Abstract
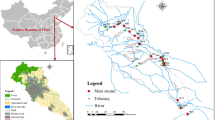
Stream samples were collected from 16 subcatchments of the South Tiaoxi River, East China, before and after incidence of Typhoon Fitow in October 2013. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), spectroscopic indices (i.e., specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm, SUVA254; spectral slope ratio, S R; fluorescence index, FI; humification index, HIX), fluorescence excitation emission matrix spectroscopy in combination with parallel factor analysis (EEMs-PARAFAC) were applied to assess how extreme storm altered the amount and composition of dissolved organic matter (DOM). DOM properties between pre- and post-storm were significantly distinguished. The torm promoted increased DOC and DON concentrations respectively by 15 and 76 %. The humic-like fluorescence intensities increased by 10 %, and the fluorescence intensities of tyrosine-like substances increased while these of tryptophan-like substances decreased. Moreover, the DOM quality in streams shifted to higher HIX and SUVA254 but lower S R and FI. In addition, 16 subcatchments were clustered into four groups according to the dominated land use types. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the differences in DOM properties among subcatchments were associated with the dominated land use types during storm. Our findings suggested that elevated DOC and DON concentration were associated with the proportion of residential area and planted forest land (Phyllostachys praecox), respectively. Humic-like materials were related to the proportion of native forest land and cropland, while protein-like components were associated with planted forest land. Extreme storm events will strengthen the linkage between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and further alter DOM in both quantity and quality in headwater streams, which is also associated with land use types in the watershed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beniston M, Stephenson DB, Christensen OB, Ferro CA, Frei C, Goyette S, Halsnaes K, Holt T, Jylhä K, Koffi B (2007) Future extreme events in European climate: an exploration of regional climate model projections. Clim Change 81:71–95
Bernal S, Butturini A, Sabater F (2005) Seasonal variations of dissolved nitrogen and DOC:DON ratios in an intermittent Mediterranean stream. Biogeochemistry 75:351–372
Bianchi TS, DiMarco SF, Cowan JH, Hetland RD, Chapman P, Day JW, Allison MA (2010) The science of hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: a review. Sci Total Environ 408:1471–1484
Bricaud A, Morel A, Prieur L (1981) Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domains. Limnol Oceanogr 26:43–53
Buffam I, Galloway JN, Blum LK, McGlathery KJ (2001) A stormflow/baseflow comparison of dissolved organic matter concentrations and bioavailability in an Appalachian stream. Biogeochemistry 53:269–306
Cory RM, McKnight DM (2005) Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 39:8142–8149
Delprat L, Chassin P, Lineres M, Jambert C (1997) Characterization of dissolved organic carbon in cleared forest soils converted to maize cultivation. Dev Crop Sci 25:257–266
Dong H, Qiang Z, Wang W, Jin H (2012) Evaluation of rural wastewater treatment processes in a county of eastern China. J Environ Monitor 14:1906–1913
Dong Q, Li P, Huang Q, Abdelhafez AA, Chen L (2014) Occurrence, polarity and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in the Huangpu River, China. J Environ Sci China 26:1843–1850
Fellman JB, D’Amore DV, Hood E, Boone RD (2008) Fluorescence characteristics and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in forest and wetland soils from coastal temperate watersheds in southeast Alaska. Biogeochemistry 88:169–184
Fellman JB, Hood E, Edwards RT, D’Amore DV (2009) Changes in the concentration, biodegradability, and fluorescent properties of dissolved organic matter during stormflows in coastal temperate watersheds. J Geophys Res 2005–2012:114
Frost PC, Larson JH, Johnston CA, Young KC, Maurice PA, Lamberti GA, Bridgham SD (2006) Landscape predictors of stream dissolved organic matter concentration and physicochemistry in a Lake Superior river watershed. Aquat Sci 68:40–51
Gao C (2013) Influences of watershed land use on C, N, P export in Tiaoxi streams, Zhejiang Province, China. Chinese Academy of Forestry, China (in Chinese)
GB7493-87. http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/shjbh/sjcgfffbz/198708/t19870801_66628.htm
Goswami BN, Venugopal V, Sengupta D, Madhusoodanan M, Xavier PK (2006) Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 314:1442–1445
Gremm TJ, Kaplan L (1998) Dissolved carbohydrate concentration, composition, and bioavailability to microbial heterotrophs in stream water. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 26:167–171
Gu L, Wu CJ, Wang X (2009) Land utilization pattern changing and driving force analysis based on remote sensing data in Lin’an. J Zhejiang For Coll 26:870–876 (in Chinese)
Hedges J, Keil R, Benner R (1997) What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org Geochem 27:195–212
Heinz M, Graeber D, Zak D, Zwirnmann E, Gelbrecht J, Pusch M (2015) A comparison of organic matter composition in agricultural versus forest affected headwaters with special emphasis on organic nitrogen. Environ Sci Technol 49:2081–2090
Helms JR, Stubbins A, Ritchie JD, Minor EC, Kieber DJ, Mopper K (2008) Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol Oceanogr 53:955–969
Hinton M, Schiff S, English M (1997) The significance of storms for the concentration and export of dissolved organic carbon from two Precambrian Shield catchments. Biogeochemistry 36:67–88
HJ/T346-2007. http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/shjbh/sjcgfffbz/200703/t20070316_101688.htm
HJ535-2009. http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/shjbh/sjcgfffbz/201001/t20100112_184155.htm
HJ636-2012. http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/shjbh/sjcgfffbz/201203/t20120307_224383.htm
Hong H, Yang L, Guo W, Wang F, Yu X (2012) Characterization of dissolved organic matter under contrasting hydrologic regimes in a subtropical watershed using PARAFAC model. Biogeochemistry 109:163–174
Hood E, Gooseff MN, Johnson SL (2006) Changes in the character of stream water dissolved organic carbon during flushing in three small watersheds, Oregon. J Geophys Res 2005–2012:111
Hosen JD, McDonough OT, Febria CM, Palmer MA (2014) Dissolved organic matter quality and bioavailability changes across an urbanization gradient in headwater streams. Environ Sci Technol 48:7817–7824
Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond J-M, Parlanti E (2009) Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org Geochem 40:706–719
Inamdar S, Singh S, Dutta S, Levia D, Mitchell M, Scott D, Bais H, McHale P (2011) Fluorescence characteristics and sources of dissolved organic matter for stream water during storm events in a forested mid-Atlantic watershed. J Geophys Res 2005–2012:116
Inamdar S, Finger N, Singh S, Mitchell M, Levia D, Bais H, Scott D, McHale P (2012) Dissolved organic matter (DOM) concentration and quality in a forested mid-Atlantic watershed, USA. Biogeochemistry 108:55–76
Jaffé R, Boyer J, Lu X, Maie N, Yang C, Scully N, Mock S (2004) Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Mar Chem 84:195–210
Lauerwald R, Hartmann J, Moosdorf N, Kempe S, Raymond PA (2013) What controls the spatial patterns of the riverine carbonate system?—a case study for North America. Chem Geol 337:114–127
Li Y, Jiang P, Chang SX, Wu J, Lin L (2010) Organic mulch and fertilization affect soil carbon pools and forms under intensively managed bamboo (Phyllostachys praecox) forests in southeast China. J Soil Sediment 10:739–747
Lu Y, Bauer JE, Canuel EA, Yamashita Y, Chambers RM, Jaffé R (2013) Photochemical and microbial alteration of dissolved organic matter in temperate headwater streams associated with different land use. J Geophys Res 118:566–580
Lytle CR, Perdue EM (1981) Free, proteinaceous, and humic-bound amino acids in river water containing high concentrations of aquatic humus. Environ Sci Technol 15:224–228
McKnight DM, Boyer EW, Westerhoff PK, Doran PT, Kulbe T, Andersen DT (2001) Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 46:38–48
Meng F, Huang G, Yang X, Li Z, Li J, Cao J, Wang Z, Sun L (2013) Identifying the sources and fate of anthropogenically impacted dissolved organic matter (DOM) in urbanized rivers. Water Res 47:5027–5039
Murphy KR, Stedmon CA, Waite TD, Ruiz GM (2008) Distinguishing between terrestrial and autochthonous organic matter sources in marine environments using fluorescence spectroscopy. Mar Chem 108:40–58
Murphy KR, Butler KD, Spencer RGM, Stedmon CA, Boehme JR, Aiken GR (2010) Measurement of dissolved organic matter fluorescence in aquatic environments: an interlaboratory comparison. Environ Sci Technol 44:9405–9412
Naden PS, Old GH, Eliot-Laize C, Granger SJ, Hawkins JM, Bol R, Haygarth P (2010) Assessment of natural fluorescence as a tracer of diffuse agricultural pollution from slurry spreading on intensely-farmed grasslands. Water Res 44:1701–1712
Nguyen HV-M, Hur J, Shin H-S (2010) Changes in spectroscopic and molecular weight characteristics of dissolved organic matter in a river during a storm event. Water Air Soil Pollut 212:395–406
Nguyen HV-M, Lee M-H, Hur J, Schlautman MA (2013) Variations in spectroscopic characteristics and disinfection byproduct formation potentials of dissolved organic matter for two contrasting storm events. J Hydrol 481:132–142
Ohno, T (2002) Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 36:742–746
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M, Kouimtzis T (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res 37:4119–4124
Stedmon CA, Bro R (2008) Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 6:572–579
Stedmon CA, Markager S, Søndergaard M, Vang T, Laubel A, Borch NH, Windelin A (2006) Dissolved organic matter (DOM) export to a temperate estuary: seasonal variations and implications of land use. Estuar Coast 29:388–400
Vähätalo AV, Salonen K, Münster U, Järvinen M, Wetzel RG (2003) Photochemical transformation of allochthonous organic matter provides bioavailable nutrients in a humic lake. Arch Hydrobiol 156:287–314
Vidon P, Wagner LE, Soyeux E (2008) Changes in the character of DOC in streams during storms in two Midwestern watersheds with contrasting land uses. Biogeochemistry 88:257–270
Wallace TA, Ganf GG, Brookes JD (2008) A comparison of phosphorus and DOC leachates from different types of leaf litter in an urban environment. Freshwater Biol 53:1902–1913
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708
Wiegner TN, Tubal RL, MacKenzie RA (2009) Bioavailability and export of dissolved organic matter from a tropical river during base- and stormflow conditions. Limnol Oceanogr 54:1233–1242
Williams CJ, Yamashita Y, Wilson HF, Jaffé R, Xenopoulos MA (2010) Unraveling the role of land use and microbial activity in shaping dissolved organic matter characteristics in stream ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr 55:1159–1171
Wilson HF, Xenopoulos MA (2008) Ecosystem and seasonal control of stream dissolved organic carbon along a gradient of land use. Ecosystems 11:555–568
Wilson HF, Xenopoulos MA (2009) Effects of agricultural land use on the composition of fluvial dissolved organic matter. Nat Geosci 2:37–41
Wu J, Jiang P, Chang SX, Xu Q, Lin Y (2010) Dissolved soil organic carbon and nitrogen were affected by conversion of native forests to plantations in subtropical China. Can J Soil Sci 90:27–36
Yang LY, Hong HS, Guo WD, Huang JL, Li QS, Yu XX (2012) Effects of changing land use on dissolved organic matter in a subtropical river watershed, southeast China. Reg Environ Change 12:145–151
Zhang Y, Yin Y, Feng L, Zhu G, Shi Z, Liu X, Zhang Y (2011) Characterizing chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Tianmuhu and its catchment basin using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and parallel factor analysis. Water Res 45:5110–5122
Zhou F, Qian YZ, Zhu XC, Du K, Jin L (2014) Cause analyssis on the severe rainfall in Zhejiang during the weakening of Fitow. Meteorological monthly 40:930–939 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41071301 and 40601095), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Nos. 13DJ1400103 and 13DJ1400104) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (0400219216). We are deeply grateful to Dr. Penghui Li for constructive comments to improve the quality of the paper; Qinghua Kong for drawing the catchment map; Dr. Jingshui Huang for improving the English text; Hengzao Cui for assistance in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Li, J., Huang, Q. et al. Impacts of land use patterns and typhoon-induced heavy rainfall event on dissolved organic matter properties in the South Tiaoxi River, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 632 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5413-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5413-z