Abstract
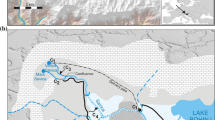
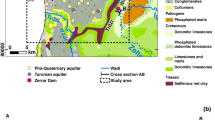
Hydrochemical and isotopic data of waters from the Zéroud aquifer have been used to potentially provide a means for locating occurrences and to trace movements of a variety of natural and anthropogenic recharge waters in the Zéroud Basin, Central Tunisia. Geochemical data have been measured during the dam water release, from May to September 2005, with a sampling time step of 15 days. An implication of dam water has been demonstrated that is noticeable up along the main flow path to a distance of 10 km far from the injection site. Environmental isotopes 2H, 18O and 3H of water molecule were studied to investigate the effect of dam water on the hydrological system, and an isotope balance was established to compute the contribution of water storage component in groundwater. Based on isotopic mass balance, we assess that an average of 13% of total groundwater in the upper aquifer came from dam water storage. Three distinctive recharge waters in the aquifer can be determined. Water from local rainfall (pre-dam Zéroud River) that infiltrated into the boundaries of the Draa Affane Mountain was easily distinguished from the water influenced by anthropogenic recharge located in the Zéroud right rivulet. Distinguishable isotopic signatures of native wadi Zéroud recharge due to “recent lineal recharge” through the riverbed were also identified.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIEA (2004) Global network of isotopes in precipitation. isotope hydrology information system. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienne. http://isohis.iaea.org
Barbier B (2002) Upstream dams and downstream water allocation the case of the Hadejia’Jama’ are Floodplain, Northern Nigeria. Paper prepared for the Environmental Policy Forum, Center for Environmental Science and Policy. Institute for International Studies, Stanford University
Bedir M (1995) Geodynamic mechanisms of the basins associated with the corridors sliding motions with the Atlasic margin, Tunisia. Seismo-statigraphie, seismo-tectonics and implications oil. PhD-es-sciences. Fac. Sc. Tunis, Tunisia
Bel Haj Salem S (2006) Artificial recharge of the Kairouan plain by the Sidi Saad dam: isotopic and geochemical study. Master, National School of Engineers, Sfax, Tunisia
Ben Ammar S, Zouari K, Leduc C, M’barek J (2006) Caractérisation isotopique de la relation barrage-nappe dans le bassin du Merguellil (plaine de Kairouan, Tunisie centrale). Hydrol Sci J 51(2):272–284
Blavoux B (2000) L’utilisation des isotopes pour l’étude des relations nappe-rivière. Colloque Hydrologie et Hydrogéologie Isotopique de l’an 2000, 7ème journée technique du Comité français de l’AIH., Avignon 24 Novembre 2000, Edition BRGM, pp 15–22
Bouzaiane S, Laforgue A (1986) Monographie hydrologique des oueds Zeroud et Merguellil. Direction Générale des Ressources en Eau en Tunisie (DGRE) en coopération avec l′institut de Recherche scientifique pour le développement (ORSTOM). Prog. Dacti
Dassi L, Zouari K, Faye S (2007) Identifying sources of groundwater recharge in the Merguellil river basin (Tunisia) using the isotopic methods: implication of dam reservoir water accounting. Environ Geol 49:114–123. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0069-0
Gay D (2004) Operation and assessment of artificial reserves in Tunisia: hydrochimic and isotopic approach. Thesis of Doctorate, University of Paris XI, Paris, France
Grünberger O, Montoroi J, Nasri S (2004) Quantification of water exchange between a hill reservoir and groundwater using hydrological and isotopic modelling (El Gouazine, Tunisia). J Geosci C R Geosci 336:1453–1462
Haimerl G (2006) Groundwater recharge in wadi channels downstream of dams—efficiency and management strategies. German Dam Research and Technology. Technische Univerität München, Germany (available from http://www.wb.bv.tum.de)
Jeribi L (2004) Hydrochimic and isotopic characterization of the aquifer system of the Zeroud basin (Plain of Kairouan, Central Tunisia). Thesis of Doct.3rd cycle, Fac. of Sciences of Tunis
Kacem A (2008) Management of water resources of Sisseb Elam basin: impact of hydraulic installations on water table recharge. Thesis of Doctoral. 3rd cycle, Faculty of sciences of Sfax
Leduc C, Ben Ammar S, Favreau G, Beji R, Virrion R, Lacombe G, Tarhouni J, Aouadi C, Zenati CB, Jebnoun N, Oi M, Michelot JL, Zouari K (2007) Impacts of hydrological changes in the Mediterranean zones: environmental modifications and rural development in the Merguellil catchment, Central Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 52(6):1162–1178
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater: an introduction. Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 296
Macpherson GL et al (2008) Increasing shallow groundwater CO2 and limestone weathering, Konza prairie, USA. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta p 19
Montoroi J, Olivier G, Nasri S (2002) Groundwater geochemistry of a small reservoir catchment in Central Tunisia. Appl Geochem J 17(2002):1047–1060
Nazoumou Y (2002) Impact of the dams on the water table in Arid region: study by numerical modeling—the case of Kairouan (Central Tunisia). Th, Doct, ENIT, Tunis, Tunisia
Parkhurst D, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey. Water resources investigation report 99-4259
Yaich C (1984) Geologic study of Cherahil, of Kherchem and Artsouma mountains (central Tunisia). Relation with the deep structures of the adjacents plains. Thesis of Doct. 3rd cycle, Fac. Sci. and Tech. University of France, Besançon
Zammouri M, Feki H (2005) Managing releases from small upland reservoirs for downstream recharge in semi-arid basins (Northeast of Tunisia). J Hydrol 314:125–138 (13 p)
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out under the project CMCU (06S/1003), which was interested in the use of environmental isotopes for the assessment of water resources of the Zéroud Basin (Central Tunisia). We would like to express our gratitude to the laboratory staff at Avignon (France) for the isotopic analysis of waters, and the laboratory staff at Sfax (Tunisia) for their help in providing hydrological data and geochemical analysis. We offer our utmost thanks to Mr Vincent Valles and Mr Mohamed El Ayachi for their continual help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bel Hadj Salem, S., Chkir, N., Zouari, K. et al. Natural and artificial recharge investigation in the Zéroud Basin, Central Tunisia: impact of Sidi Saad Dam storage. Environ Earth Sci 66, 1099–1110 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1316-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1316-1