Abstract
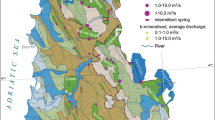
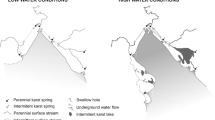
Mediterranean karstic aquifers are a major source of water supply for drinking water and agricultural use. In semiarid areas, the risk of causing an intensive exploitation is high, leading to degradation processes of water quality, not only due to limited agricultural activities developed on the karstic rocks—being generally poorly developed soils—but to the presence of deep evaporates which can be mobilised, or because of being coastal aquifers where seawater intrusion can progress rapidly. Moreover, karstic massifs constitute often positive reliefs that can generate barriers for civil works, more and more saved by building sophisticated tunnels; such works can affect the quantity and quality of the waters from the karst. Five examples of human impacts on some karst aquifers in SE of Spain are shown in this paper, three of them with impacts on water quality and the other two correspond to the impact of tunnels in high-speed trains drilling below the water table.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera H, Murillo JM (2009) The effect of possible climate change on natural groundwater recharge based on a simple model: a study of four karstic aquifers in SE Spain. Environ Geol 57:963–974
Andreo B, Ravbar N, Vías JM (2009) Source vulnerability mapping in carbonate (karst) aquifers by extension of the COP method: application to pilot sites. Hydrogeol J 17:749–758
Andreu JM (1997) Contribución de la sobreexplotación al conocimiento de los acuíferos kársticos de Crevillente, Cid y Cabeçó d’Or (provincia de Alicante). Doctoral Thesis, Universidad de Alicante, p 377
Andreu JM, Pulido-Bosch A, Llamas MR, Bru C, Martínez-Santos P, García-Sánchez E, Villacampa L (2008) Overexploitation and water quality in the Crevillente aquifer (Alicante, SE Spain). In: Water pollution, IX. WIT Press, pp 75–84
Andreu JM, García-Sánchez E, Pulido-Bosch A, Jorreto S, Francés I (2010) Influence of Triassic deposits on water quality of some karstic aquifer to the south of Alicante (Spain). Estud Geol 66(1):131–138
Bakalowicz M, El Hakim M, El-Hajj A (2008) Karst groundwater resources in the countries of eastern Mediterranean: the example of Lebanon. Environ Geol 54:597–604
Barrocu G (2003) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Italy. In: Coastal aquifers intrusion technology: mediterranean countries. Publicaciones del Instituto Geológico y Minero de España. Serie Hidrogeología y Aguas Subterráneas, 8:207–223
Bicalho CC, Batiot-Guilhe C, Seidel JL, Van Exter S, Jourde H (2012) Hydrodynamical changes and their consequences on groundwater hydrochemistry induced by three decades of intense exploitation in a Mediterranean karst system. Environ Earth Sci 65:2311–2319
Chiocchini U, Castaldi F (2011) The impact of groundwater on the excavation of tunnels in two different hydrogeological settings in central Italy. Hydrogeol J 19:651–669
Cotecchia V, Grassi D, Polemio M (2005) Carbonate aquifers in apulia and seawater intrusion. Giornale di Geologia Applicata 1:219–231
Custodio E (2002) Aquifer overexploitation: what does it mean? Hydrogeol J 10:254–277
Daher W, Pistre S, Kneppers A, Bakalowicz M, Najem W (2011) Karst and artificial recharge: theoretical and practical problems. A preliminary approach to artificial recharge assessment. J Hydrol 408:189–202
Daniele L, Vallejos A, Corbella M, Molina L, Pulido-Bosch A (2013) Geochemical simulations to assess water–rock interactions in complex carbonate aquifers: the case of Aguadulce (SE Spain). Appl Geochem 29:43–54
Day MJ (2004) Karstic problems in the construction of Milwaukee’s deep tunnels. Environ Geol 45:859–863
Delle Rose M, Parise M (2002) Karst subsidence in south-central Apulia, southern Italy. Int J Speleol 31:181–199
Díaz-Puga MA, Vallejos A, Daniele L, Sola F, Rodríguez-Delgado D, Molina L, Pulido-Bosch A (2011) An oceanographic survey for the detection of a possible submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone of Campo de Dalias, SE Spain. In: Lambrakis N, Stournaras G, Katsanou K (eds) Advances in the research of aquatic environment. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 417–424
Dörfliger N (2003) The state of the French Mediterranean coastal aquifers. In coastal aquifers intrusion technology: mediterranean countries. Publicaciones del Instituto Geológico y Minero de España. Serie Hidrogeología y Aguas Subterráneas 8:187–206
Einsiedl F, Radke M (2010) Assessing the vulnerability of a karst groundwater system to contamination by pharmaceuticals. Geophys Res Abstr 12:EGU2010–7907
Einsiedl F, Radke M, Maloszewski P (2010) Occurrence and transport of pharmaceuticals in a karst groundwater system affected by domestic wastewater treatment plants. J Contam Hydrol 117:26–36
El Gaouzi FJ, Sebilo M, Ribstein P, Plagnes V, Boeckx P, Xue D, Derenne S, Zakeossian M (2013) Using δ15N and δ18O values to identify sources of nitrate in karstic springs in the Paris basin (France). Appl Geochem 35:230–243
Elkhatib H, Günay G (1993) Analysis of sea water intrusion associated with karstic channels beneath Ovacik plain, Southern Turkey. Hydrogeol Processes Karst Terr IAHS Publ. 207:129–132
Fidelibus MD, Gutiérrez F, Spilotro S (2011) Human-induced hydrogeological changes and sinkholes in the coastal gypsum karst of Lesina Marina area (Foggia Province, Italy). Eng Geol 118:1–19
Fleury P, Bakalowicz M, de Marsily G (2007) Submarine springs and coastal aquifers: a review. J Hydrol 339:79–92
Foster J (2008) Water quality near wastewater treatment systems in alluvial and karst hydrogeologic settings, Black Hills, South Dakota. South Dakota Geological Survey. Report of Investigations 117, p 141
Garing C, Luquot L, Pezard PA, Gouze P (2013) Geochemical investigations of saltwater intrusion into the coastal carbonate aquifer of Mallorca, Spain. Appl Geochem 39:1–10
Gisbert J, Vallejos A, González A, Pulido-Bosch A (2009) Environmental and hydrogeological problems in karstic terrains crossed by tunnels: a case study. Environ Geol 58:347–357
Günay G (2003) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of the Mediterranean coast of Turkey. In coastal aquifers intrusion technology: mediterranean countries. Publicaciones del Instituto Geológico y Minero de España. Serie Hidrogeología y Aguas Subterráneas 8:265–277
Heinz B, Birk S, Liedl R, Geyer T, Straub KL, Andresen J, Bester K, Kappler A (2009) Water quality deterioration at a karst spring (Gallusquelle, Germany) due to combined sewer overflow: evidence of bacterial and micro-pollutant contamination. Environ Geol 57:797–808
IGME (2003) Results of the project on the knowledge of aquifers in the South of Sierra de Gádor-Campo de Dalías (in Spanish). Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología. p 26, Madrid
Jemcov I (2014) Estimating potential for exploitation of karst aquifer: case example on two Serbian karst aquifer. Environ Earth Sci 71:543–551
Jiménez P, Andreo B (2012) Estudio comparativo de la respuesta hidrodinámica de varios acuíferos carbonáticos del sur de España a partir del análisis correlatorio y espectral. Geogaceta 52:133–136
Jiménez P, Carrasco F, Durán JJ, Andreo B, López-Geta JA (2004) Análisis de la respuesta hidrodinámica de acuíferos carbonáticos de la Cordillera Bética occidental (Sur de España). Boletín Geológico y Minero 115:187–198
Kaçaroğlu F (1999) Review of groundwater pollution and protection in karst areas. Water Air Soil Pollut 113:337–356
Katz BG, Griffin DW, Davis JH (2009) Groundwater quality impacts from the land application of treated municipal wastewater in a large karstic spring basin: chemical and microbiological indicators. Sci Total Environ 407:2872–2886
Kitterod NO, Colleuille H, Wong WK, Pedersen TS (2000) Simulation of groundwater drainage into a tunnel in fractured rocks and numerical analysis of leakage remediation, Romeriksporten tunnel, Norway. Hydrogeol J 8:480–493
Kollarits S, Kuschnig G, Veselic M, Pavicic A, Soccorso C, Aurighi M (2006) Decision-support systems for groundwater protection: innovative tools for resource management. Environ Geol 49:840–848
Lambrakis NJ (1998) The impact of human activities in the Malia coastal area (Crete) on groundwater quality. Environ Geol 36(1–2):87–92
Larocque M, Mangin A, Razack M, Banton O (1998) Contribution of correlation and spectral analyses to the regional study of a large karst aquifer (Charente, France). J Hydrol 205:217–231
Leibundgut C (1998) Vulnerability of karst aquifers. IAHS Publication, Paris, pp 45–60
Li SL, Liu CQ, Lang YC, Zhao ZQ, Zhou ZH (2010) Tracing the sources of nitrate in karstic groundwater in Zunyi, Southwest China: a combined nitrogen isotope and water chemistry approach. Environ Earth Sci 60:1415–1423
Long DT, Voice TC, Niagolova ND, McElmurry SP, Petropoulos EA, Ganev VS, Havezov I, Chou K (2003) Aqueous geochemistry of groundwater in a region affected by Balkan Endemic Nephropathy. In: 8th International Conferences on environmental science and technology. Lemnos island, Greece, pp 557–564
Long DT, Voice TC, Niagolova ND, McElmurry SP (2012) Effects of human activities on karst groundwater geochemistry in a rural area in the Balkans. Appl Geochem 27:1920–1931
Mangin A (1981) Utilisation des analyses corrélatoire et spectrale dans l’approche des systèmes hydrologiques. CR Acad Sci Paris 293:401–404
Mangin A (1984) Pour une meilleure conaissance des systèmes hydrologiques à partir des analyses corrélatoire et spectrale. J Hydrol 67:25–43
Mangin A, Pulido-Bosch A (1983) Aplicación de los análisis de correlación y espectral en el estudio de acuíferos kársticos. Tecniterrae 51:53–65
Maramathas A, Marouli Z, Marinos-Kouris D (2003) brackish karstic springs model application to Almiros spring in Crete. Groundwater 41:608–619
Marín AI, Dörfliger N, Andreo B (2012) Comparative application of two methods (COP and PaPRIKa) for groundwater vulnerability mapping in Mediterranean karst aquifers (France and Spain). Environ Earth Sci 65:2407–2421
Milanovic P (2002) The environmental impacts of human activities and engineering constructions in karst regions. Episodes 25:13–21
Molina L, Vallejos A, Pulido-Bosch A, Sánchez-Martos F (2002) Water temperature and conductivity variability as indicators of groundwater behaviour in complex aquifer systems in the south-east of Spain. Hydrol Process 16:3365–3378
Molina L, Sánchez-Martos F, Pulido-Bosch A, Vallejos A (2003) Origin of boron from a complex aquifer in Southeast of Spain. Environ Geol 44:301–307
Molinero J, Samper J, Luanes R (2002) Numerical modelling of the transient hydrogeological response produced by a tunnel construction in fractured bedrocks. Eng Geol 64:369–386
Mudarra M, Andreo B (2011) Relative importance of the saturated and the unsaturated zones in the hydrogeological functioning of karst aquifers: the case of Alta Cadena (Southern Spain). J Hydrol 397:263–280
Mudarra M, Andreo B, Barberá JA, Mudry J (2014) Hydrochemical dynamics of TOC and NO3 − contents as natural tracers of infiltration in karst aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 71:507–523
Padilla A, Pulido-Bosch A (1995) Study of hydrographs of karstic aquifers by means of correlation and cross-spectral analysis. J Hydrol 168:73–89
Padilla A, Pulido-Bosch A, Mangin A (1994) Relative importance of baseflow and quickflow from hydrographs of karst spring. Ground Water 32:267–277
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Kelly WR (2001) Determination of the sources of nitrate contamination in karst springs using isotopic and chemical indicators. Chem Geol 179:113–128
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Greenberg SE, Krapac IG, Landsberger S, O’Kelly DJ (2006) Characterization and identification of Na–Cl sources in ground water. Ground Water 44:176–187
Parise M, Qiriazi P, Sala S (2004) Natural and anthropogenic hazards in karst areas of Albania. Nat Haz Earth Syst Sci 4:569–581
Parise M, De Waele J, Gutierrez F (2008) Engineering and environmental problems in karst—An introduction. Eng Geol 99:91–94
Potié L, Ricour J (1974) Etudes et captage de resurgences d’eau douce sous-marines. Ressources en eau 5:26
Pu J, Cao M, Zhang Y, Yuan D, Zhao H (2014) Hydrochemical indications of human impact on karst groundwater in a subtropical karst area, Chongqing, China. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3073-4
Pulido-Bosch A (1985) L’exploitation minière de l’eau dans l’aquifère de la Sierra de Crevillente et ses alentours (Alicante, Espagne). Hydrogeology in the Service of Man. 18th Cong. IAH, Cambridge, pp 142–149
Pulido Bosch A et al (2005) Recharge in the Sierra de Gádor and hydrogeochemistry of aquifers in Campo de Dalías (in Spanish) Cajamar. Almería, p 337
Pulido-Bosch A (1999) Karst water exploitation. In: Karst Hydrogeology and Human Activities. Impacts, Consequences and Implications.Eds: D Drew, Heinz Hötzl, International contributions to hydrogeology, 20, 235–240. Balkema, Rotterdam
Pulido-Bosch A, Morell I, Andreu JM (1995) Hydrogeochemical effects of groundwater mining of the Sierra de Crevillente Aquifer (Alicante, Spain). Environ Geol 26:232–239
Pulido-Bosch A, Andreu JM, Estévez A, Ayanz J (1998) Zonation hydrogéochimique verticale dans l’aquifère karstique du Cid (Alicante, Espagne). Comptes Rendus de la Academie de Science de Paris, 326, ser II: 421–426
Pulido-Bosch A, Bensi S, Molina L, Vallejos A, Calaforra JM, Pulido-Leboeuf P (2000) Nitrates as indicators of aquifer interconnection. Application to the Campo de Dalias (SE Spain). Environ Geol 39:791–799
Raposo JR, Molinero J, Dafonte J (2010) Quantitative evaluation of hydrogeological impact produced by tunnel construction using water balance models. Eng Geol 116:323–332
Ravbar N, Goldscheider N (2009) Comparative application of four methods of groundwater vulnerability mapping in a Slovene karst catchment. Hydrogeol J 1:725–733
Schmidt S, Geyer T, Marei A, Guttman J, Sauter M (2013) Quantification of long-term wastewater impacts on karst groundwater resources in a semi-arid environment by chloride mass balance methods. J Hydrol 502:177–190
Sjolander-Lindqvist A (2005) Conflicting perspectives on water in a Swedish railway tunnel project. Environ Values 14:221–239
Sola F, Pulido-Bosch A (2014) Tunnels as observation points of aquifer response; the Archidona case (Malaga, Spain) (in Spanish). Rev Soc Geol España 27(1):319–326
Tatu CA, Orem WH, Finkelman RB, Feder GL (1998) The etiology of Balkan endemic nephropathy: still more questions than answers. Environ Health Perspect 106:689–700
Tulipano L, Fidelibus MD (1995) National report for Italy. In: Hydrogeological aspects of groundwater protection in karstic areas. COST action 65, Final report, pp 171–201. Brussels
Vengosh A, Keren R (1996) Chemical modifications of groundwater contaminated by recharge of sewage effluent. J Contam Hydrol 23:347–360
Vincenzi V, Gargini A, Goldscheider N (2009) Using tracer tests and hydrological observations to evaluate effects of tunnel drainage on groundwater and surface waters in the Northern Apennines (Italy). Hydrogeol J 17:135–150
Yang FR, Lee CH, Kung WJ, Yeh HF (2009) The impact of tunneling construction on the hydrogeological environment of “Tseng-Wen Reservoir Transbasin Diversion Project” in Taiwan. Eng Geol 103(1–2):39–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallejos, A., Andreu, J.M., Sola, F. et al. The anthropogenic impact on Mediterranean karst aquifers: cases of some Spanish aquifers. Environ Earth Sci 74, 185–198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3994-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3994-y