short Course, vol 22, pp 105–133
Boardman JW, Kruse FA (2011) Analysis of imaging spectrometer data using n-dimensional geometry and a mixture-tuned matched filtering approach. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(11):4138–4152. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2011.2161585
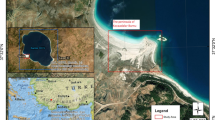
California Dept of Health Services (2003) Public health assessment: evaluation of Leviathan mine site. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/HAC/pha/PHA.asp?docid=33&pg=0. Accessed 1 Sept 2015
California Regional Water Quality Control Board, Lahontan Region (2007) Year-end report for the 2006 field season at Leviathan mine. http://www.swrcb.ca.gov/rwqcb6/water_issues/projects/leviathan_project/docs/2006rpt_noappx.pdf. Accessed 11 Apr 2016
California Regional Water Quality Control Board, Lahontan Region (2015) Year-end report for the 2014 field season at Leviathan mine. http://www.swrcb.ca.gov/lahontan/water_issues/projects/leviathan_project/docs/lev2014rpt.pdf. Accessed 20 Aug 2015
Campbell JB, Wynne RH (2011) Plant sciences, Ch 17. In: Introduction to remote sensing, 5th edn. Guilford Press, New York, pp 549–584
Clark RN, Roush TL (1984) Reflectance spectroscopy: quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J Geophys Res 89(B7):6329–6340. doi:10.1029/JB089iB07p06329
Cloutis EA, Hawthorne FC, Mertzman SA, Krenn K, Craig MA, Marcino D, Methot M, Strong J, Mustard JF, Blaney DL, Bell JF, Vilas F (2006) Detection and discrimination of sulfate minerals using reflectance spectroscopy. Icarus 184(1):121–157. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.04.003
Crowley JK (1991) Visible and near-infrared (0.4–2.5 µm) reflectance spectra of Playa evaporate minerals. J Geophys Res 96(B10):16231–16240. doi:10.1029/91JB01714
Crowley JK, Williams DE, Hammarstrom JM, Piatak N, Chou IM, Mars JC (2003) Spectral reflectance properties (0.4–2.5 μm) of secondary Fe-oxide, Fe-hydroxide, and Fe-sulphate-hydrate minerals associated with sulphide-bearing mine wastes. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 3(3):219–228. doi:10.1144/1467-7873/03-001
Crowley JK, Williams DE, Hammarstrom JM, Piatak N, Mars JC, Chou IM (2006) Spectral reflectance properties (0.4–2.5 um) of secondary Fe-oxide, Fe-hydroxide, and Fe-sulfate-hydrate minerals associated with sulfide-bearing mine waste. USGS Open File Report Rep. 2003–196
Dalton JB, King TVV, Bove DJ, Kokaly RG, Clark RN, Vance JS, Swayze GA (2000) Distribution of acid-generating and acid-buffering minerals in the animas river watershed as determined by AVIRIS spectroscopy. In: Proceedings of the SME-ICARD 2000 meeting, Denver, CO, USA, May 21–24, 2000; pp. 1541–1550
Davies GE, Calvin WM (2016) Quantifying iron concentration in local and synthetic acid mine drainage: a new technique using handheld field spectrometers. Mine Water Environ. doi:10.1007/s10230-016-0399-z
Environmental Protection Agency (2003) Implementation, information, and statutory obstacles impede achievement of environmental results from EPA’s National Hardrock Mining Framework, Report No. 2003-P-00010
Environmental Protection Agency (2006) EPA hardrock mining innovative technology case study, Leviathan mine. http://semspub.epa.gov/src/collection/HQ/SC32068. Accessed 3 Nov 2015
Evans JR (1977) Zaca mine and Leviathan mine. In: Clark WB (ed) Mines and mineral resources of alpine county, California, county report 8. California division of mines and geology, pp 22–27
Farrand WH, Harsanyi JC (1997) Mapping the distribution of mine tailings in the Coeur d’Alene River Valley, Idaho, through the use of constrained energy minimization technique. Remote Sens Environ 59:64–76. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00080-6
Gao BC, Heidebrecht KH, Goetz AFH (1993) Derivation of scale surface reflectances from AVIRIS data. Remote Sens Environ 44:165–178. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(93)90014-O
Guanter L, Kaufmann H, Segl K, Foerster S, Rogass C, Chabrillat S, Kuester T, Hollstein A, Rossner G, Chlebek C (2015) The EnMAP spaceborne imaging spectroscopy mission for earth observation. Remote Sens 7:8830–8857. doi:10.3390/rs70708830
Hunt GR, Ashley RP (1979) Spectra of altered rocks in the visible and near infrared. Econ Geol 74:1613–1629. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.74.7.1613
Hunt GR, Salisbury JW (1970) Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: I silicate minerals. Mod Geol 1:283–300
King TVV, Clark RN, Swayze GA (2000) Applications of imaging spectroscopy data: a case study at Summitville, Colorado. In: Kuehn F et al (eds) Remote sensing for site characterization Ch. 6.7. Springer, Berlin, pp 164–175
Kokaly RF, Couvillion BR, Holloway JM, Roberts DA, Ustin SL, Peterson SH, Khanna S, Piazza SC (2013) Spectroscopic remote sensing of the distribution and persistence of oil from the Deepwater Horizon spill in Barataria Bay marshes. Remote Sens Environ 129:210–230. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.028
Kopackova V (2014) Using multi spectral feature analysis for quantitative pH mapping in a mining environment. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 28:28–42. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2013.10.008
Kruse FA (1999) Visible-infrared sensors and case studies. In: Rencz AN (ed) Remote sensing for the Earth sciences: manual of remote sensing, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 567–611
Langmuir D (1997) Iron and sulfur geochemistry, Ch 12. In: Aqueous environmental geochemistry. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 431–474
Lee CM, Cable ML, Hook SJ, Green RO, Ustin SL, Mandl DJ, Middleton (2015) An introduction to the NASA Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI) mission and preparatory activities. Remote Sens Environ 167:6–19. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.06.012
Lottermoser BG (2003) Mine water, Ch 3. In: Mine wastes. Springer, New York, pp 83–141
Lottermoser BG (2005) Evaporative mineral precipitates from a historical smelting slag dump, Rio Tinto, Spain. Neues Jahrbuch Fur Mineralogie-Abhandlungen 181(2):183–190. doi:10.1127/0077-7757/2005/0016
Mielke C, Boesche NK, Rogass C, Kaufmann Christoph G, de Wit M (2014) Spaceborne mine waste mineralogy monitoring in South Africa, application for modern push-broom missions: hyperion/OLI and EnMAP/Sentinel-2. Remote Sens 6:6790–6816. doi:10.3390/rs6086790
Montero IC, Brimhalla GH, Alpers CN, Swayze GA (2005) Characterization of waste rock associated with acid drainage at the Penn mine, California, by ground-based visible to short-wave infrared reflectance spectroscopy assisted by digital mapping. Chem Geol 215:453–472. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.045
MSE Technology Applications, Inc. (2000) Mine waste technology program, annual report. http://www2.epa.gov/nscep. Accessed 30 Oct 2015
Nordstrom DK et al (1978) Redox equilibria of iron in acid mine waters. In: Jenne EA (ed) Chemical modeling in aqueous systems: speciation, sorption, solubility, and kinetics, American Chemical Society Symposium Series, vol 93. pp 51– 79
Nordstrom DK (1982) Aqueous pyrite oxidation and consequent formation of secondary iron minerals, Ch.3. In: Kittrick JA (ed) Acid sulfate weathering Soil science society of America, vol 10. SSSA special publication, Fitchburg, pp 37–58
Riaza A, Buzzi J, Garcia-Melendez E, Vazquez I, Bellido E, Carrere V, Müller A (2012a) Pyrite mine waste and water mapping using Hymap and Hyperion hyperspectral data. Environ Earth Sci 66:1957–1971. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1422-0
Riaza A, Buzzi J, Garcia-Melendez E, Carrere V, Sarmiento A, Muller A (2012b) River acid mine drainage: sediment and water mapping through hyperspectral Hymap data. Int J Remote Sens 33(19):6163–6185. doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.675454
Riaza A, Buzzi J, Garcia-Melendez E, Carrere V, Sarmiento A, Muller A (2015) Monitoring acidic water in a polluted river with hyperspectral remote sensing (HyMap). Hydrol Sci J 60(6):1064–1077. doi:10.1080/02626667.2014.899704
Sherman DM, Waite TD (1985) Electronic spectra of Fe3+ oxides and oxide hydroxides in the near IR to near UV. Am Mineral 70:1262–1269
Slonecker T, Fisher GB, Aiello DP, Haack B (2010) Visible and infrared remote imaging of hazardous waste: a review. Remote Sens 2:2471–2508. doi:10.3390/rs2112474
Swayze GA, Smith KS, Clark RN, Sutley SJ, Pearson RM, Vance SJ, Hageman PL, Briggs PH, Meier AL, Singleton MJ, Roth S (2000) Using imaging spectroscopy to map acidic mine waste. Environ Sci Technol 34:47–54. doi:10.1021/es990046w
Thompson DR, Gao BC, Green RO, Roberts DA, Dennison PE, Lundeen SR (2015) Atmospheric correction for global mapping spectroscopy: ATREM advances for the HyspIRI preparatory campaign. Remote Sens Environ 167:64–77. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.02.010
Tucker CJ (1979) Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens Environ 8:127–150. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(79)90013-0
US Geologic Service (2013) USGS Digital spectral library 06. http://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/spectral.lib06/. Accessed 30 Oct 2015
Zabcic N, Rivard B, Ong C, Mueller A (2014) Using airborne hyperspectral data to characterize the surface pH and mineralogy of pyrite mine tailings. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 32:152–162. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2014.04.008
Acknowledgements
We thank Doug Carey and Taylor Zetner from the Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board for granting us access to Leviathan mine Superfund site. Funding for this project was provided by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) HyspIRI Preparatory Airborne Activities for Energy and Mineral Resources through Grant NNX12AQ17G to the University of Nevada, Reno.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davies, G.E., Calvin, W.M. Mapping acidic mine waste with seasonal airborne hyperspectral imagery at varying spatial scales. Environ Earth Sci 76, 432 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6763-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6763-x