Abstract
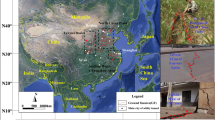
Xi’an City is located at the central region of the Fenwei Plain, and there are 14 ground fissures (labelled GF1–GF14) which have been closely monitored in the urban area of Xi’an City. When a shield tunnel is constructed in a region with ground fissures, problems (such as cracking or failure of the tunnel lining, leakage of groundwater into the tunnel, damage to the completed tunnels and shield, and long-term instability) may be encountered due to the activity of ground fissure. To mitigate the adverse impact caused by the activity of ground fissure, a series of countermeasures are suggested in this paper, which include installation of movement joints, installation of a flexible layer for controlling deformation, foundation reinforcement with cement grouting, and improvement of existing water resistance. A case history regarding the metro tunnel (Xi’an Metro Line 1) which has been intersected the ground fissure 5 (GF5) obliquely was analyzed. The aforesaid countermeasures were applied to this case history. After improving the existing water resistance, the permeability of the surrounding soils was effectively reduced to about 4.0 × 10−8 cm/s and the groundwater leakage into the tunnel was minimal. Observations of the accumulative ground surface settlement near the fissure verified the effectiveness of the countermeasures applied to this case history.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui QL, Wu HN, Shen SL, Xu YS, Ye GL (2015) Chinese karst geology and measures to prevent geohazards during shield tunnelling in karst regions with caves. Nat Hazards 77:129–152
Du YJ, Jiang NJ, Shen SL, Jin F (2012) Experimental investigation of influence of acid rain on leaching and hydraulic characteristics of cement-based solidified/stabilized lead contaminated clay. J Hazard Mater 225–226:195–201
Du YJ, Jiang NJ, Liu SY, Jin F, Singh DN, Pulppara A (2014) Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of cement solidified zinc-contaminated kaolin clay. Can Geotech J 51(3):289–302
Fan W, Deng LS, Peng JB (2008) Study on the physical model experiment of subway tunnel crossing the ground fissure belt. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(9):1917–1923 (in Chinese)
Fargnoli V, Boldini D, Amorosi A (2013) TBM tunnelling-induced settlements in coarse-grained soils: the case of the new Milan underground line 5. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 38:336–347
Huang QB, Peng JB, Fan W, Men YM, Zhang JM (2007) Estimation of the maximum displacement of ground fissures along Xi’an Metro Line 2 and its engineering classification. J Eng Geol 15(4):469–474 (in Chinese)
Huang QB, Peng JB, Men YM (2008) Model test study on effect of ground fissure on open-cut metro tunnel with integral lining. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(11):2324–2331 (in Chinese)
Huang QB, Peng JB, Fan HW, Yang PM, Men YM (2009) Metro tunnel hazards induced by active ground fissures in Xi’an and relevant control measures. Chin J Geotech Eng 31(5):781–788 (in Chinese)
IHEG (Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology), China Geology Bureau (1979) Hydrogeological Atlas of China. China Map Publisher, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ju SJ, Zhu WB (2007) Study on geological investigation methods for shield tunneling in mixed ground. Tunnel Constr 27(6):10–14 (in Chinese)
Lee CF, Zhang JM, Zhang YX (1996) Evolution and origin of the ground fissures in Xian, China. Eng Geol 43(1):45–55
Li FR (2006) Technical scheme of running tunnels of line 2 of Xi’an mass rapid transit system crossing ground cracking zones. Tunnel Constr 26(6):30–33 (in Chinese)
Li YL, Yang JC, Hu XM (2000) Origin of ground fissures in the Shanxi Graben System, Northern China. Eng Geol 55(4):267–275
Li XS, Wang J, Wang WP, Wang PP, Song YH, Li ZS, Zhang FZ, Peng JB, Li XA (2007) Ground fissures along Xi’an subway line 2: characteristics, harms and measures. J Eng Geol 15(4):463–468 (in Chinese)
Liang YH, Shao SJ, Wang TT (2009) Analysis of current status of Xi’an cracks and MTR measures for tunnel construction. Rock Soil Mech 30(S2):399–403 (in Chinese)
Liao SM, Peng FL, Shen SL (2008) Analysis of shearing effect on tunnel induced by load transfer along longitudinal direction. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 23(4):421–430
Liao SM, Liu JH, Wang RL, Li ZM (2009) Shield tunneling and environment protection in Shanghai soft ground. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 24(4):454–465
Peng JB (2012) Hazards caused by ground fissures in Xi’an. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Qu FF, Zhang Q, Lu Z, Zhao CY, Yang CS, Zhang J (2014) Land subsidence and ground fissures in Xi’an, China 2005–2012 revealed by multi-band InSAR time-series analysis. Remote Sens Environ 155:366–376
Shen SL, Xu YS (2011) Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can Geotech J 48(9):1378–1392
Shen SL, Xu YS, Hong ZS (2006) Estimation of land subsidence based on groundwater flow model. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 24(2):149–167
Shen SL, Horpibulsuk S, Liao SM, Peng FL (2009) Analysis of the behavior of DOT tunnel lining caused by rolling correction operation. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 24(1):84–90
Shen SL, Du YJ, Luo CY (2010) Evaluation of the effect of double-o-tunnel rolling-correction via apply one-side block loading. Can Geotech J 47(10):1060–1070
Shen SL, Wang ZF, Yang J, Ho EC (2013a) Generalized approach for prediction of jet grout column diameter. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139(12):2060–2069
Shen SL, Wang ZF, Sun WJ, Wang LB, Horpibulsuk S (2013b) A field trial of horizontal jet grouting using the composite-pipe method in the soft deposits of Shanghai. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 35:142–151
Shen SL, Wang ZF, Horpibulsuk S, Kim YH (2013c) Jet-Grouting with a newly developed technology: the Twin-Jet method. Eng Geol 152(1):87–95
Shen SL, Wu HN, Cui YJ, Yin ZY (2014) Long-term settlement behavior of the metro tunnel in Shanghai. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 40:309–323
Shen SL, Wang JP, Wu HN, Xu YS, Ye GL, Yin ZY. (2015) Evaluation of hydraulic conductivity for both marine and deltaic deposit based on piezocone test. Ocean Engineering, published online
Suo CM, Wang DQ, Liu ZZ (2005) Land fissures and subsidence prevention in Xi’an. Quat Sci 25(1):23–28 (in Chinese)
Tan Y, Wang DL (2013a) Characteristics of a large-scale deep foundation pit excavated by central-island technique in Shanghai soft clay. I: bottom-up construction of the central cylindrical shaft. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139(11):1875–1893
Tan Y, Wang DL (2013b) Characteristics of a large-scale deep foundation pit excavated by central-island technique in Shanghai soft clay. II: top-down construction of the peripheral rectangular pit. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139(11):1894–1910
Wu Q, Chen PP (2003) Research on state of art and prospect of earth fissures. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 14(1):22–27 (in Chinese)
Wu HN, Huang RQ, Sun WJ, Shen SL, Xu YS, Liu YB, Du SJ (2014) Leaking behaviour of shield tunnels under the Huangpu River of Shanghai with induced hazards. Nat Hazards 70(2):1115–1132
Wu HN, Shen SL, Liao SM, Yin ZY (2015) Longitudinal structural modelling of shield tunnels considering shearing dislocation between segmental rings. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 50:317–323
Xu YS, Shen SL, Cai ZY, Zhou GY (2008) The state of land subsidence and prediction activities due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat Hazards 45(1):123–135
Xu JS, Lu QZ, Fu HY (2012a) Ground fissures along Xi’an subway line 4: hazard analysis and countermeasures. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 23(1):76–82 (in Chinese)
Xu YS, Ma L, Shen SL, Sun WJ (2012b) Evaluation of land subsidence by considering underground structures that penetrate the aquifers of Shanghai, China. Hydrogeol J 20(8):1623–1634
Xu YS, Ma L, Du YJ, Shen SL (2012c) Analysis on urbanization induced land subsidence in Shanghai. Nat Hazards 63(2):1255–1267
Xu YS, Shen SL, Du YJ, Chai JC, Horpibulsuk S (2013a) Modelling the cutoff behavior of underground structure in multi-aquifer-aquitard groundwater system. Nat Hazards 66(2):731–748
Xu YS, Huang RQ, Han J, Shen SL (2013b) Evaluation of allowable withdrawn volume of groundwater based on observed data. Nat Hazards 67(2):513–522
Yang YS (2006) A scheme for the transit tunnels of Xi’an Metro Line 2 to pass through ground fissures. Urban Rapid Rail Transit 19(3):67–69 (in Chinese)
Ye GL, Ye B, Zhang F (2013) Strength and dilatancy of overconsolidated clays in drained true triaxial tests. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 140(4):06013006
Ye GL, Hashimoto T, Shen SL, Zhu HH, Bai TH (2015) Important lesson learnt from unusual ground settlement during Double-O-Tube tunneling in soft ground. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 49:79–91
Acknowledgments
The research work described herein was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 41372283 and 51378004), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (310821161022), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M570803) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program: 2015CB057806). These financial supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZF., Shen, SL., Cheng, WC. et al. Ground fissures in Xi’an and measures to prevent damage to the Metro tunnel system due to geohazards. Environ Earth Sci 75, 511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5169-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5169-x