Abstract
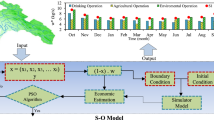
Temporal changes in system’s topology and/or socioeconomic criteria may force the authorities to enforce waste load reallocation strategies to sustain water quality standards in a receiving body. This paper proposes a simulation–optimization model to tackle the challenging waste load reallocation in a river–reservoir system. This study links a 2-dimensional process-based water quality simulation model and a surrogate data-driven model with an efficient optimization algorithm to structure a systematic approach and methodology for reallocation of waste loads in a river–reservoir system. Long response time of the reservoir is accounted for by the continuous and long-term simulation of the system for identification of the vulnerable conditions and their consequences. The proposed methodology is particularly suitable for high-dimensional river–reservoir operation optimization with water quality–quantity objectives. To reduce the computational burden, we substitute the simulation model with a surrogate model in an online-dynamically refined routine. The optimum waste load reallocation strategies, for prior and after dam construction, are compared, and their impacts on waste allocation are discussed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshar MH (2013) Extension of the constrained particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimal operation of multi-reservoirs system. Electr Power Energy Syst 51:71–81
Afshar A, Saadatpour M (2009) Reservoir eutrophication modeling, sensitivity analysis and assessment: application to Karkheh reservoir, Iran. Environ Eng Sci 26(7):1227–1238
Afshar A, Saadatpour M, Marino MA (2012) Development of a complex system dynamic eutrophication model: application to Karkheh reservoir. Environ Eng Sci. doi:10.1089/ees.2010.0203
Afshar A, Shojaei N, Sagharjooghifarahani M (2013) Multiobjective calibration of reservoir water quality modeling using multiobjective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO). Water Resour Manag 27:1931–1947
Back AD, Trappenberg TP (2001) Selecting inputs for modeling using normalized higher order statistics and independent component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(3):612–617
Burn DH, McBean EA (1985) Optimization modeling of water quality in an uncertain environment. Water Resour Res 21(7):934–940
Burn DH, Yulianti JS (2001) Waste-load allocation using genetic algorithms. Water Resour Plan Manag 127(2):121–129
Castelletti A, Zaiacomo M.D, Galelli S, Restelli M, Sanavia P, Soncini-Sessa R, Antenucci J (2009) An emulation modelling approach to reduce the complexity of a 3D hydrodynamic-ecological model of a reservoir. Paper presented at international symposium on environmental software systems. Environ. Inf. Inst., Venice, Italy, 2–9 Oct
Castelletti A, Antenucci JP, Limosani D, Quach TX, Soncini-Sessa R (2011) Interactive response surface approaches using computationally intensive models for multiobjective planning of lake water quality remediation. Water Resour Res 47:W09534
Chaves P, Kojiri P (2005) Water quality control. Water Encyclop. doi:10.1002/047147844X.wq601
Cole TM, Wells SA (2008) User’s Guide for CE-QUAL-W2: a two-dimensional, laterally averaged, hydrodynamic and water quality model, version 3.5. U.S. Army Corps of Eng, Draft File report, 20314-1000, Washington, DC
Cui Z, Cai X, Zeng J, Sun G (2008) Particle swarm optimization with FUSS and RWS for high dimensional functions. Appl Math Comput 205:98–108
Dai T, Labadie J (2001) River basin network model for integrated water quantity/quality management. J Water Resour Plan Manag 127(5):295–305
Diogo PA, Fonseca M, Coelho PS, Mateus NS, Almeida MC, Rodrigues AC (2008) Reservoir phosphorous sources evaluation and water quality modeling in a transboundary watershed. Desalination 226:200–214
Eberhart RC, Shi Y (1998) Comparison between genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Evolutionary Programming VII: Proc. 7th annual conference on Evolutionary Programming Conf., San Diego, CA
Friedl G, Wuest A (2002) Disrupting biogeochemical cycles—consequences of damming. Aquat Sci 64:55–65
Fujiwara O, Gnanendran SK, Ohgaki S (1986) River quality management under stochastic stream flow. J Environ Eng ASCE 112(2):185–198
Gelda RK, Effler SW (2007) Simulation of operations and water quality performance of reservoir multilevel intake configurations. J Water Resour Plan Manag 133(1):78–86
Ghosh S, Mujumdar PP (2006) Risk minimization in water quality control problems of a river system. Adv Water Resour 29(2006):458–470
Harmon TS, Smoak JM, Matthew N, Waters MN, Sanders CJ (2014) Hydrologic fragmentation induced eutrophication in Dove Sound, Upper Florida Keys, USA. Environ Earth Sci 71:4387–4395
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2006) Grey fuzzy optimization model for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 29(7):1088–1105
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the fourth IEEE international conference on neural networks, Perth, Australia. IEEE Service Center, pp 1942–1948
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2006) Optimal reservoir operation considering the water quality issues: a stochastic conflict resolution approach. Water Resour Res 42:W12401. doi:10.1029/2005WR004575
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2007) A stochastic conflict resolution model for water quality management in reservoir–river systems. Adv Water Resour 30(4):866–882
Mousavi SJ, Shourian M (2010) Adaptive sequentially space filling metamodeling applied in optimal water quantity allocation at basin scale. Water Resour Res 46:W03520. doi:10.1029/2008WR007076
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Karimi A, Azadnia AA (2013) Optimal water and waste-load allocations in rivers using a fuzzy transformation technique: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 185(3):2483–2502
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Karimi A, Azadnia AA, Jafazadegan K (2014) Optimal water and waste load allocation in reservoir–river systems: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 71:4127–4142
Ostadrahimi L, Marino MA, Afshar A (2012) Multi reservoir operation rules: multi swarm PSO based optimization approach. Water Resour Manage 26:407–427
Ostfeld A, Salomons E (2005) Solving the inverse problem of deliberate contaminants intrusions into water distribution systems. EWRI ASCE conference, Anchorage, Alaska, USA (published at ASCE web database)
Parmar DL, Keshari AK (2014) Waste load allocation using wastewater treatment and flow augmentation. Environ Model Assess 19:35–44
Saadatpour M, Afshar A (2007) Waste load allocation modeling with fuzzy goals; simulation–optimization approach. Water Resour Manag 21(7):1207–1224
Sasikumar K, Mujumdar PP (2000) Application of fuzzy probability in water quality management of a river system. Int J Syst Sci 31(5):575–591
Shourian M, Mousavi SJ, Menhaj MB, Jabbari E (2008) Neural-network-based simulation–optimization model for water allocation planning at basin scale. J Hydroinform 10(4):331–343
Sindelar R, Babuska R (2004) Input selection for nonlinear regression models. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 12(5):688–696
Skardi MJE, Afshar A, Saadatpour M, Solis SS (2014) Hybrid ACO–ANN-based multi-objective simulation–optimization model for pollutant load control at basin scale. Environ Model Assess. doi:10.1007/s10666-014-9413-7
Takyi AK, Lence BJ (1999) Surface water quality management using a multiple-realization chance constraint method. Water Resour Res 35(5):1657–1670
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA) (1999) Storm water technology fact sheet. Wet Detention Ponds, Office of Water, Washington, DC. EPA 832-F-99-048
Wagner BJ (1995) Sampling design methods for groundwater modeling under uncertainty. Water Resour Res 31(10):2581–2591
Wang GG, Shan S (2006) Review of metamodeling techniques in support of engineering design optimization. ASME Trans J Mech Des 129(4):370–380
Yandamuri SR, Srinivasan K, Bhallamudi MS (2006) Multiobjective optimal waste load allocation models for rivers using nondominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. J Water Resour Plan Manag 132(3):133–143
Zhang XS, Srinivasan R, Liew MV (2009) Approximating SWAT model using artificial neural network and support vector machine. J Am Water Resour Assoc 45(2):460–474
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afshar, A., Masoumi, F. Waste load reallocation in river–reservoir systems: simulation–optimization approach. Environ Earth Sci 75, 53 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4812-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4812-x