Abstract
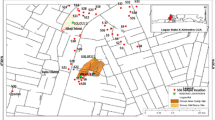
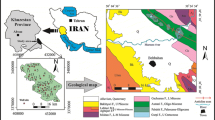
Shallow aquifers underlying sewage disposal facilities contain salts much higher than non-contaminated shallow aquifers of surrounding areas. This study focuses on the spatial distribution of boron in an alluvial aquifer subjected to sewage waste contamination. Nineteen groundwater samples were collected from the water wells present in the Wadi Bani Malik area known to have a history of sewage waste disposal. The sampling locations were carefully selected to cover an area upstream and downstream to the dam axis, within the boundary as well as around the lake perimeter. Prior to sampling, in situ field parameters such as top of the casing, depth to water table, temperature, salinity, electrical conductivity (EC) and the pH were measured. A total of 10 trace elements most commonly found in the groundwater contamination context were selected for the analysis which are: Li, Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Ba, Hg, Pb and B. The results of this study indicate that concentrations of all the trace elements except boron are largely less than 1.0 mg/L. The concentration of boron varies between 3.70 and 44.98 mg/L with an average of 13.24 mg/L. The highest boron concentration is found in the cluster of wells located adjacent to a point source. The lowest concentration of boron is upgradient to this location. When compared with the EC data, the pattern of highs and lows of boron corresponds well with the EC. This pattern is consistent with the description of other plumes in sand and gravel of somewhat similar grain-size distributions. Also, the correlation coefficient analysis performed on the dataset indicates a strong correlation coefficient (r = 0.8) between the boron and EC. This suggests the possibility of using boron as an indicator for plumes originating from sewage waste disposal facilities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Sharar TM, Hani BN, Al-Khader S (2014) Boron adsorption–desorption characteristics of irrigated soils in the Jordan Valley. Geoderma Reg 2–3:50–59
Aitchison-Earl P, Ettema M, Hanson C, Hayward S, Larking R, Sanders R, Scott D, Veltman A (2003) Coastal aquifer saltwater intrusion assessment guidelines. Environ Canterb 46
American Socitety for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (1980) Natural building stones; soil and rock. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, part 19, Philadelphia
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Bahabri AA (2011) Geoenvironmental Assessment of Polluted Water and Soil due to Sewage Water at Wadi Uranah, South-west of Makkah. (unpublished). Ph.D., King Abdulaziz University Jeddah
Elfeki A, Ewea H, Al-Amri N (2011) Linking groundwater flow and transport models, GIS technology, satellite images and uncertainty quantification for decision making: Buraiman lake case study Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Int J Water Resour Arid Environ 1(4):295–303
EPA (2008) Regulatory determinations support document for selected contaminants for the second drinking water contaminant candidate list (CCL2), Office of Water (4607M), EPA 815-R-08-012
Ewea H (2010) Hydrological analysis of floeeding wasterwater lake in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J King Abdel Aziz Univ Meterol Environ Arid Land Agric Fac 21(1):125–145
Fetter CW (2000) Applied hydrogeology. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Hazen A (1911) Discussions: dams on sand foundations. Am Soc Civ Eng Trans 73:37–58
Hudak PF (2004) Boron and selenium contamination in south Texas groundwater. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 39(11–12):2827–2834
Hughes JL (1975) Evaluation of ground-water degradation resulting from waste disposal to alluvium near Barstow, California. US Government Print Office, p 33
ISO 9390 (1990) Water quality—determination of borate—Spectrometric method using azomethine-H. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
Jabal MSA, Abustan I, Rozaimy MR, El Najar H (2015) Groundwater beneath the urban area of Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine): hydrochemistry and water quality. Arab J Geosci 8:2203–2215
Kalaivani K, Krishnaveni M (2015) Multivariate statistical analysis of pollutants in Ennore Creek, south-east coast of India. Glob NEST J 17(3):618–627
Kimmel GE, Braids OC (1977) Leachate plumes in ground water from Babylon and Islip landfills, Long Island, New York. US Geological Survey professional paper 1085, p 38
Koerner EL, Haws DA (1979) Long-term effects of land application of domestic wastewater: Vineland, New Jersey, rapid infiltration site. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, [Office of Air, Land, and Water Use], Robert S. Kerr Environmental Research Laboratory
LeBlanc DR (1984) Sewage plume in a sand and gravel aquifer, Cape Cod. USGPO, Massachusetts
Moore T, Al-Rehaili M (1989) Geologic map of the Makkah Quadrangle: Sheet 21D, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources, Deputy Ministry For Mineral Resources Publication, Jeddah
Moss SA, Nagpal N, Branch WP (2003) Ambient water quality guidelines for boron. Water Protection Branch, Ministry of Water, Land and Air Protection, British Columbia technical report, p 112
Mtoni Y, Mjemah IC, Bakundukize C, Van Camp M, Martens K, Walraevens K (2013) Saltwater intrusion and nitrate pollution in the coastal aquifer of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1091–1111
Pahl MV, Culver BD, Strong PL, Murray FJ, Vaziri ND (2001) The effect of pregnancy on renal clearance of boron in humans: a study based on normal dietary intake of boron. Toxicol Sci 60(2):252–256
Ravenscroft P, McArthur J (2004) Mechanism of regional enrichment of groundwater by boron: the examples of Bangladesh and Michigan, USA. Appl Geochem 19(9):1413–1430
Rehman F, Cheema T (2016) Effects of sewage waste disposal on the groundwater quality and agricultural potential of a floodplain near Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 9:1
Rehman F, Abuelnaga HSO, Harbi HM, Cheema T, Atef AH (2016a) Using a combined Electrical resistivity imaging and induced polarization techniques with the chemical analysis in determining of groundwater pollution at Al Misk Lake, Eastern Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 9:1
Rehman F, Helmy SOA, Hussein MH, Ali HA (2016b) Application of vertical electrical sounding and water analysis for study the contaminated area at Al Misk Lake, Eastern Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 15(1):311
Sharaf M (2012) Hydrochemistry of the groundwater aquifer in Wadi Madsus area, Makkah district, western Saudi Arabian Shield, Saudi Arabia. Egypt J Geol 56:19–31
Sharaf M (2013) Trace elements hydrochemistry and suitability of the groundwater in Wadi an Numan area, Makkaah District, Western Arabian Shield, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Sci Eng 38(7):1871–1887
Vengosh A, Kolodny Y, Spivack A (1998) Application of isotopes techniques to investigate groundwater pollution. IAEA TECHDOC 1046:17–38
Weast RC (1985) CRC handbook on chemistry and physics. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton
WHO (2006) A compendium of standards for wastewater reuse in the eastern Mediterranean region. WHO, Geneva
WHO (2009) Boron in drinking-water: background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality, Report WHO/HSC/WSH/09.01/2, p 28
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, F., Cheema, T. Boron contamination in groundwater at a sewage waste disposal facility near Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Environ Earth Sci 76, 218 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6528-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6528-6