Abstract
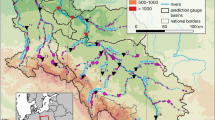
The understanding of the spatial and temporal dynamic of river systems is essential for developing sustainable water resource management plan. For the Senegal River, this subject is very complex according to the context of (1) transboundary basin, (2) several contrasted climatic zones (Guinea, South Sudanian, North Sudanian and Sahelian) with high rainfall variability and (3) high human pressures (dam construction and water uses). From 1954 to 2000, 80% (mean value) of the Senegal River flows recorded downstream part of the basin are provided by three majors tributaries (Bafing, Bakoye and Faléme) located in the upstream part. Then, in our study, this upper Senegal River basin was chosen in order to investigate the hydrological responses to rainfall variability and dam construction. Two nonparametric statistical methods, Mann–Kendall and Hubert test, were used to detect the long-term changes in the time series of precipitation and water discharge (1954–2000) at the annual and seasonal scales. The continuous wavelet transform (Morlet Wavelet) was employed to characterize the different mode in the water discharge variability. Flow duration curve and cumulative curve methods were used to assess the impact of dams on the hydrological regime of the Senegal River. Results showed that the Senegal River flows have been changing under the influence of both rainfall variation and dam construction. The long-term evolution of water discharge depend on long-term rainfall variability: The wet periods of the 1950s and 1960s correspond to periods of higher river flows, while the droughts of the 1970s and 1980s led to unprecedented river flows deficits. The new period, since 1994, show a high inter-annual variability of rainfall and discharge without clear trend. At seasonal scale, the results showed also a strong relationship between rainfall and runoff (R 2 > 0.8) resulting from alternating wet and dry seasons and rapid hydrological responses according to annual rainfall. Nevertheless, the observed flows during dry seasons highlighted the influence of water storage and restitution of infiltrated waters in soils and surficial formations during wet seasons. In the dry seasons, the water budget of the three upstream tributaries showed a water deficit at the downstream gauging station. This deficit was characterized by water loss to underlying aquifers and highlighted the influence of geological setting on water balance. However, in this context, water restitution during the dry season remained dependent on climatic zone and on the total annual rainfall volume during the previous wet season. The results have highlighted an impact of the Manantali dam previously obscured: The dam has no effect on the regulation of high river flows. That is what explains that since its construction in 1988, flooding of coastal cities, like Saint-louis, by seasonal river floods has not ceased. The flooding risk in coastal cities is not avoided, and the dams caused hyper-salinization of the Senegal lower estuary. The breach created in the coastal barrier of the Langue of Barbary in October 2003 promotes direct export of excess floodwater to the sea and reduces this risk of flooding in the delta area. But, this solution led to considerable loss of potential water resources, and the authors recommend a new water management plan with a global focus. However, this study shows the positives impacts of the two dams. They allow the availability of freshwater in order to support agricultural irrigation in the valley and delta zone, in particular during low flows periods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albergel J, Lamagat JP (1991) Plan directeur de la haute vallée du fleuve Sénégal: Climatologie, hydrologie. Rapport final, ORTOM, p 125
Ali A, Lebel T (2009) The Sahelian standardized rainfall index revisited. Int J Climatol 29:1705–1714
Anctil F, Coulibaly P (2004) Wavelet analysis of the inter-annual variability in southern quebec streamflow. J Clim 17:163–173
ANSD (2014) Recensement général de la Population, de l’Habitat, de l’Agriculture et de l’Elevage au Sénégal. Rapport final, Agence Nationale de la Statistique et de la Démographie, p 418
BAD/BID (2013) Projet d’alimentation en eau potable de la ville de Nouakchott (Aftout Essahli). Rapport d’évaluation intérimaire conjointe, Banque Africaine de Développement (BAD)/Banque Islamique de Développement (BID), de performance du projet. Départements de l’évaluation des operations, République Islamique de Mauritanie, p 88
Bell MA, Lamb PJ (2006) Integration of weather system variability to multidecadal regional climate change: the West African sudan-sahel zone 1951–98. J Clim 19(20):5343–5365
Bhavnani R, Vordzorgbe S, Owor M, Bousquet F (2008) Report on the status of disaster risk reduction in the sub-saharian Africa region. Commission of the African Union, United nations and the World Bank, http://www.unisdr.org/files/2229_DRRinSubSaharanAfricaRegion
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Holden Day, San Francisco
Bricquet JP, Bamba F, Mahe G, Toure M, Olivry JC (1997) Evolution récente des ressources en eau de l’Afrique atlantique. Rev Sci Eau 3:321–337
Caldwell JC (1975) La sécheresse dans le Sahel et ses conséquences démographiques. Cahier OLC, n°8, p 116
Cappelaere B, Descroix L, Lebel T, Boulain N, Ramier D, Laurent JP, Favreau G, Boubkraoui S, Boucher M, Bouzou Moussa I, Chaffard V, Hiernaux P, Issoufou HBA, Le Breton E, Mamadou I, Nazoumou Y, Oi M, Ottlé C, Quantin G (2009) The AMMA-CATCH experiment in the cultivated Sahelian area of south-west Niger—investigating water cycle response to a fluctuating climate and changing environment. J Hydrol 375:34–51
Cisse MT, Sambou S, Dieme Y, Diatta C, Bop B (2014) Analyse des écoulements dans le bassin du fleuve Sénégal de 1960 à 2008. Revue des sciences de l’eau 27(2):167–187
Cleveland WS (1979) Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J Am Stat Assoc 74:829–836
Cleveland WS, Devlin SJ (1988) Locally weighted regression: an approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J Am Stat Assoc 83:596–610
Dai A, Lamb PJ, Trenberth KE, Hulme M, Jones PD, Xie P (2004) The recent Sahel Drough is real. Int J Climatol 24:1323–1331
Dai SB, Yang SL, Cai AM (2008) Impacts of dams on the sediment flux of the Pearl River, southern China. CATENA 76:36–43
Descroix L, Mahé G, Lebel T, Favreau G, Galle S, Gautier E, Olivry J-C, Albergel J, Amogu O, Cappelaere B, Dessouassi R, Diedhiou A, Le Breton E, Mamadou I, Sighomnou D (2009) Spatio-temporal variability of hydrological regimes around the boundaries between Sahelian and Sudanian areas of West Africa: a synthesis. J Hydrol 375:90–102
Descroix L, Genthon P, Amogu O, Rajot JL, Sighomnou D, Vauclin M (2012) Change in Sahelian Rivers hydrograph: the case of recent red floods of the River Niger in the Niamey region. Glob Planet Change 98–99:18–30
Diaw M, Faye S, Stichler W, Maloszewski P (2012) Isotopic and geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Senegal River delta aquifer: implication of recharge and flow regime. Environ Earth Sci 66:1011–1020
Dione O (1996) Evolution climatique récente et dynamique fluviale dans les hauts bassins des fleuves Sénégal et Gambie. Thèse de doctorat, Université Lyon 3 Jean Moulin, p 477
Durand P, Anselme B, Thomas YF (2010) L’impact de l’ouverture de la brèche dans la langue de Barbarie à Saint-Louis du Sénégal en 2003: un changement de nature de l’aléa inondation? Cybergeo. Eur J Geogr Environnement, Nature, Paysage, document 496, p 25
El Janyani S, Massei N, Dupont JP, Fournier M, Dörfliger N (2012) Hydrological responses of the chalk aquifer to the regional climatic signal. J Hydrol 464–465:485–493
El Janyani S, Dupont JP, Massei N, Slimani S, Dörfliger N (2014) Hydrological role of karst in the Chalk aquifer of Upper Normandy, France. Hydrogeol J 22:663–677. doi:10.1007/s10040-013-1083-z
Fall S, Semazzi FHM, Miyogi DDS, Anyah RO, Bowden J (2006) Spatio-temporal climate variability over Senegal and its relationship to global climate. Int J Climatol 26:2057–2076
Faure H, Gac J (1981) Will the Sahelian drought end in 1985? Nature 291:475–478
Favreau G, Cappelaere B, Massuel S, Leblanc M, Boucher M, Boulain N, Leduc C (2009) Land clearing, climate variability and water resources increase in semiarid south-west Niger: a review. Water Resour Res 45:W00A16. doi:10.1029/2007WR006785
Fischer T, Gemmer M, Su B, Scholten T (2013) Hydrological long-terme dry and wet periods in the Xijiang River basin, South China. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:135–148
Hipel KW, McLeod AI (1994) Time series modelling of water resources and environmental systems. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0-444-89270-2
Hubert P, Bader J-C, Bendjoudi H (2007) Un siècle de débits annuels du fleuve Sénégal. Hydrol Sci J 52(1):68–73
Hulme M (1992) Rainfall changes in Africa: 1931–1960 to 1961–1990. Int J Climatol 12:685–699
Jenkins GM, Watts DG (1968) Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden Days, San Francisco, p 525
Kamagaté B (2006) Fonctionnement hydrologique et origines des écoulements sur un bassin versant de milieu tropical de socle au Bénin: bassin versant de la Donga (haute vallée de l’Ouémé). Thèse de Doctorat, Université de Montpellier II, France
Kamagaté B, Séguis L, Favreau G, Seidel J-L, Descloitres M, Affaton P (2007) Processus et bilan des flux hydriques d’un bassin versant de milieu tropical de socle au Bénin (Donga, Haut Ouémé). Comptes Rendus Géoscience 339:418–429
Kannan N, Jeong J (2011) An approach for estimating stream health using flow duration curves and indices of hydrologic alteration. Report of Texas AgriLife Research and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, p 59
Khan MYA, Daityari S, Chakrapani GJ (2016) Factors responsible for temporal and spatial variations in water and sediment discharge in Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. Environ Earth Sci 75(283):2–18
Korzoun VI, Sokolov AA, Budyko MI, Voskresensky KP, Kalinin GP, Kono-plyantsev AA, Korotkevich ES, L’vovich MI (1978) Atlas of world water balance. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris
L’Hôte Y, Mahé G, Somé B, Triboulet JP (2002) Analysis of a Sahelian annual rainfall index from 1896 to 2000; the drought continues. Hydrol Sci J 47:563–572
L’vovich MI, White GF (1990) Use and transformation of terrestrial water Systems. In Anthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle. BioScience 50(9):753–765
Labat D, Ronchail J, Guyot JL (2005) Recent advances in wavelet analyses: part 2-Amazon, Parana, Orinoco and Congo discharges time scale variability. J Hydrol 314(1–4):289–311
Larocque M, Mangin A, Razack M, Banton O (1998) Contribution of correlation and spectral analyses to the regional study of a large karst aquifer (Charente, France). J Hydrol 205:217–231
Lavieren BV, Wetten VJ (1990) Profil de l’environnement de la vallée du fleuve Sénégal. 40 fig., 16 photos, 68p., Euroconsult, RIN
Le Barbé L, Alé G, Millet B, Texier H, Borel Y, Gualde R (1993) Les ressources en eaux superficielles de la République du Bénin. Monographie hydrologique Orstom, 11, Orstom editions, Paris, p 535
Le Barbé L, Lebel T, Tapsoba D (2002) Rainfall variability in West Africa during the years 1950–1990. J Clim 15:187–2002
Lebel T, Ali A (2009) Recent trends in the Central and Western Sahel rainfall regime (1990–2007). J Hydrol 375(1–2):52–64
Lebel T, Vischel T (2005) Climat et cycle de l’eau en zone tropicale: un problème d’échelle. C R Geosci 337:29–38
Lebel T, Diedhiou A, Laurent H (2003) Seasonal cycle and interannual variability of the Sahelian rainfall at hydrological scales. J Geophys Res 108:8389–8392
Leduc C, Favreau G, Schroeter P (2001) Long-term rise in a Sahelian water-table: the continental terminal in South-West Niger. J Hydrol 243(1–2):43–54
Mahé G, Paturel JE (2009) 1896–2006 Sahelian annual rainfall variability and runoff increase of Sahelian Rivers. C R Geosci 341:538–546
Mahé G, Dessouassi R, Cissoko B, Olivry JC (1998) Comparaison des fluctuations interannuelles de piézometrie, precipitation et debit sur le bassin versant du Bani à Douna au Mali. Water ResourcesVariability in Africa during the XXth Century In: Proceedings of the Abidjan’98 Conference held at Abidjan, Cote d’lvoire, IAHS, p 252
Mahé G, Olivry JC, Dessouassi R, Orange D, Bamba F, Servat E (2000) Relations eaux de surface—eaux souterraines d’une rivière tropicale au Mali. Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences, Serie IIa 330, 689–692
Mahé G, Paturel JE, Servat E, Conway D, Dezetter A (2005) Impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river modelling of the Nakambe River in Burkina-Faso. J Hydrol 300:33–43
McKee TBN, Doesken J, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Eight Conference on Applied Climatology. American Meteorological Society, Anaheim, pp 179–184
Michel P (1973) Les bassins des fleuves Sénégal et Gambie. Étude géomorphologique. Thèse, Université de Strasbourg, Mémoire ORSTOM, Paris, n° 63, 3 tomes, 752 p
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391:202–216
Nicholson SE, Some B, Kone B (2000) An analysis of recent rainfall conditions in West Africa, including the rainy seasons of the 1997 E1Nino and the 1998 La Nina years. J Clim 13:2628–2640
Olivry JC, Bricquet JP, Mahé G (1993) Vers un appauvrissement durable des ressources en eau de l’Afrique humide ? Hydrology of Warm Humid Regions In: Proceedings of the Yokohama Symposium, July1993), IAHS Publ, 216, 67–78
Ozer P, Erpicum M, Demarée G, Vandiepenbeeck M (2003) The Sahelian drought may have ended during 1990s. Hydrol Sci J 48(3):489–492
Padilla AA, Pulido-Bosch A (1995) Study of hydrographs of karstic aquifers by means of correlation and cross-spectral analysis. J Hydrol 168:75–89
Paturel JP, Servat E, Kouamé B, Lubès-Niel H, Ouedraogo M, Masson JM (1997) Climatic variability in humid Africa along the Gulfe of Guinea, Part II: an integrated regional approach. J Hydrol 191:16–36
Rochette, C. 1974. Le bassin du fleuve Sénégal. Monographies hydrologique, N°1 ORSTOM, 450 p
Rojas O, Vrieling A, Rembold F (2011) Assessing drought probability for agricultural areas in Africa with coarse resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens Environ 115:343–352
Rossi A, Massei N, Laignel B, Sebag D, Copard Y (2009) The response of the Mississippi River to climate fluctuations and reservoir construction as indicated by wavelet analysis of stream flow and suspended-sediment load, 1950–1975. J Hydrol 377(3–4):237–244
Roudier P, Ducharne A, Feyen L (2014) Climate change impacts on runoff in West Africa: a review. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18:2789–2801
Sadowski J (1996) Investigation of signal characteristics using the continuous wavelet transform. Johns Hopkins APL Tech Dig 17(3):258–269
Sakho I, Mesnage V, Deloffre J, Lafite R, Niang I, Faye G (2011) The influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on mangrove dynamics over 60 years: the Somone Estuary, Senegal. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 94:93–101
Schneider K, Farge M, (2006) Wavelets: Mathematical theory. In: Françoise JP, Naber G, Tsun TS (eds) Encyclopedia of mathematical physics, pp 426–438
Séguis L, Cappelaere B, Milési G, Peugeot C, Massuel S, Favreau G (2004) Simulated impacts of climate change and land-clearing on runoff from a small Sahelian catchment. Hydrol Process 18:3401–3413
Servat E, Paturel JE, Kouame B, Travaglio M, Ouedraogo M, Bqyer JF, Lubes- Niel H, Fritsch JM, Masson JM, Marieu B (1998) Identification, caracterisation et consequences d’une variabilite hydrologique en Afrique de I’Ouest et centrale. IAHS Publication 252:323–337
Stige LC, Stave J, Chan KS, Ciannelli L, Pretorelli N, Glantz P, Herren HR, Stenseth NC (2006) The effect of climate variation on agro-pastoral production in Africa. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 103, 3049–3053
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:61–78
Troin M, Vallet-Coulomb C, Piovano E, Sylvestre F (2012) Rainfall–runoff modeling of recent hydroclimatic change in a subtropical lake catchment: laguna Mar Chiquita, Argentina. J Hydrol 475:379–391
Vicente-Serranoa SM, Beguería S, Gimeno L, Eklundh L, Giuliani G, Weston D, El Kenawy A, López-Moreno JI, Nieto R, Ayenew T, Konte D, Ardö J, Pegram GGS (2012) Challenges for drought mitigation in Africa: the potential use of geospatial data and drought information systems. Appl Geogr 34:471–486
Vörösmarty CJ, Sahagian D (2000) Anthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle. Bioscience 50(9):753–765
Vörösmarty CJ, Sharma KP, Fekete BM, Copeland AH, Holden J, Marble J, Lough JA (1997) The storage and aging of continental runoff in large reservoir systems of the world. Ambio 26:210–219
Walling DE, Fang D (2003) Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world rivers. Glob Planet Change 39:111–126
Wisner B, Blaikie P, Cannon T, Davis L (2003) At risk: natural hazards, people’s vulnerability and disasters, 2nd edition, p 124
Yue S, Pilon P (2004) A comparison of the power of the t test, MannKendall and bootstrap tests for trend detection. Hydrol Sci J 49(1):21–37
Zhang S, Lu XX (2009) Hydrological responses to precipitation variation and diverse human activities in a mountainous tributary of the lower Xijiang, China. CATENA 77:130–142
Zhang S, Lu XX, Higgitt DL, Chen CTA, Han J, Sun H (2008) Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Basin, China. Glob Planet Change 60:365–380
Acknowledgements
This work is a contribution to the “MARC Project,” an international collaboration between the Universities of Rouen (France) and Thiès (Senegal). The authors would like to thank Mr. Moussa Sall (Centre de Suivi Ecologique de Dakar) and the Hydraulic division of Saint-Louis for providing access to the dataset. The authors warmly acknowledge the anonymous reviewers who assessed the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakho, I., Dupont, JP., Cisse, M.T. et al. Hydrological responses to rainfall variability and dam construction: a case study of the upper Senegal River basin. Environ Earth Sci 76, 253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6570-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6570-4