Abstract
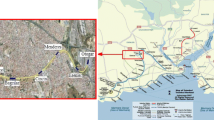
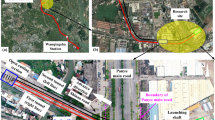
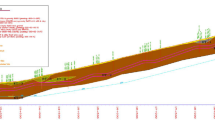
Increasing demand on infrastructures has led to increased attention to shallow soft ground tunneling methods in urbanized areas. Especially in metro tunnel excavations, it is important to control the surface settlements which are observed before and after excavation, which may cause damage to surface structures. Unlike motorway, sewage and other infrastructure tunnels, metro tunnels generally have to be excavated as twin tunnels and must have a larger diameter. Metro tunnels also have shallow depth. Due to their shallow depth, metro tunnels generally have been constructed in weak rocks or weak soils in cities. The construction of twin tunnels will generate ground movements which have the potential to cause damage to existing surface and subsurface structures. To solve this settlement problem, experts have used the Earth pressure balance machine (EPBM) and the slurry balance machine. In such excavations, especially in twin tunnels, the main challenges for constructers are estimating the maximum surface settlement, controlling the interaction of transverse surface settlement and shaping the settlement curve. Incorrect estimation of these parameters can lead to significant problems above the tunnels and in nearby structures. This paper focuses on surface settlement measurements, on the interaction of twin tunnel transverse surface settlement and on the relationship between shield parameters and transverse surface settlement for parallel tunnels using EPBM shields in clay and sand soils in shallow depth. Also, a new equation is proposed for estimating the transverse settlement curve of twin tunnels. The results from this proposed equation are compared with the results of field observations. The transverse settlement curve values obtained from the proposed equation have good agreement with the actual results for the Otogar–Kirazli metro case studies.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addenbrooke TI (1996) Numerical analysis of tunnelling in stiff clay. PhD Theses, Imperial College, London, p 373
Addenbrooke TI, Potts DM (2001) Twin tunnel interaction—surface and subsurface effects. Int J Geomech 1:249–271
Arioglu E (1992) Surface movements due to tunneling activities in urban areas and minimization of building damages. Short Course, Istanbul Technical University, Mining Engineering Department (in Turkish)
Chapman DN, Rogers CDF, Hunt DVL (2004) Predicting the settlements above twin tunnels constructed in soft ground. In: Proceedings of the 30th ITA-AITES World tunnel congress Singapore, p 378
Chen RP, Zhu J, Liu W, Tang XW (2011) Ground movement induced by parallel EPB tunnels in silty soils. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26(1):163–171
Cooper ML, Chapman DN, Rogers CDF (2002) Prediction of settlement in an existing tunnel cause by the second of twin tunnels. Transp Res Rec 1814(1):103–112
Cording EJ, Hansmire WH (1975) Displacements around soft ground tunnels. General Report 5th Pan American conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, vol IV, pp 571–632
Divall S, Goodey RJ, Taylor RN (2012) Ground movements generated by sequential twin tunneling in over-consolidated clay. doi:10.4233/uuid:f71fabea-424b-42e5-93aa-701715eed17d
Ercelebi SG, Copur H, Ocak I (2011) Surface settlement predictions for Istanbul metro tunnels excavated by EPB-TBM. Environ Earth Sci 62(2):357–365
Hunt DVL (2005) Predicting the ground movements above twin tunnels constructed in London Clay. PhD Thesis, University of Birmingham
Jancsecz S, Steiner W (1994) Face support for a large Mix-Shield in heterogeneous ground conditions. In: Proceedings of the 7th International symposium ‘Tunneling 94’, London, pp 531–550
Mair RJ (1979) Centrifugal modelling of tunnel construction in soft clay. PhD Thesis, Cambridge University
Mair RJ, Taylor RN (1997) Bored tunnelling in the urban environment. In: Proceedings of the fourteenth international conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, vol 4, pp 2353–2385
Mroueh H, Shahrour I (2008) A simplified 3D model for tunnel construction using tunnel boring machines. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 23(1):38–45
Nyren R (1998) Field measurements above twin tunnels in London clay. PhD Thesis, Imperial College
O’Reilly MP, New BM (1982) Settlements above tunnels in the United Kingdom—their magnitude and prediction. 3rd international symposium, Inst of Mining and Metallurgy, London, England, pp 173–181
Ocak I (2008a) Estimating the modulus of elasticity of the rock material from compressive strength and unit weight. S Afr Inst Min Metall 108(10):621–626
Ocak I (2008b) Control of surface settlements with umbrella arch method in second stage excavations of Istanbul Metro. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 23(6):674–681
Ocak I (2009a) Environmental problems caused by Istanbul subway excavation and suggestions for remediation. Environ Geol 58(7):1557–1566
Ocak I (2009b) Environmental effects of tunnel excavation in soft and shallow ground with EPBM: the case of Istanbul. Environ Earth Sci 59(2):347–352
Ocak I (2013) Interaction of longitudinal surface settlements for twin tunnels in shallow and soft soils: the case of Istanbul metro. Environ Earth Sci 69(5):1673–1683
Ocak I, Bilgin N (2010) Comparative studies on the performance of a roadheader, impact hammer and drilling and blasting method in the excavation of metro station tunnels in Istanbul. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 25(2):181–187
Ocak I, Seker SE (2013) Calculation of surface settlements caused by EPBM tunneling using artificial neural network, SVM, and Gaussian processes. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1263–1276
Pantet A (1991) Creusement des galeries a faible profondeur a l’aide d’un tunnelier a pression de boue. Mesures in situ et étude théorique champ de de′placement. PhD thesis, INSA, Lyon
Peck RB (1969) Deep excavation and tunneling in soft ground. In: Proceedings of 7th international conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, Mexico City, State of the Art Volume, pp 225–290
Schmidt B (1969) A method of estimating surface settlement above tunnels constructed in soft ground. Can Geotech J 20:11–22
Shirlaw JN, Doran S, Bejamin B (1988) A case study of two tunnels driven in the Singapore ‘Boulder Bed’ and in Grout Coral Sands. Engineering Geology and Underground Movements, Geological Society Engineering Geology Special Publication, vol 5, pp 93–103
Suwansawat S (2006) Superposition technique for mapping surface settlement troughs over twin tunnels. In: International symposium on underground excavation and tunnelling, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 353–362
Taylor RN (1984) Ground movements associated with tunnels and trenches. PhD Thesis, University of Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocak, I. A new approach for estimating the transverse surface settlement curve for twin tunnels in shallow and soft soils. Environ Earth Sci 72, 2357–2367 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3145-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3145-5