Abstract
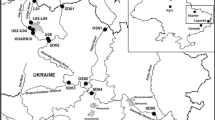
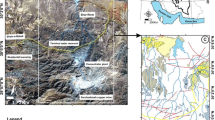
Sited in the Poços de Caldas Plateau, in south-eastern Brazil, the Uranium Mining and Milling Facilities (UMMF) of Caldas are in the process of decommissioning. The main environmental problem in this site is the generation of acid mine drainage (AMD) in the tailings dam, open pit and waste rock piles. The aim of this work is to evaluate, by hydrochemical studies, the influence of acidic effluents from the Caldas UMMF, on the hydrochemistry of surface water along three watersheds: Consulta Brook, Soberbo Creek and Taquari River. Twelve sampling stations were established to carry out the investigation. Two of them were located at effluent retention ponds. Sampling was performed in the rainy and dry seasons of 2011, and the measured parameters were Eh, pH, EC (electrical conductivity), SO4 2−, HCO3 −, Cl−, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe. The results have shown that iron is not a main constituent of the ionic composition of the local AMD. It could also be observed that acidic effluents were being discharged from retention ponds into the watercourses, causing a pronounced increase of the sulfate and calcium concentrations downstream. To trace the AMD migration the (SO4 2−/HCO3 −)/(Na+ + K+/Ca2+) ratio was used. A detailed investigation of the near-surface groundwater is recommended downstream of the effluent ponds sites to evaluate the need for mitigating actions such as constructing hydraulic barriers. The present article shows that using simple techniques, such as Eh–pH and Piper diagrams, it is possible to depict the AMD fluvial migration pattern, which is an important information both to the authority responsible incumbent upon the remediation of the site, and to the affected interested parties who inhabit the impacted region.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campos MB, Azevedo H, Nascimento MRL, Roque CV, Rodgher S (2011) Environmental assessment of water from a uranium mine (Caldas, Minas Gerais State, Brazil) in a decommissioning operation. Environ Earth Sci 62:857–863
Canovas CR, Olias M, Nieto JM, Sarmiento AM, Ceron JC (2007) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the Tinto and Odiel Rivers (SW Spain). Factors controlling metal contents. Sci Total Environ 373:363–382
Chadha DK (1999) A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7:431–439
Cipriani M (2002) Mitigation of social and environmental impacts caused by the definitive closure of uranium mines, Ph.D. Thesis (in Portuguese), State University of Campinas
Custódio E (1983) Princípios básicos de química y radioquímica de aguas subterrâneas. In: Custódio E, Llamas MR (ed) Hidrologia Subterrânea. Barcelona: Ediciones Omega. 2. Ed., Tomo 1, Sección 4, pp 174–246
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural waters, surface and groundwater environments, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Fernandes HM, Franklin MR (2001) Assessment of acid rock drainage pollutants released at the uranium mining site of Poços de Caldas—Brazil. J Environ Radioact 54:5–25
Fernandes HM, Veiga LHS, Franklin MR, Prado VCS, Taddei JF (1995) Environmental impact assessment of uranium and milling facilities: a study case at the Poços de Caldas uranium mining and milling site, Brazil. J Geochem Explor 52:161–173
Fernandes HM, Franklin MR, Veiga LHS, Freitas P, Gomiero LA (1996) Management of uranium mill tailing: geochemical process and radiological risk assessment. J Environ Radioact 30:69–95
Fernandes HM, Franklin MR, Veiga LHS (1998) Acid rock drainage and radiological environmental impacts: a study case of the Uranium mining and milling facilities at Poços de Caldas. Waste Manag 18:169–181
Fernandes HM, Franklin MR, Gomiero MR (2008) Critical analysis of the waste management performance of two uranium production units in Brazil-part I: Poços de Caldas production centre. J Environ Manage 87:59–72
Fetter CW (1994) Applied hydrogeology, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Franklin MR (2007) Numerical modeling of water flow and geochemical processes applied to the prediction of acid drainage at a waste rock pile in the uranium mine of Poços de Caldas—MG, Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro
Garrals RM, Christ CL (1965) Solutions, minerals, and equilibria. Harper and Row, New York
Golder Associates Brazil Consulting and Projects Ltd. (2012) Plan for de Recovery of Degraded areas—INB UTM Caldas. Technical Report No. RT-006_099-515-3023_01-j
Gomes AFS, Lopez DL, Ladeira ACQ (2012) Characterization and assessment of chemical modifications of metal-bearing sludges arising from unsuitable disposal. J Hazard Mater 199–200:418–425
Jambor JL (2003) Mine-waste mineralogy and mineralogical perspectives of acid-basic accounting. In: Jambor JL, Blowes DW, Ritchie AIM (eds) Environmental aspects of mine wastes. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Vancouver, pp 117–145
Majdalani AA, Tavares AM (2001) Status of uranium in Brazil. In: Assessment of uranium deposit types and resources — a worldwide perspective. In: Proceedings of a Technical Committee Meeting organized by the International Atomic Energy Agency and the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency and held in Vienna, IAEA TECDOC 1258, December 2001. International Atomic Energy Agency, Viena
Ptacek CJ, Blowes DW (2003) Geochemistry of concentrated waters at mine-waste sites. In: Jambor JL, Blowes DW, Ritchie AIM (eds) Environmental aspects of mine wastes. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Vancouver, pp 239–251
Rodgher S, Azevedo H, Ferrari CR, Roque CV, Ronqui LB, Campos MB, Nascimento MRL (2013) Evaluation of surface water quality in aquatic bodies under the influence of uranium mining (MG, Brazil). Environ Monit Assess 185:2395–2406
Schorscher HD, Shea ME (1992) The regional geology of the Poços de Caldas alkaline complex: mineralogy and geochemistry of selected nepheline syenites and phonolites. J Geochem Explor 45:25–51
U. S. EnvironmentaL Protection Agency—USEPA (1994) Acid mine drainage prediction. Office of Solid Waste, Washington DC
Waber N, Schorscher HD, Peters T (1992) Hydrothermal and supergene uranium mineralization at the Osamu Utsumi mine, Poços de Caldas, Minas Gerais, Brazil. J Geochem Explor 45:53–112
Williams RE (1975) Waste production and disposal in mining, milling, and metallurgical industries. Miller-Freeman Publishing Company, San Francisco
Williamson MA, Rimstidt JD (1994) The kinetics and electrochemical rate-determining step of aqueous pyrite oxidation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:5443–5454
Wooley AR (1987) Alkaline rocks and carhonatites of the World, Part 1. North and South America. British Museum (Natural History), London, p 216
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the Brazilian Scientific and Technological Development Council (CNPq), the Minas Gerais Foundation for Research Support (Fapemig) for financial support, the Brazilian Institute for Mineral, Water, and Biodiversity Resources (INCT-Acqua), and the Brazilian Nuclear Industries (INB) for operational and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Carvalho Filho, C.A., Moreira, R.M., Guimarães, B.F. et al. Hydrochemical assessment of surface water in watersheds near the Uranium Mining and Milling Facilities of Caldas, Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 75, 187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5070-7