Abstract
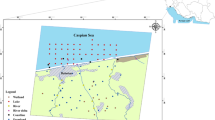
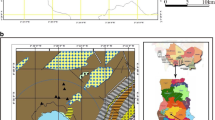
Investigating the mechanisms that influence the concentration of heavy metals (Cu, Cr, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cd) and possible sources of these elements is vital in developing lake management strategies and conserving lake ecosystems. This is the first systematic research focusing on the content, distribution, and origin of heavy metals in Poyang Lake area, the largest freshwater lake in China. Samples were collected, and the concentration of trace elements was measured. The distribution, sources, and potential ecological risk, which has undergone rapid economic development and intensive anthropogenic activity, was evaluated. Multivariate statistical analyses were carried out to determine the relationship between these trace elements and to identify the possible pollution sources. Assessment methods were carried out by applying the geoaccumulation index (I geo) along with potential ecological risk indices (PERI) and USEPA guidelines. The results show that: (1) in comparison to Chinese Soil Standard I, the study area was polluted with Cd and Cr, which had an average concentration that was higher than the Class I criteria. However, the results showed that the heavy metal concentration of Cd was lower than that in other areas. (2) The correlation analysis indicates that Pb and Cd may potentially have the same pollution source. (3) The geoaccumulation (Igeo) and potential ecological risk index (PERI) of these metals were evaluated. The average pollution degree of Igeo decreased in the following order: Cd > Cr > Ni > Cu > Zn > Pb > As, which is similar to that observed from the EF values. PERI varied between 48.64 and 453.45 for all metals, and the general average was calculated as 113.71. Both Igeo and ER indicate that the study area was polluted by Cd. The results of FA show that 87.90 % of the variance could be explained by three factors and an independent variable. The research results obtained from this study can provide the scientific impetus to create policies for the economic development and environmental protection in Poyang Lake and other areas of the world.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An YJ, Kampbell DH (2003) Total, dissolved, and bioavailable metals at Lake Texoma marinas. Environ Pollu 122(2):253–259
Bai JH, Xiao R, Cui BS, Zhang KJ, Wang QG, Liu XH, Gao HF, Huang LB (2011) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollu 159(3):817–824
Bai JH, Xiao R, Zhang KJ, Gao HF (2012) Arsenic and heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from tidal freshwater and salt marshes before and after the flow-sediment regulation regime in the Yellow River Delta, China. J Hydrol 450:244–253
Canuto FAB, Garcia CAB, Alves JPH, Passos EA (2013) Mobility and ecological risk assessment of trace metals in polluted estuarine sediments using a sequential extraction scheme. Environ Monit Assess 185(7):6173–6185
Cao XZ, Shao Y, Deng WJ, Wang H, Wang SL (2014) Spatial distribution and potential ecologic risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of the Nansi Lake in China. Environ Monit Assess 186(12):8845–8856
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (CNEMC) (1990) Soil element background values in China (330–483). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Förstner U, Wittman GTW (1981) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer, Berlin
Fytianos K, Lourantou A (2004) Speciation of elements in sediment samples collected at lakes Volvi and Koronia. N Greece Environ Int 30(1):11–17
Gao HF, Bai JH, Xiao R, Liu PP, Jiang W, Wang JJ (2013) Levels, sources and risk assessment of trace elements in wetland soils of a typical shallow freshwater lake, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27(1):275–284
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control- a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Hallare AV, Kosmehl T, Schulze T, Hollert H, Köhler HR, Triebskorn R (2005) Assessing contamination levels of Laguna lake sediments (Philippines) using a contact assay with zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci Total Environ 347(1–3):254–271
Jian MF, Lu SB, Zhu D (2010) Distribution characteristic of heavy metal pollution in the sediments of topsoil in some representative region of Poyang Lake wetland. Chin J Soil Sci 41(4):981–984 (in Chinese)
Kim KH, Kim SH (1999) Heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils in central regions of Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut 111(1):109–122
Kukrer S, Seker S, Abaci ZT, Kutlu B (2014) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of northern littoral zone of Lake Cldir, Ardahan, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 186(6):3847–3857
Li M, Wu JC, Zhang XL, Zou XJ (2008) Assessment on heavy metal pollution at five estuaries of Poyang. J Nanchang Univ (Natural Sci) 32(5):483–485 (in Chinese)
Liu E, Birch G, Yuan H, Zhang E, Cao Y (2012) Comprehensive evaluation of heavy metal contamination in surface and core sediments of Taihu Lake, the third largest freshwater lake in China. Environ Earth Sci 67(1):39–51
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Severn CG, Hong CB (2000) Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with empirically derived sediment quality guideline. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(10):2598–2601
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39(1):20–31
Mohammad BNA, Lin CY, Cleophas F, Abdullah MH, Musta B (2015) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in Mamut river sediments using sediment quality guidelines and geochemical indices. Environ Monit Assess 187(1):4190
Pakzad HR, Pasandi M, Rahimi H (2014) Distribution of heavy metals in the clastic fine-grained sediments of Gavkhuni playa lake (Southeast of Isfahan, Iran). Environ Earth Sci 71(11):4683–4692
Pradit S, Wattayakorn G, Angsupanich S, Baeyens W, Leemakers M (2010) Distribution of trace elements in sediments and biota of Sonkhla Lake, southern Thailand. Water Air Soil Pollut 206(1–4):155–174
Sheikh JA, Jeelani G, Gavali RS, Shah RA (2014) Weathering and anthropogenic influences on the water and sediment chemistry of Wular Lake, Kashmir Himalaya. Environ Earth Sci 71(6):2837–2846
Skordas K, Kelepertzis E, Kosmidis D, Panagiotaki P, Vafidis D (2015) Assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in the surface sediments of the artificially lake water reservoir Karla, Thessaly, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 73(8):4483–4493
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamyb V, Venkatachalapathyc R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Exotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Swarnalatha K, Letha J, Ayoob S, Nair AG (2015) Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of a tropical lake. Environ Monit Assess 187(6):322. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4558-7
Taylor SR, McLennan S (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241–265
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wan JB, Yan WW, Xie T (2007) Research on heavy metals pollution status of Le’an River, Poyang Lake basin. J Lake Sci 19(4):421–427 (in Chinese)
Wang ME, Markert B, Chen WP, Peng C, Ouyang ZY (2012) Identification of heavy metal pollutants using multivariate analysis and effects of land uses on their accumulation in urban soils in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(10):5889–5897
Xie ZL, Sun ZG, Zhang H, Zhai J (2014) Contamination assessment of arsenic and heavy metals in a typical abandoned estuary wetland—a case study of the Yellow River Delta Natural Reserve. Environ Monit Assess 186(11):7211–7232
Yang J, Chen L, Liu LZ, Shi WL, Meng XZ (2014) Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai. Ecotox Environ Saf 102:129–135
Yang LY, Wang LF, Wang YQ, Zhang W (2015) Geochemical speciation and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Nansi Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 187(5):261. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4480-z
Yi YJ, Yang ZF, Zhang SH (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fisher in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159(10):2575–2585
Yin HB, Gao YN, Fan CX (2011) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Taihu China. Environ Res Lett 6(4):044012
Yu H, Zhang WB, Yu JP (2011) Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments of Hongze Lake. Environ Sci 32(2):437–444
Yu T, Zhang Y, Meng W, Hu X (2012) Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4367–4382
Zhang Y, Hu XN, Tao Yu (2012) Distribution and risk assessment of metals in sediments from Taihu Lake, China using multivariate statistics and multiple tools. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89(5):1009–1015
Zhang J, Chen X, Liu QC, Wu L (2014a) Distribution and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in the main estuaries of lake Poyang’s tributaries. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 23(1):95–100 (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Li ZH, Chen J, Wang M, Tao R, Liu D (2014b) Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environ Earth Sci 72(4):1279–1288
Zhang H, Wang ZF, Zhang YL, Ding MJ, Li LH (2015) Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai-Tibet highway. Sci Total Environ 521–522:160–172
Zheng LG, Liu GJ, Kang Y, Yang RK (2010) Some potential hazardous trace elements contamination and their ecological risk in sediments of western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 166(1–4):379–386
Zhuang W, Gao XL (2014) Integrated assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay and the coastal waters of the Zhangzi Island, China: comparision among typical marine sediment quality indices. PLoS One 9(4):e94145
Acknowledgments
This research is founded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41361018, 41401587), the Collaborative Innovation Center for Major Ecological Security Issues of Jiangxi Province and Monitoring Implementation (No. JXS-EW-00), the opening fund (PK2013003) of Key Laboratory of Poyang Lake Wetland and Watershed Research, Ministry of Education (Jiangxi Normal University), the open fund of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmental Change and Ecological Construction (Nanjing Normal University). We also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Collaborative Innovation Center for Major Ecological Security Issues of Jiangxi Province and Monitoring Implementation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Assessing heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Poyang Lake area, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 549 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5240-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5240-7