Abstract
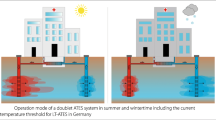
Large thermal extractions and extensive implementation of groundwater heat pumps (GWHP) necessitate a validation of the sustainability of their use and possible detrimental effects on groundwater. The goal of this work is to develop a regional heat transport model (of ~13 km × 5 km) for real site conditions. This model should consider all relevant transport processes, despite the large area under investigation. The model is based on a two-dimensional, transient-calibrated groundwater flow model for the “Leibnitzer Feld” (Styria, Austria). The two-dimensional horizontal model is linked via the FEFLOW interface manager with a newly developed “Multi-Layer-Model”-tool, which reproduces thermal aquifer–atmosphere interaction. Based on the regional heat transport model, scenarios are delineated for heating and cooling purposes for large GWHPs, which are appropriate for a small manufacturing business, an administrative building and 10 family homes. First of all, these have large spacing and thereafter, effects of area-covering usage of geothermal systems are evaluated for five administrative buildings located in close proximity to one another (200–350 m) and also for a large number of smaller heat extractions (each representing a one family house system). Modeled spatial and temporal temperature effects on the shallow aquifer are discussed. It was possible to present a simulation of realistic heating and cooling scenarios. This simulation may be introduced into practice once some further simplifications to the system are made. Locally limited heat plumes (max. length: 625 m) were observed for the manufacturing business. Any thermal effects coming from the geothermal systems were shown to be temporally stable. As such, no distinct trend of reduced annual temperatures could be observed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen A, Milenic D, Sikora P (2003) Shallow gravel aquifers and the urban ‘heat island’ effect: a source of low enthalpy geothermal energy. Geothermics 32(4–6):569–578
Appel S, Kirsch F, Mittag J, Mahabadi OK, Richter T (2007) Die Bemessung von Großanlagen der Oberflächengeothermie-Beispiele und Berechnungsmodelle. GUD Geotechnik und Dynamik Consult GmbH, Berlin
Baccino G, Lo Russo S, Taddia G, Verda V (2010) Energy and environmental analysis of an open-loop ground-water heat pump system in an urban area. Therm Sci 14:693–706
Banks D (2009) Thermogeological assessment of open-loop well-doublet schemes: a review and synthesis of analytical approaches. Hydrogeol J 17(5):1149–1155
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. American Elsevier Publishing Company Inc., New York
Blum P, Campillo G, Münch W, Kölbel T (2010) CO2 savings of ground source heat pump systems: a regional analysis. Renew Energ 35:122–127
Bonte M, Stuyfzand PJ, Hulsmann A, Van Beelen P (2011) Underground thermal energy storage: environmental risks and policy developments in the Netherlands and European Union. Ecol Soc 16(1):22
Böttcher N (2007) Simulation von Wasserfluss, Wärme- und Stofftransport auf Lysimeterskala. Diploma thesis, Institut for Ground Water Management, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden
Cathomen N (2002) Wärmetransport im Grundwasser-Auswirkung von Wärmepumpenanlagen auf die Grundwassertemperatur am Beispiel der Gemeinde Altach im Vorarlberger Rheintal. Diploma Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich
Diersch H-JG (2009) DHI-WASY Software FEFLOW. Finite element subsurface flow & transport simulation system. Reference Manual, DHI-WASY GmbH, Berlin
Epting J, Händel F, Huggenberger P (2012) Thermal management of an urban groundwater body. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 9:7181–7225
Fank J (1999) Die Bedeutung der ungesättigten Zone für Grundwasserneubildung und Nitratbefrachtung des Grundwassers in quartären Lockersediment-Aquiferen am Beispiel des Leibnitzer Feldes (Steiermark, Österreich). Beiträge zur Hydrogeologie 49/50:101–388 Graz
Florides G, Kalogirou S (2007) Ground heat exchangers: a review of systems, models and applications. Renew Energ 32:2461–2478
Gelhar LW, Welty C, Rehfeldt KR (1992) A critical review on field-scale dispersion in aquifers. Water Resour Res 28(7):1955–1974
Hähnlein S, Blum P, Bayer P (2010a) Oberflächennahe Geothermie-aktuelle rechtliche Situation in Deutschland. Grundwasser 16:69–75
Hähnlein S, Bayer P, Blum P (2010b) International legal status of the use of shallow geothermal energy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:2611–2625
Händel F (2010) Modellierung von Wärmetransport für flache Grundwasserleiter. Diploma thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden
Hecht-Méndez J, Molina-Giraldo N, Blum P, Bayer P (2010) Verifying the solute transport model MT3DMS for heat transport simulation of closed shallow geothermal systems. Ground Water 48:741–756
Ingerle K (1988) Beitrag zur Berechnung der Abkühlung des Grundwasserkörpers durch Wärmepumpen, Österreichische Wasserwirtschaft 40 H. 11/12
Kastner O, Sippel J, Scheck-Wenderoth M, Huenges E (2013) The deep geothermal potential of the Berlin area. Environ Earth Sci
Kupfersberger H (2009) Heat transfer modelling of the Leibnitzer Feld aquifer, Austria. Environ Earth Sci 59:561–571
Liang J, Yang Q, Liu L, Li X (2011) Modeling and performance evaluation of shallow ground water heat pumps in Beijing plain, China. Energ Build 43:3131–3138
Lund JW (2007) Characteristics, development and utilization of geothermal resources. Geo-Heat Center, Oregon Institute of Technology, Klamath Falls
Lund JW (2010) Direct utilization of geothermal energy. Energies 2010:1443–1471
Molson JW, Frind EO, Palmer CD (1992) Thermal energy storage in an unconfined aquifer. 2. Model development, validation, and application. Water Resour Res 28:2857–2867
Nam Y, Ooka R (2010) Numerical simulation of ground heat and water transfer for groundwater heat pump system based on real-scale experiment. Energ Build 42:69–75
Omer MA (2008) Ground-source heat pumps systems and applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12:344–371
ÖWAV-Regelblatt 207 (2008) Thermische Nutzung des Grundwassers und des Untergrunds-Heizen und Kühlen. ÖWAV, Vienna
Palmer DP, Blowes DW, Frind EO, Molson JW (1992) Thermal energy storage in an unconfined aquifer. 1. Field injection experiment. Water Resour Res 28(10):2845–2856
Pannike S, Kölling M, Panteleit B, Reichling J, Scheps V, Schulz HD (2006) Auswirkungen hydrogeologischer Kenngrößen auf die Kältefahnen von Erdwärmesondenanlagen in Lockersedimenten. Grundwasser 11:6–18
Pouloupatis PD, Florides G, Tassou S (2011) Measurements of ground temperatures in Cyprus for ground thermal applications. Renew Energ 36(2):804–814
Prettenthaler F, Gobiet A, Habsburg-Lothringen C, Steinacker R, Töglhofer C, Türk A (2007) Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf Heiz-und Kühlenergiebedarf in Österreich, Universität für Bodenkultur Wien, Department für Wasser-Atmosphäre-Umwelt, Institut für Meteorologie, JOANNEUM RESEARCH, Universität Graz, Graz
Pruess K, Oldenburg C, Moridis G (2012) TOUGH2 User’s Guide, Version 2.1. Report LBNL-43134, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA
Rauch W (1992) Ausbreitung von Temperaturanomalien im Grundwasser. Universität Innsbruck, Innsbruck
Russo SL, Civita MV (2010) Hydrogeological and thermal characterization of shallow aquifers in the plain sector of Piemonte region (NW Italy): implications for groundwater heat pumps diffusion. Environ Earth Sci 60:703–713
Sanner B, Karytsas C, Mendrinos D, Rybach L (2003a) Current status of ground source heat pumps and underground thermal energy storage in Europe. Geothermics 32:579–588
Sanner B, Mands E, Sauer MK (2003b) Larger geothermal heat pump plants in the central region of Germany. Geothermics 32:589–602
Šimůnek J, Šejna M (2011) Software package for simulating the two- and three-dimensional movement of water, heat and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Hydrus User Manual, PC-Progress, Prague
Sippel J, Fuchs S, Cacace M, Kastner O, Huenges E, Scheck-Wenderoth M (2013) Deep 3D thermal modelling for the city of Berlin (Germany). Environ Earth Sci
Söll T (1988) Berechnungsverfahren zur Abschätzung anthropogener Temperaturanomalien im Grundwasser. Dissertation, Institut für Wasserbau, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart
Staffell I, Brett D, Brandonc N, Hawkesd A (2012) A review of domestic heat pumps. Energ Environ Sci 5:9291–9306
UM Baden-Württemberg (2009) Arbeitshilfe zum Leitfaden zur Nutzung von Erdwärme mit Grundwasserwärmepumpe. Umweltministerium Baden-Württemberg, Stuttgart
Vandenbohede A, Hermans T, Nguyen F, Lebbe L (2011) Shallow heat injection and storage experiment: heat transport simulation and sensitivity analysis. J Hydrol 409:262–272
Wolkersdorfer C (2008) Abriss der Hydrologie. Warum fließt Grundwasser?. Ludwig Maximilan Universität München, Munich
Wong LW, Watanabe N, Cacace M, Blöcher G, Kastner O, Zimmermann G (2013) Sensitivity analysis of permeability and apertures of natural internal fault zones on fluid flow and heat transfer in a deep geothermal reservoir. Environ Earth Sci
Yang H, Cui P, Fang Z (2010) Vertical-borehole ground-coupled heat pumps: a review of models and systems. Appl Energ 87:16–27
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank DHI WASY for providing FEFLOW and a plug-in for groundwater heat pumps during the diploma thesis in which this work was realized. We acknowledge Thomas Reimann for contributing discussions during this work and Christopher Higgins for reviewing of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Händel, F., Liedl, R., Fank, J. et al. Regional modeling of geothermal energy systems in shallow aquifers: the Leibnitzer Feld case study (Austria). Environ Earth Sci 70, 3433–3446 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2469-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2469-x