Abstract
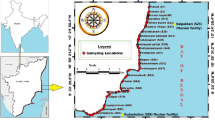
The activity concentrations of Cs-137 and K-40 radio nuclides in the natural spring waters of the Eastern Black Sea region of Turkey were measured using gamma-ray spectrometry. Annual effective dose equivalents of Cs-137 and K-40 in babies, children and adults were calculated from the obtained measurements. These results were compared with other studies and the limit values of World Health Organization. The activity concentrations were calculated and kriging-geostatistical method was used to plot the obtained data on the radioactive maps of Eastern Black Sea Region. Frequency distributions of the water samples for each province were determined. This study provides background values of investigated Cs-137 and K-40 in the water from the region, which could, also, be useful in forensic investigations to distinguish potential contributions from point pollution sources.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajayi OS, Achuka J, State O (2009) Radioactivity in drilled and dug well drinking water of Ogun State Southwestern Nigeria and consequent dose estimates. Radiat Prot Dosim 135:54–63. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncp095
Alam MN, Chowdhury MI, Kamal M, Ghose S, Islam MN, Anwaruddin M (1999) Radiological assessment of drinking water of the chittagong region of Bangladesh. Radiat Prot Dosim 82:207–214. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a032626
Bunzl K, Albers BP, Schimmack W, Belli M, Ciu L, Menegon S (2000) Examination of a relationship between Cs concentrations in soils and plants from alpine pastures. J Environ Radioact 48:145–158
Cevik U, Damla N, Karahan G, Celebi N, Kobya AI (2006) Natural radioactivity in tap waters of Eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Radiat Prot Dosim 118:88–92. doi:10.1093/rpd/nci325
Chau ND, Michalec B (2009) Natural radioactivity in bottled natural spring, mineral and therapeutic waters in Poland. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279:121–129. doi:10.1007/s10967-007-7276-6
Ciuffo LEC, Belli M, Pasquale A, Menegon S, Velasco HR (2002) Cs-137 and K-40 soil-to-plant relationship in a seminatural grassland of the Giulia Alps, Italy. Sci Total Environ 295:69–80
D’Agostino R, Belanger A, D’Agostino R (1990) A suggestion for using powerful and informative tests of normality. Am Stat 44:316–321
Dai L, Wei H, Wang L (2007) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of radionuclides in soils around a coal-fired power plant: a case study from the city of Baoji, China. Environ Res 104(2):201–208. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2006.11.005
El Arabi AM, Ahmed NK, Din KS (2006) Natural radionuclides and dose estimation in natural water resources from Elba protective area. Egypt. Radiat Prot Dosim 121:284–292. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncl022
El-Mageed AIA, El-Kamel AEH, Abbady AEB, Harb S, Saleh II (2013) Natural radioactivity of ground and hot spring water in some areas in Yemen. Desalination 321:28–31. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.022
Fatima I, Zaidi JH, Arif M, Tahir SNA (2007) Measurement of natural radioactivity in bottled drinking water in Pakistan and consequent dose estimates. Radiat Prot Dosim 123:234–240. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncl093
Fujita M, Iwamoto J, Kondo M (1996) Comparative metabolism of cesium and potassium in mammals: Interspecies correlation between body weight and equilibrium level. Health Phys 12:1237–1248
Haciyakupoglu S, Ertek TA, Walling DE, Ozturk ZF, Karahan G, Erginal AE, Celebi N (2005) Using caesium-137 measurements to investigate soil erosion rates in western Istanbul (NW Turkey). Catena 64:222–231. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2005.08.006
International Commission Radiological Protection (1991) Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP Publ. 60. Pergamon Press, Oxford
International Commission Radiological Protection (1993) Protection against Radon-222 at home and at work, ICRP Publ. 65. Pergamon Press, Oxford
İskender FY, Landsberger S, Waren S (2000) Determination of Cs-137 in soil samples by low-level compton suppression gamma-counting. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 244:159–163
Kabadayı Ö, Gümüş H (2012) Natural activity concentrations in bottled drinking water and consequent doses. Radiat Prot Dosim 150:532–535. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncr430
Kovács T, Bodrogi E, Dombovári P, Somlai J, Németh Cs, Capote A, Tarján S (2004) U-238, Ra-226, Po-210 concentrations of bottled mineral waters in Hungary and their committed effective dose. Radiat Prot Dosim 108:175–181. doi:10.1093/rpd/nch006
Krige DG (1966) Two-dimensional weighted moving average trend surfaces for ore-evaluation. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 66:13–38
Lenka P, Sahoo SK, Mohapatra S, Patra AC, Dubey JS, Vidyasagar D, Puranik D (2013) Ingestion dose from 238U, 232Th, 226Ra, 40 K and 137Cs in cereals, pulses and drinking water to adult population in a high background radiation area, Odisha, India. Radiat Prot Dosim 153:328–333. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncs115
McGrath D, Zhang C, Carton OT (2004) Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environ Pollut 127(2):239–248. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.07.00
Rusconi R, Forte M, Badalamenti P, Bellinzona S, Gallini R, Romeo C, Sgorbati G (2004) The monitoring of tap waters in Milano: planning, methods and results. Radiat Prot Dosim 111:373–376. doi:10.1093/rpd/nch057
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on Effects of Atomic Radiation, New York
Whicker FW, Schultz V (1982) Radioecology: Nuclear Energy and the Environment. CRC Press, Florida
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization Press, Geneva
Wright SM, Howard BJ, Strand P, Nyle T (1999) Prediction of Cs-137 deposition from atmospheric nuclear weapons tests within the Arctic. Environ Pollut 104:131–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobya, Y., Yeşilkanat, C.M. Investigation of Cs-137 and K-40 activities of natural spring waters of the Eastern Black Sea Region, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5375–5382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3792-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3792-6