Abstract
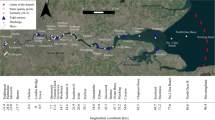
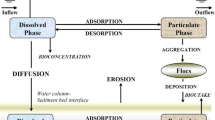
A vertical, two-dimensional heavy metal (lead) transport model incorporated into the hydrodynamic, salt, and sediment transport modules was developed to simulate the lead concentration in the tidal Keelung River estuary of northern Taiwan. We validated the developed model with measured data, including longitudinal velocity, salinity, suspended sediment, and heavy metal (lead) concentration, obtained in 1998. An exponential relationship relating the salinity and suspended-sediment concentrations was established to calculate the partition coefficient of lead in the estuary. The simulated results of dissolved, particulate, and total lead concentrations agreed well with the measured data. A model sensitivity analysis indicated that the partition coefficient plays an important role in the distribution of dissolved and particulate lead concentrations along the tidal Keelung River estuary.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckers JM, Achterberg EP, Braungardt CH (2007) Comparison of high spatial resolution trace metal distribution with model simulations for surface waters of the Gulf of Cadiz. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 74:599–609
Blumberg AF (1977) Numerical model of estuarine circulation. J Hydraul Eng Div ASCE 103:295–310
Chang ST (2004) Field survey of water quality and suspended sediment in the Danshuei River estuary. Institute of Hydrological Sciences, National Central University, Taipei, p 96
Davies JL (1964) A morphogenic approach to world shorelines. Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie 8:27–42
Delo EA (1988) Estuarine muds manual. Report No. SR 164, Hydraulic Research, Wallingford, 64 pp
Dyer KR (1997) Estuaries: a physical introduction. Wiley, New York, p 195
Elliott AJ (1976) A numerical model of the internal circulation in a branching estuary. Chesapeake Bay Institute, Special Report, 54, The Johns Hopkins University, 85 pp
Hartnett M, Berry A (2010) Transport of lead in the Mersey Estuary: the development of a novel approach to deriving partition coefficients. Adv Eng Softw 41:84–91
Hartnett M, Lin BL, Jones PD, Berry A (2006) Modelling the fate and transport of nickel in the Mersey Estuary. J Environ Sci Health A 41:825–847
Hsu MH, Kuo AY, Kuo JT, Liu WC (1999) Procedure to calibrate and verify numerical models of estuarine hydrodynamics. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 125:166–182
Huang KM, Lin S (2003) Consequences and implication of heavy metal spatial variations in sediments of the Keelung River drainage basin, Taiwan. Chemosphere 53:1113–1121
Jay DA, Smith JD (1990) Residual circulation in shallow estuaries. 2. Weakly stratifies and partially mixed, narrow estuaries. J Geophys Res 95:733–748
Ji ZG, Hamrick JH, Pagenkopf J (2002) Sediment and metals modeling in shallow river. J Environ Eng ASCE 128:105–119
Krone RB (1962) Flume studies of the transport in estuarine shoaling processes. Final report, hydraulic engineering laboratory and sanitary engineering research laboratory. University of California, Berkeley
Liu WC (2005) Modeling the influence of settling velocity on cohesive sediment transport in Tanshui River estuary. Environ Geol 47:535–546
Liu WC, Hsu MH, Kuo JT (2002) Modelling of hydrodynamics and cohesive sediment transport in Tanshui river estuarine system, Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 44:1076–1088
Liu WC, Liu SY, Hsu MH, Kuo AY (2005) Water quality modeling to determine minimum instream flow for fish survival in tidal rivers. J Environ Manage 76:293–308
Liu WC, Hsu MH, Kuo JT (2007) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic and salinity transport modeling of Danshuei River estuarine system and adjacent coastal sea, Taiwan. Hydrol Process 21:3057–3071
Liu WC, Chen WB, Kuo JT (2008) Modeling residence time response to freshwater discharge in a mesotidal estuary, Taiwan. J Mar Syst 74:295–314
Mwanuzi F, De Smedt F (1999) Heavy metal distribution model under estuarine mixing. Hydrol Process 13:789–804
Ng B, Turner A, Tyler AO, Falconer RA, Millward GE (1996) Modelling contaminant geochemistry in estuaries. Water Res 30:63–74
Ng SMY, Wai OWH, Li YS, Li ZL, Jiang Y (2009) Integration of a GIS and a complex three-dimensional hydrodynamic, sediment and heavy metal transport numerical model. Adv Eng Softw 40:391–401
Odd NVM, Owen MW (1972) A two-layer model of mud transport in the Tames estuary. Proceedings of Institute of Civil Engineers, London, pp 195–202
Partheniades E (1965) Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils. J Hydraul Eng Div ASCE 91:105–139
Prandle D (2009) Estuaries: dynamics, mixing, sedimentation and morphology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pritchard DW (1960) The movement and mixing of contaminants in tidal estuaries. In: Pearson EA (ed) Waste disposal in marine environment. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 512–525
Rajar R, Zagar D, Cetina M, Akagi H, Yano S, Tomiyasu T, Horvat M (2004) Application of three-dimensional mercury cycling model to coastal seas. Ecol Model 171:139–155
Shrestha PL, Orlob GT (1996) Multiphase distribution of cohesive sediments and heavy metals in estuarine systems. J Environ Eng ASCE 122:730–740
Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (2003) Investigation report of the Danshuei River water pollution (in Chinese)
Turner A, Millward GE (1994) The partitioning of trace metals in a macrotidal estuary: Implications for contaminant transport model. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 39:45–58
Turner A, Millward GE (2002) Suspended particles: their role in estuarine biogeochemical cycles. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:857–883
Turner A, Millward GE, Le Roux SM (2001) Sediment-water partitioning of inorganic mercury in estuaries. Environ Sci Technol 35:4648–4654
Van Maldegem DC, Mulder HPJ, Langerak A (1993) A cohesive sediment balance for the Scheldt estuary. Neth J Aquat Ecol 27:247–256
Wang DP, Kravitz DW (1980) A semi-implicit two-dimensional model of estuarine circulation. J Phys Oceanogr 10:441–454
Wang CF, Hsu MH, Liu WC, Hwang JS, Wu JT, Kuo AY (2007) Simulation of water quality and plankton dynamics in the Danshuei River estuary, Taiwan. J Environ Sci Health A 42:933–953
Wu Y, Falconer RA, Lin B (2005) Modelling trace metal concentration distributions in estuarine waters. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64:699–709
Acknowledgments
The project under which this study was conducted was supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan, under grant No. NSC 98-2625-M-239-001. The authors would like to express their appreciation to the Taiwan Water Resources Agency and the Environmental Protection Administration for providing the measured data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WC., Chen, WB. & Chang, YP. Modeling the transport and distribution of lead in tidal Keelung River estuary. Environ Earth Sci 65, 39–47 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1063-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1063-3